Unveiling the Palette of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Color Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Palette of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Color Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Palette of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Color Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Palette of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Color Maps
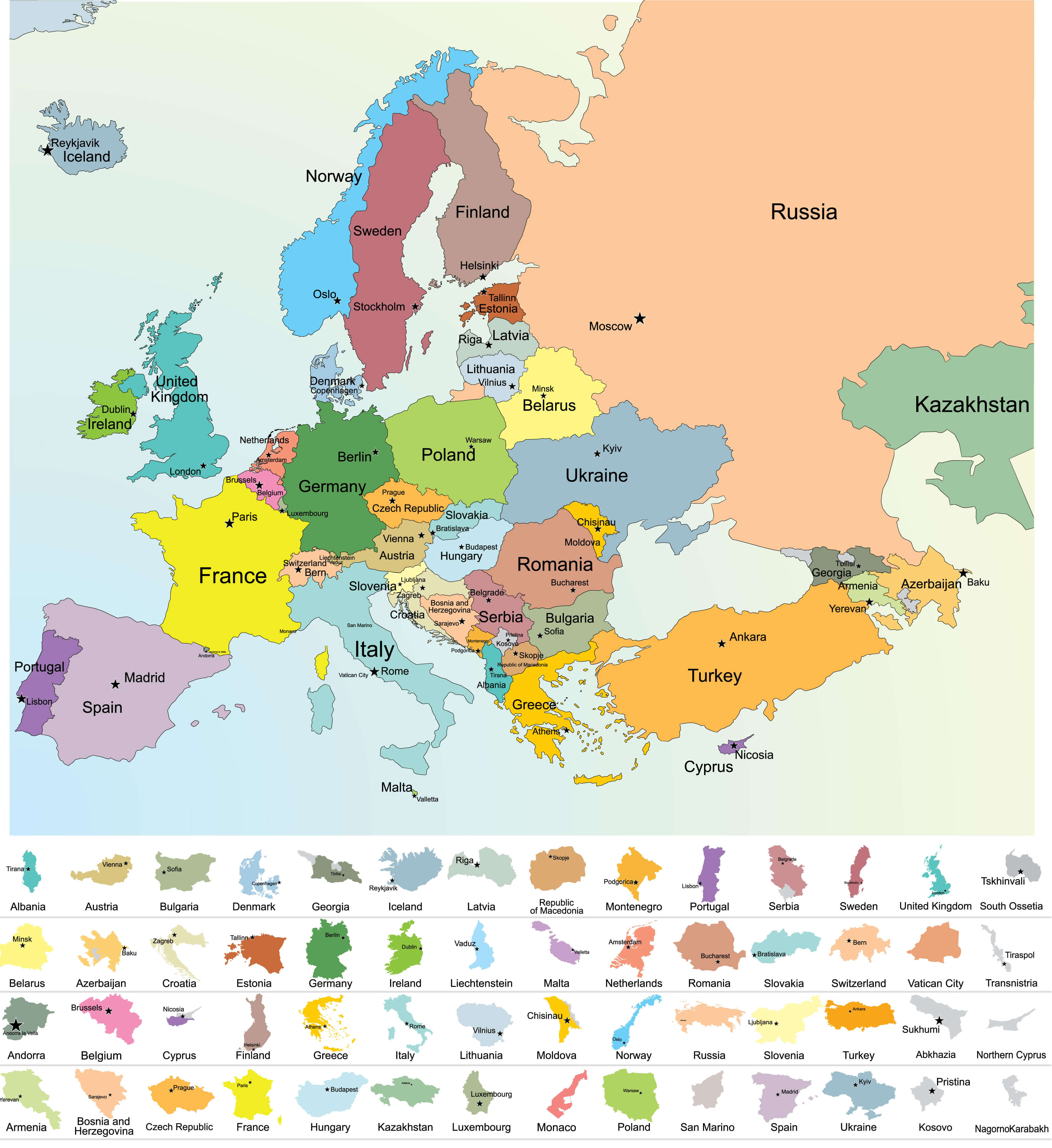
Color maps, also known as choropleth maps, are powerful visual tools that utilize color variations to depict spatial data. They offer a clear and intuitive way to understand geographical patterns and trends, making them invaluable for analyzing and communicating information across various disciplines, including geography, history, economics, and social sciences. This article delves into the world of color maps focusing specifically on Europe, exploring their construction, applications, and significance.
The Essence of Color Maps
Color maps function by assigning different shades or hues to geographical regions, with each color representing a specific value or category of data. This visual representation allows viewers to quickly grasp the spatial distribution of the data, identifying areas with high or low values, clusters, and anomalies. The effectiveness of a color map hinges on the careful selection of colors, ensuring clarity, contrast, and accessibility for all viewers.
Constructing Effective Color Maps
Creating a compelling color map requires a systematic approach:
-
Data Selection: The first step involves identifying the relevant data to be visualized. This could encompass population density, economic indicators, language distribution, or any other variable of interest.
-
Data Classification: Once the data is gathered, it needs to be classified into distinct categories or intervals. This process ensures that the color variations accurately represent the data range. Common methods include equal intervals, quantiles, natural breaks, and standard deviation.
-
Color Scheme Selection: The choice of colors plays a crucial role in conveying the data effectively. A well-chosen color scheme should be visually appealing, contrasting, and appropriate for the data type. For instance, a diverging color scheme might be used to highlight differences between high and low values, while a sequential scheme would represent a continuous range.
-
Map Projection: The map projection determines the shape and size of the geographical regions. Choosing the right projection is essential to minimize distortion and ensure accurate representation of the data.
-
Legend and Labeling: A clear legend is essential to explain the meaning of each color and its corresponding data value. Additionally, labeling regions with relevant names or data values enhances readability and understanding.
Applications of Color Maps in Europe
Color maps find diverse applications in analyzing and understanding the European landscape:
-
Population Density: Color maps can visualize the distribution of population across Europe, revealing densely populated urban areas and sparsely populated rural regions. This information is crucial for urban planning, resource allocation, and understanding social dynamics.
-
Economic Activity: Color maps can depict the spatial distribution of economic activity, highlighting regions with high industrial output, agricultural production, or tourism. This information is vital for economic development strategies, investment decisions, and understanding regional disparities.
-
Environmental Issues: Color maps can illustrate the distribution of environmental issues such as air pollution, water quality, or deforestation. This information is essential for environmental policy development, conservation efforts, and sustainable development planning.
-
Political Landscape: Color maps can visualize the distribution of political parties, voting patterns, or regional autonomy. This information provides insights into political trends, electoral dynamics, and the geographical basis of political power.
-
Cultural Diversity: Color maps can illustrate the distribution of languages, religions, or ethnic groups across Europe. This information helps understand cultural diversity, promotes tolerance and inclusion, and informs cultural policy initiatives.
Benefits of Color Maps
Color maps offer numerous advantages over traditional text-based representations:
-
Visual Clarity: They provide a clear and concise overview of the data, allowing viewers to quickly identify patterns and trends.
-
Data Communication: They facilitate effective communication of complex spatial data, making it accessible to a wider audience.
-
Comparative Analysis: They enable comparisons between different regions, revealing spatial variations and highlighting areas of interest.
-
Trend Identification: They help identify geographical trends, patterns, and anomalies, leading to deeper insights into the data.
-
Policy Support: They provide valuable information for policymakers, informing decision-making and strategic planning.
FAQs about Color Maps of Europe
Q: What are some common data sets used for color maps of Europe?
A: Common data sets include population density, GDP per capita, unemployment rates, life expectancy, carbon emissions, renewable energy production, language distribution, and ethnic diversity.
Q: How can I create my own color map of Europe?
A: Several software programs are available for creating color maps, including ArcGIS, QGIS, and Google Earth Engine. These tools offer a range of features for data visualization, including map projections, color schemes, and legend creation.
Q: What are some examples of color maps of Europe that have been widely used?
A: Examples include maps depicting the distribution of languages in Europe, the spread of the Black Death in the 14th century, and the economic development of European regions.
Q: What are some limitations of color maps?
A: Color maps can be subject to misinterpretation if the data is not accurately classified or if the color scheme is poorly chosen. They also cannot capture all aspects of complex spatial phenomena.
Tips for Interpreting Color Maps
-
Pay attention to the legend: Understand the meaning of each color and its corresponding data value.
-
Consider the color scheme: Recognize the intended message conveyed by the color scheme, whether it emphasizes differences or trends.
-
Look for patterns and trends: Identify areas with high or low values, clusters, and anomalies.
-
Consider the data source: Evaluate the reliability and accuracy of the data used to create the map.
-
Be aware of limitations: Recognize that color maps are simplifications of complex spatial phenomena and may not capture all nuances.
Conclusion
Color maps of Europe provide a powerful visual tool for understanding the spatial distribution of various phenomena. Their applications span diverse fields, offering insights into population dynamics, economic activity, environmental issues, political landscapes, and cultural diversity. By carefully selecting data, employing appropriate classification and color schemes, and interpreting maps with critical awareness, we can harness the power of color maps to gain valuable knowledge about the European continent and its diverse landscape. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and informative color maps to emerge, further enriching our understanding of Europe’s complex and dynamic geography.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Palette of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Color Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!