Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: Exploring Physical Map Examples
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: Exploring Physical Map Examples
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: Exploring Physical Map Examples. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: Exploring Physical Map Examples
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: Exploring Physical Map Examples
- 3.1 Examples of Physical Maps
- 3.2 Importance and Benefits of Physical Maps
- 3.3 FAQs about Physical Maps
- 3.4 Tips for Using Physical Maps
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: Exploring Physical Map Examples
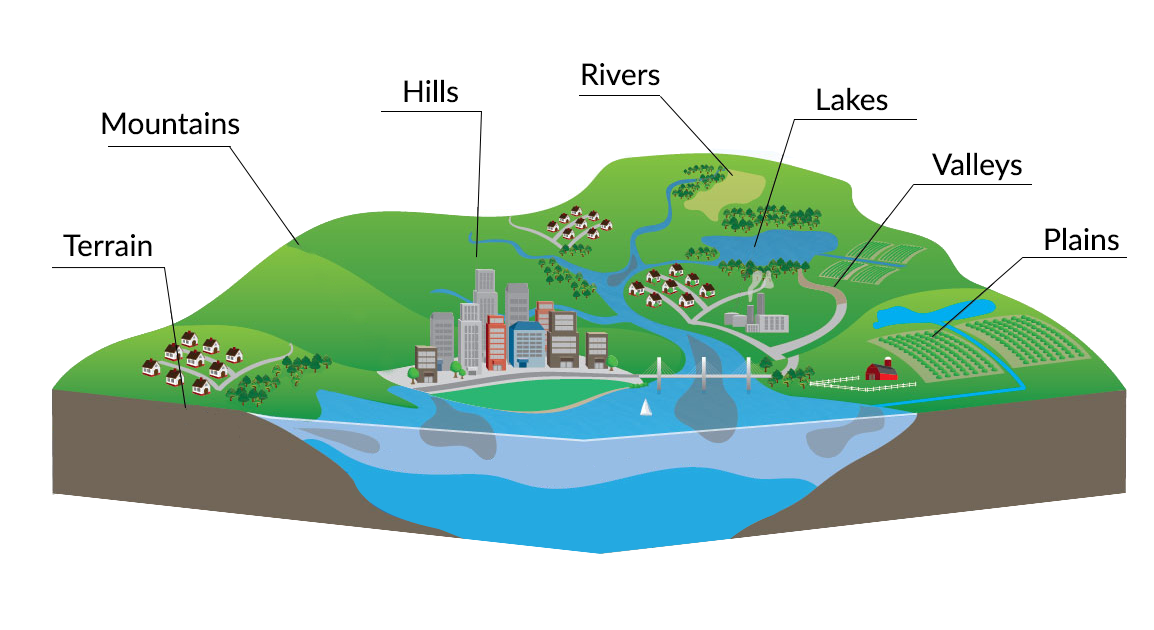
Physical maps, often referred to as relief maps, serve as visual representations of the Earth’s surface, highlighting its physical features and topography. These maps provide a unique perspective on the planet’s diverse landscapes, encompassing mountains, valleys, plains, rivers, lakes, and oceans. Unlike political maps that focus on human-made boundaries, physical maps prioritize the natural world, offering invaluable insights into the Earth’s physical characteristics.
Examples of Physical Maps
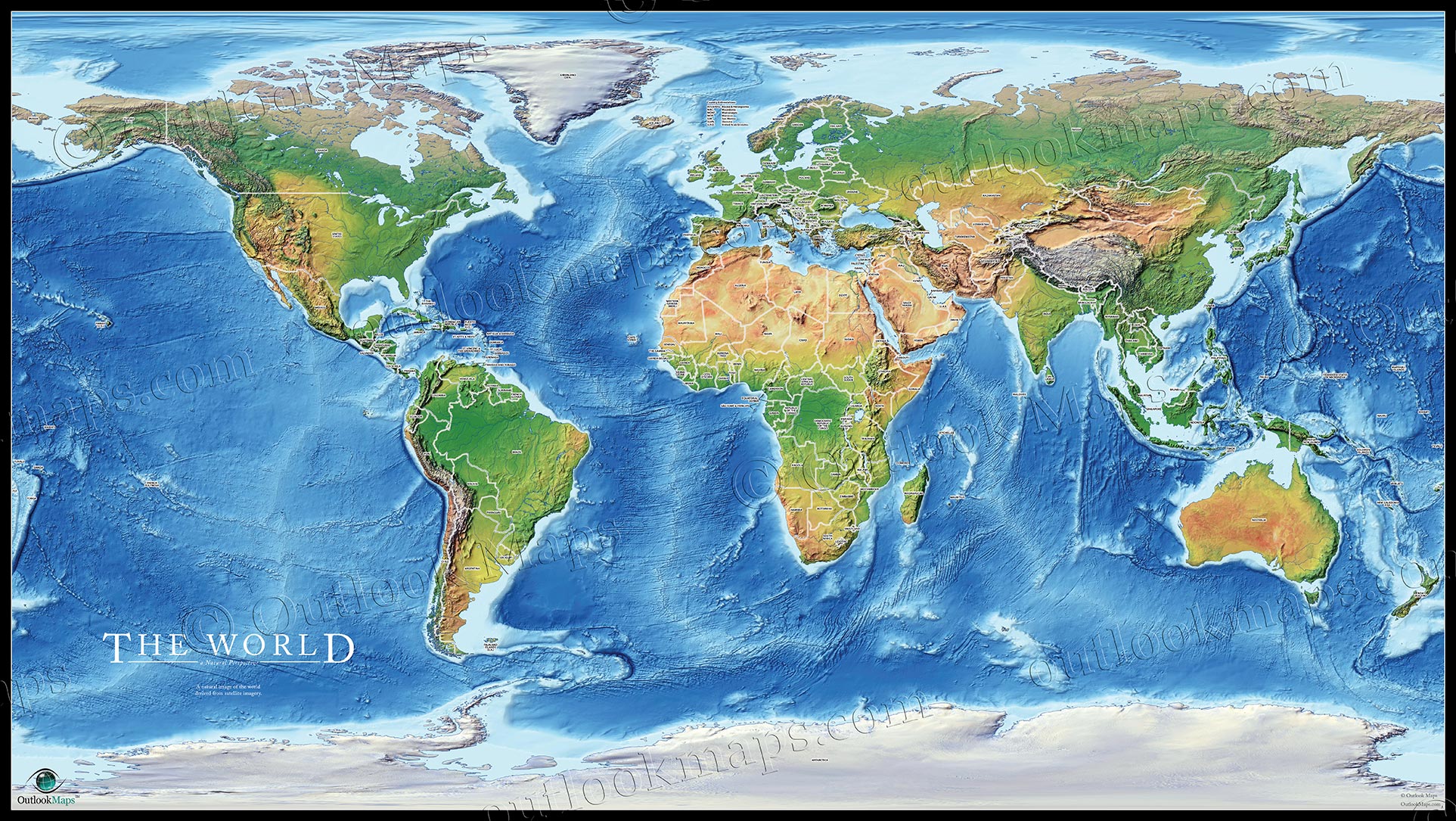
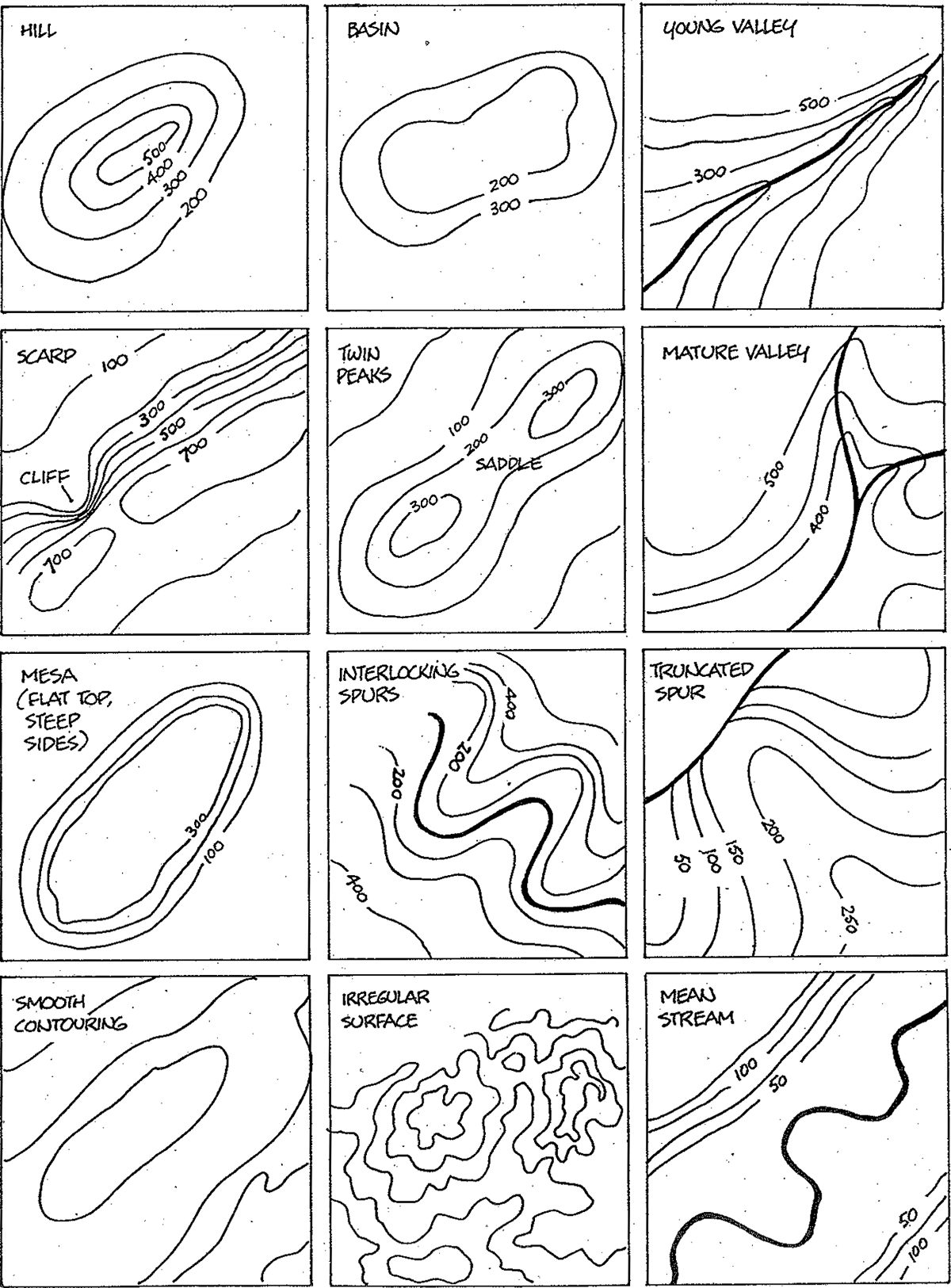
1. Topographic Maps:
Topographic maps are perhaps the most common type of physical map. They utilize contour lines to depict elevation changes, creating a three-dimensional representation of the terrain. Each contour line connects points of equal elevation, allowing users to visualize the shape and slope of the land. These maps are extensively used in various fields, including:
- Navigation: Hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts rely on topographic maps to navigate challenging terrain, identify potential hazards, and plan routes.
- Engineering: Civil engineers utilize topographic maps for site planning, infrastructure development, and construction projects, ensuring accurate representation of the existing landscape.
- Environmental Studies: Environmental scientists use topographic maps to study erosion patterns, analyze land use, and assess the impact of human activities on the environment.
2. Shaded Relief Maps:
Shaded relief maps employ shading techniques to simulate the effects of light and shadow on the terrain. This method creates a realistic three-dimensional effect, highlighting the peaks, valleys, and slopes of the landform. Shaded relief maps are often used in:
- Education: They provide a visually appealing and engaging way to teach students about the Earth’s physical features and understand the concept of topography.
- Tourism and Recreation: Shaded relief maps are commonly used in travel brochures, guidebooks, and promotional materials to showcase the scenic beauty of a particular region.
- Geography and Cartography: These maps serve as valuable tools for researchers and cartographers, enabling them to analyze and interpret topographic data.
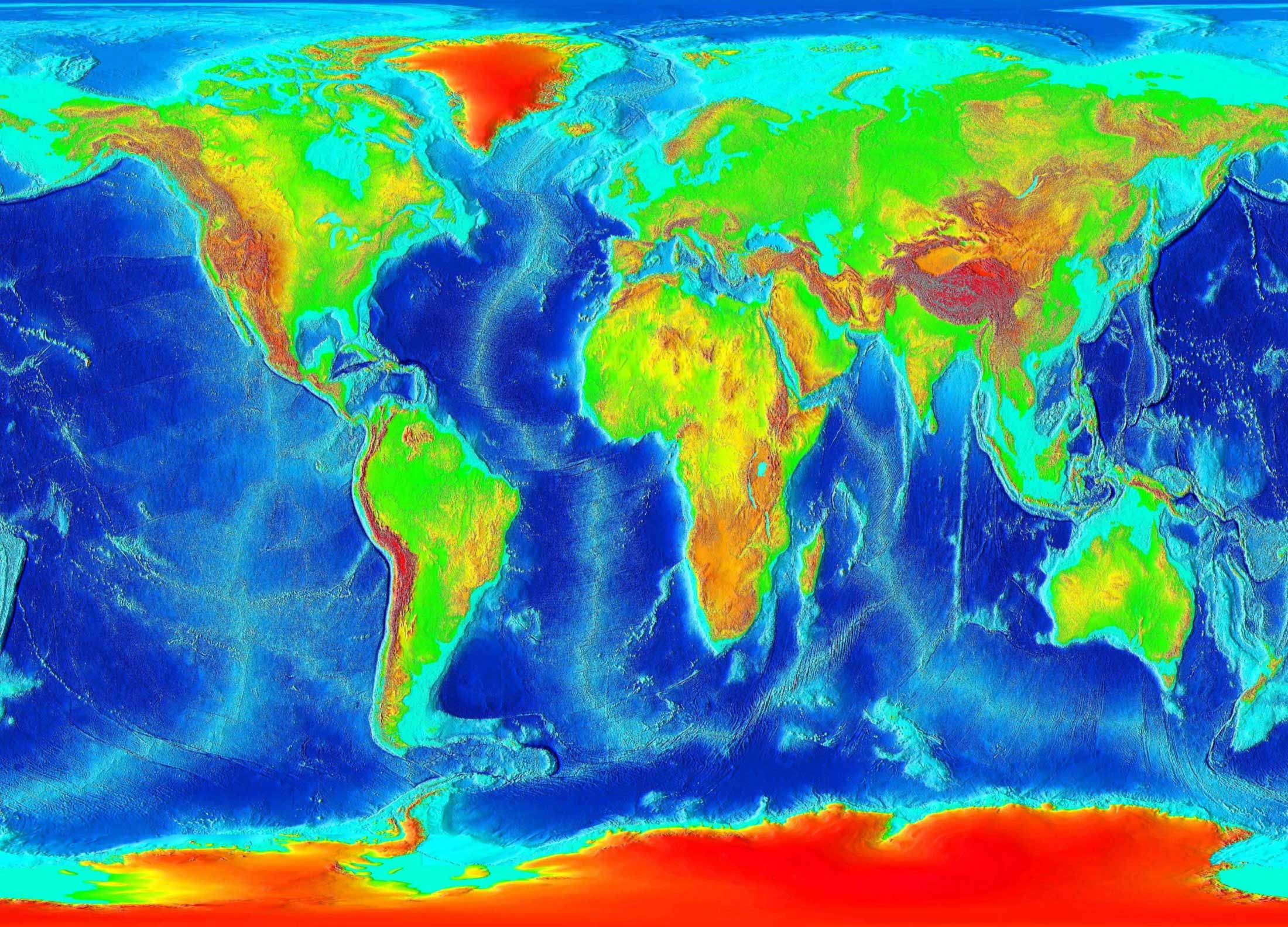
3. Hypsometric Maps:
Hypsometric maps, also known as elevation maps, use color gradients to represent different elevation zones. This method allows for quick and efficient visualization of the relative heights of various landforms. Hypsometric maps are particularly useful for:
- Geospatial Analysis: Researchers use hypsometric maps to study the distribution of elevation across different regions, identifying patterns and trends.
- Climate Modeling: Climate scientists utilize these maps to understand the influence of elevation on temperature, rainfall, and other climatic variables.
- Resource Management: Hypsometric maps assist in the management of natural resources by highlighting areas with specific elevation ranges, influencing factors like water availability and vegetation types.
4. Geomorphological Maps:
Geomorphological maps focus on the Earth’s landforms, showcasing their origin, evolution, and characteristics. These maps typically combine topographic data with geological information, providing a comprehensive understanding of the landscape’s formation. Geomorphological maps are essential for:
- Geological Studies: Geologists use these maps to investigate the geological history of a region, analyzing the processes that shaped its current landforms.
- Environmental Planning: Geomorphological maps assist in land use planning, identifying areas prone to natural hazards like landslides and floods.
- Resource Exploration: They aid in the exploration of natural resources, such as minerals and groundwater, by highlighting areas with specific geological formations.
5. Oceanographic Maps:
Oceanographic maps specialize in depicting the physical features of the ocean floor, including seamounts, trenches, and ridges. They also showcase ocean currents, water temperature, and salinity levels, providing valuable insights into the ocean’s dynamics. Oceanographic maps are crucial for:
- Marine Research: Scientists use these maps to study ocean currents, marine life distribution, and the impact of climate change on the ocean environment.
- Navigation: Mariners rely on oceanographic maps to navigate safely, avoiding hazards and optimizing routes.
- Resource Management: Oceanographic maps assist in managing marine resources, identifying fishing grounds, and protecting sensitive marine ecosystems.
Importance and Benefits of Physical Maps
Physical maps offer a wide range of benefits, making them indispensable tools across various disciplines and applications:
- Visual Understanding: Physical maps provide a clear and intuitive visualization of the Earth’s topography, facilitating understanding of the relationship between physical features and human activities.
- Spatial Analysis: They enable the analysis of spatial patterns and relationships, identifying areas of high elevation, dense vegetation, or significant water bodies.
- Environmental Awareness: Physical maps raise awareness about the diversity and complexity of the Earth’s landscapes, promoting appreciation for the natural world and its importance.
- Decision-Making: They provide valuable data for informed decision-making in fields like urban planning, resource management, and disaster preparedness.
- Educational Value: Physical maps serve as engaging and effective tools for teaching students about geography, Earth science, and environmental concepts.
FAQs about Physical Maps
1. What is the difference between a physical map and a political map?
Physical maps focus on the Earth’s natural features, like mountains, rivers, and oceans. Political maps, on the other hand, depict human-made boundaries, such as countries, states, and cities.
2. How are physical maps used in navigation?
Topographic maps are widely used for navigation, especially in challenging terrain. They provide detailed information about elevation changes, allowing hikers and climbers to plan safe routes and avoid hazards.
3. What are the different types of physical map projections?
Physical maps can be represented using various map projections, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some common projections include the Mercator projection, the Lambert conformal conic projection, and the Albers equal-area conic projection.
4. How are physical maps created?
Physical maps are created using a combination of data sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, and ground surveys. This data is then processed and analyzed to generate accurate representations of the Earth’s topography.
5. What are the limitations of physical maps?
Physical maps are two-dimensional representations of a three-dimensional world, inherently introducing some distortion. They may also be limited in their ability to accurately depict certain features, such as the precise shape of mountains or the depth of the ocean floor.
Tips for Using Physical Maps
- Choose the Right Map: Select a map that is appropriate for your specific needs, considering the scale, projection, and the level of detail required.
- Understand the Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and legends used on the map to accurately interpret its information.
- Consider the Context: Always consider the context of the map, including the date it was created and the potential for changes in the landscape over time.
- Use Additional Resources: Combine physical maps with other resources, such as online maps, GPS devices, and field observations, for a comprehensive understanding of the area.
- Practice Map Reading: Develop your map reading skills through practice and experimentation, enhancing your ability to extract valuable information from physical maps.
Conclusion
Physical maps are powerful tools for understanding and analyzing the Earth’s diverse landscapes. From navigating challenging terrain to studying the formation of mountains and the dynamics of ocean currents, physical maps provide invaluable insights into the planet’s physical characteristics. By appreciating the benefits and limitations of these maps, we can harness their power to enhance our understanding of the natural world and make informed decisions about our interactions with it. As technology advances, physical maps continue to evolve, incorporating new data sources and visualization techniques, ensuring their continued relevance and importance in the future.

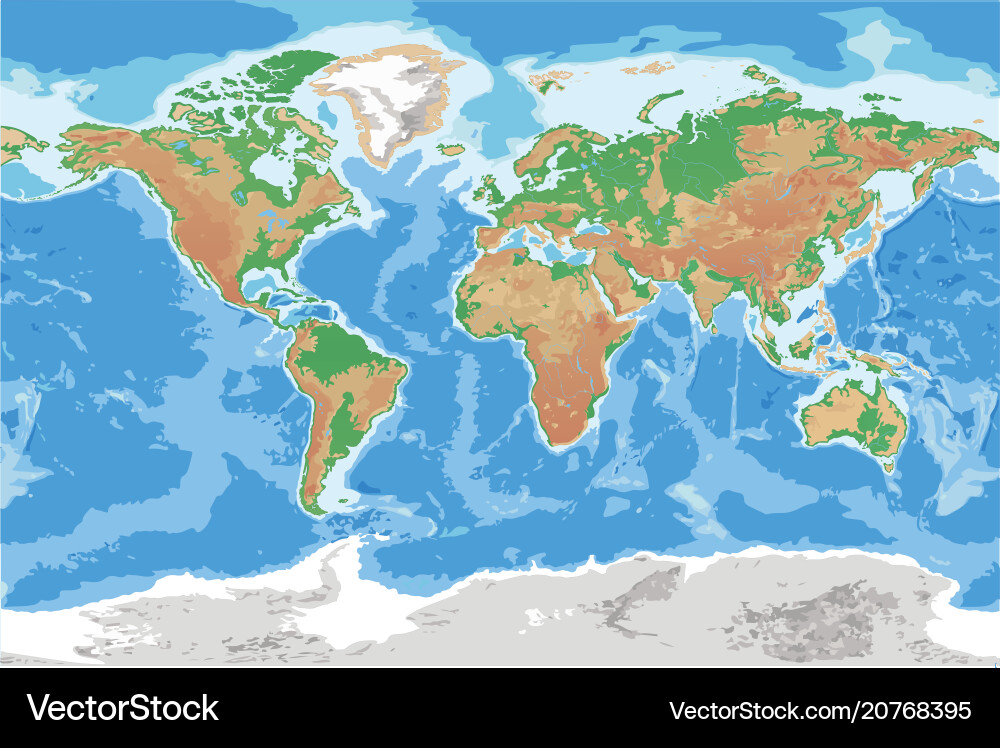
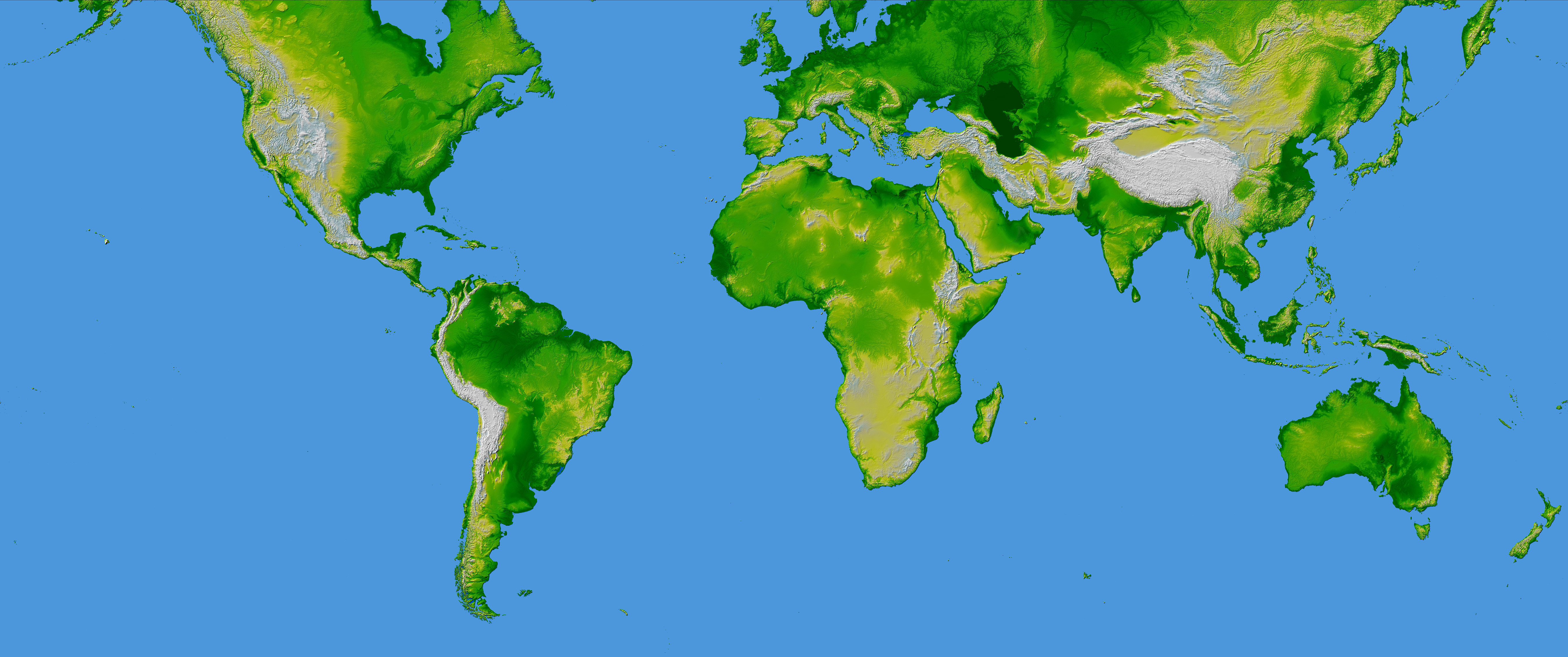
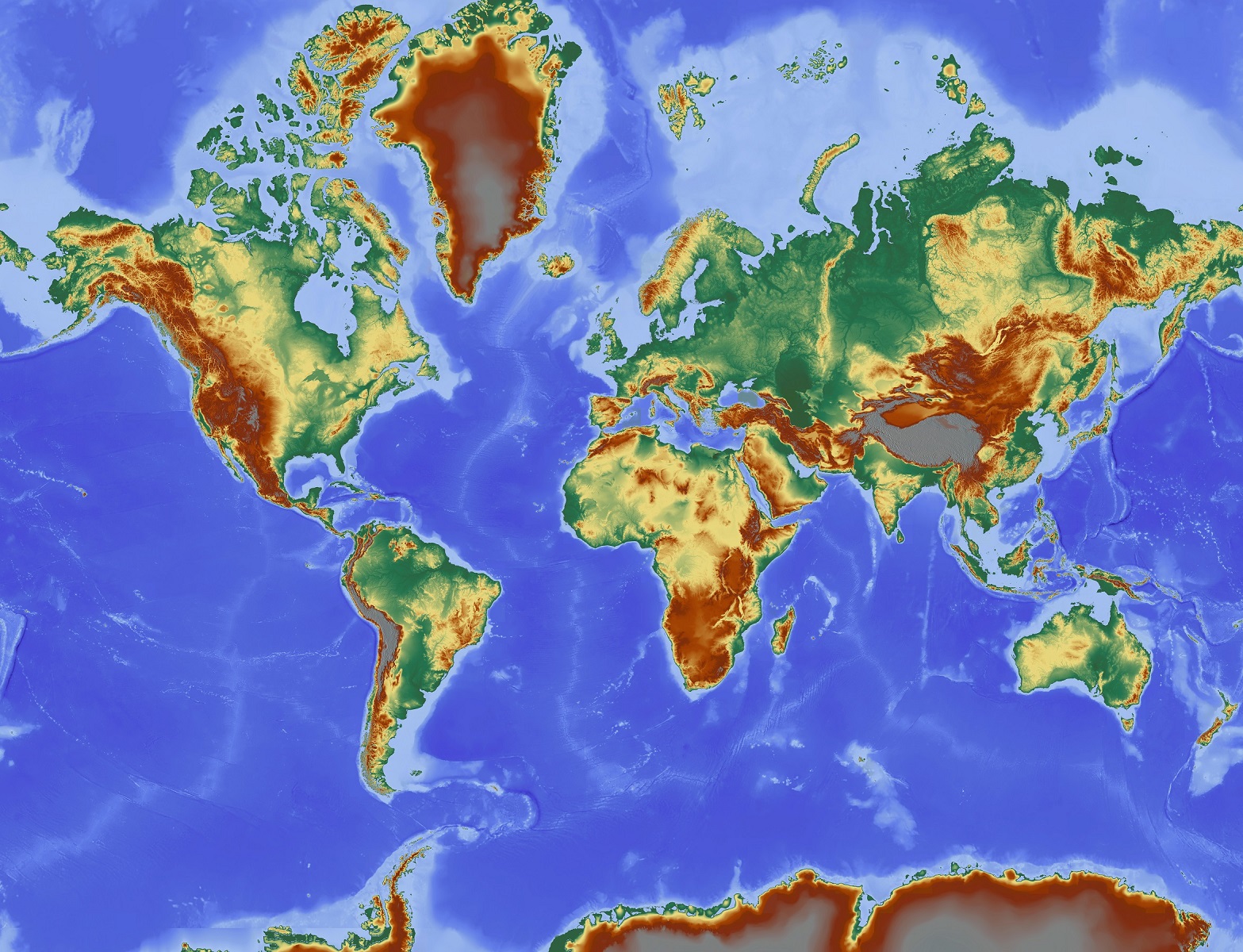
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: Exploring Physical Map Examples. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
