Unveiling the Earth’s Hidden Layers: A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Map Surveys
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Hidden Layers: A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Map Surveys
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Hidden Layers: A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Map Surveys. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Hidden Layers: A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Map Surveys

The Earth’s surface, seemingly uniform, conceals a complex tapestry of soils, each with unique characteristics and capabilities. Understanding this subterranean diversity is paramount for sustainable land management, agricultural productivity, and environmental stewardship. Soil map surveys, akin to deciphering the Earth’s hidden language, provide the key to unlocking this vital information.
Delving into the Essence of Soil Map Surveys
A soil map survey is a systematic process of mapping and characterizing the spatial distribution of soil types across a defined area. This intricate process involves a meticulous combination of field observations, laboratory analyses, and advanced spatial technologies, yielding a comprehensive representation of the soil landscape.
The Building Blocks of a Soil Map Survey
A comprehensive soil map survey typically involves the following stages:
-
Planning and Reconnaissance: This initial stage involves defining the survey area, its geographical and environmental context, and the specific objectives of the survey. Existing data, such as aerial photographs, satellite imagery, and historical soil maps, are consulted to gain preliminary insights into the soil landscape.
-
Field Sampling and Characterization: This crucial stage involves collecting soil samples at strategically chosen locations across the survey area. The collected samples are then subjected to detailed laboratory analyses to determine their physical, chemical, and biological properties, including texture, pH, nutrient content, and organic matter content.
-
Mapping and Interpretation: The collected data, encompassing both field observations and laboratory results, are then integrated and analyzed using specialized software and techniques. This process involves the creation of a soil map, visually representing the distribution of different soil types across the survey area. The map is accompanied by a detailed soil description, providing information on each soil type’s properties, limitations, and potential uses.
-
Data Management and Dissemination: The final stage involves the organization, storage, and dissemination of the collected data and the generated soil map. This ensures accessibility for various stakeholders, including farmers, land managers, researchers, and policymakers, who can utilize the information for informed decision-making.
The Significance of Soil Map Surveys: A Multifaceted Impact
Soil map surveys play a pivotal role in various aspects of land management, agriculture, and environmental protection:
-
Optimizing Agricultural Practices: Soil maps provide valuable insights into soil fertility, drainage, and other crucial factors influencing crop yields. This enables farmers to tailor their farming practices, such as fertilization and irrigation, to specific soil types, maximizing productivity and minimizing environmental impact.
-
Guiding Land Use Planning: Soil maps assist in identifying areas suitable for different land uses, such as agriculture, forestry, and urban development. By understanding soil limitations and potential hazards, policymakers can make informed decisions regarding land allocation, promoting sustainable development and minimizing environmental risks.
-
Assessing Environmental Risks: Soil maps are instrumental in identifying areas susceptible to erosion, salinity, or other environmental degradation. This information enables proactive measures to be implemented, mitigating risks and preserving soil health for future generations.
-
Supporting Environmental Restoration: Soil maps provide valuable data for guiding restoration efforts in degraded lands. By understanding the soil properties and limitations, restoration projects can be tailored to specific sites, maximizing success and ensuring long-term sustainability.
-
Facilitating Scientific Research: Soil maps serve as a crucial foundation for various scientific research endeavors, including studies on soil formation, climate change impacts, and biodiversity. By providing detailed information on soil distribution and properties, they enable researchers to develop a deeper understanding of the Earth’s complex soil ecosystems.
FAQs about Soil Map Surveys
1. What is the difference between a soil survey and a soil map survey?
A soil survey encompasses a broader scope, including not only mapping soil types but also evaluating their properties and limitations, assessing their suitability for different land uses, and providing recommendations for land management practices. A soil map survey, on the other hand, focuses primarily on mapping the spatial distribution of soil types.
2. How often should soil maps be updated?
The frequency of soil map updates depends on various factors, including the rate of land use change, the intensity of agricultural practices, and the presence of natural hazards. Generally, updates are recommended every 5-10 years to ensure the map remains relevant and accurate.
3. How are soil maps used in precision agriculture?
Precision agriculture relies heavily on soil maps to guide site-specific management practices. By understanding the variability in soil properties across a field, farmers can apply fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation water more efficiently, minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization.
4. What are the limitations of soil map surveys?
Soil maps are inherently simplified representations of complex soil landscapes. Their accuracy can be influenced by factors such as the scale of the survey, the sampling density, and the variability of soil properties. It’s important to note that soil maps are not static, and their interpretation should consider the dynamic nature of soil systems.
5. What are the future trends in soil map surveys?
Advances in remote sensing, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and machine learning are revolutionizing soil map surveys. These technologies enable the development of more detailed, accurate, and dynamic soil maps, providing a deeper understanding of soil variability and its implications for sustainable land management.
Tips for Effective Soil Map Surveys
-
Collaboration and Communication: Effective soil map surveys require collaboration among various stakeholders, including soil scientists, land managers, farmers, and policymakers. Open communication and a shared understanding of the survey objectives are crucial for successful implementation.
-
Data Quality and Accuracy: Ensuring the quality and accuracy of data collected during field surveys is paramount. This involves employing standardized methods, using calibrated instruments, and implementing rigorous quality control measures.
-
Integration of Technologies: Incorporating advanced technologies, such as remote sensing, GIS, and machine learning, can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of soil map surveys.
-
Dissemination and Accessibility: The generated soil maps and associated data should be readily accessible to various stakeholders. This includes developing user-friendly formats, providing online platforms, and promoting workshops and training programs.
Conclusion: Illuminating the Path towards Sustainable Land Management
Soil map surveys, by revealing the intricate tapestry of soils beneath our feet, provide invaluable insights into the Earth’s vital resource. They empower informed decision-making, optimize agricultural practices, guide land use planning, and facilitate environmental protection. By embracing the power of soil map surveys, we can illuminate the path towards sustainable land management, ensuring the health and productivity of our soils for generations to come.






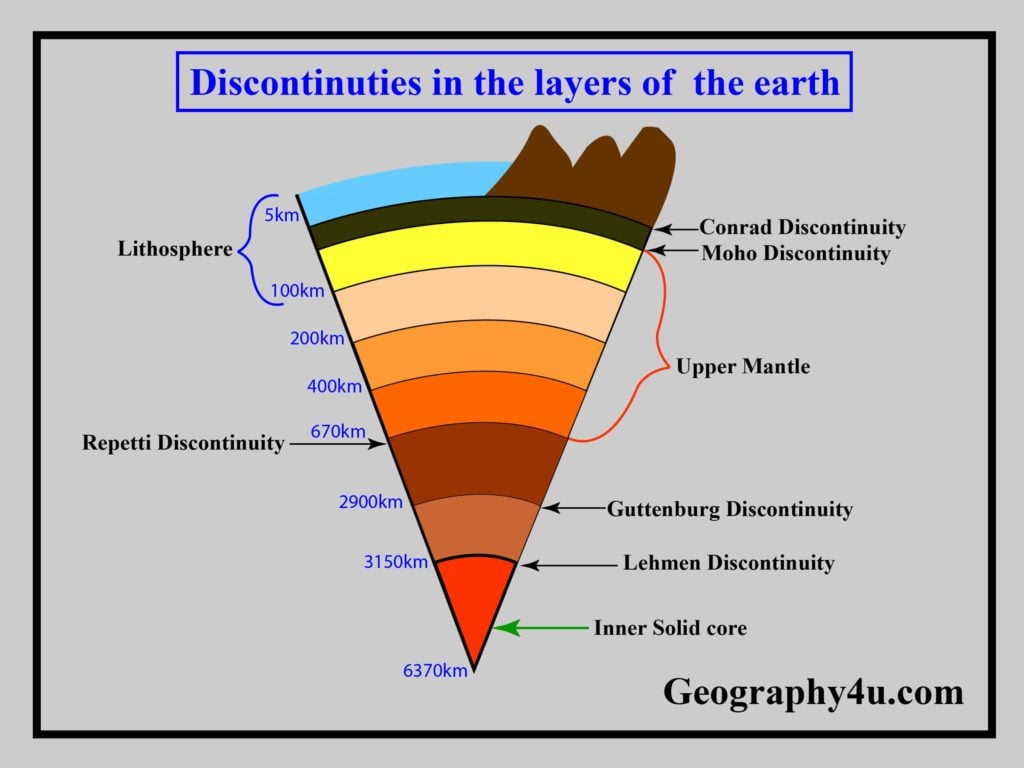
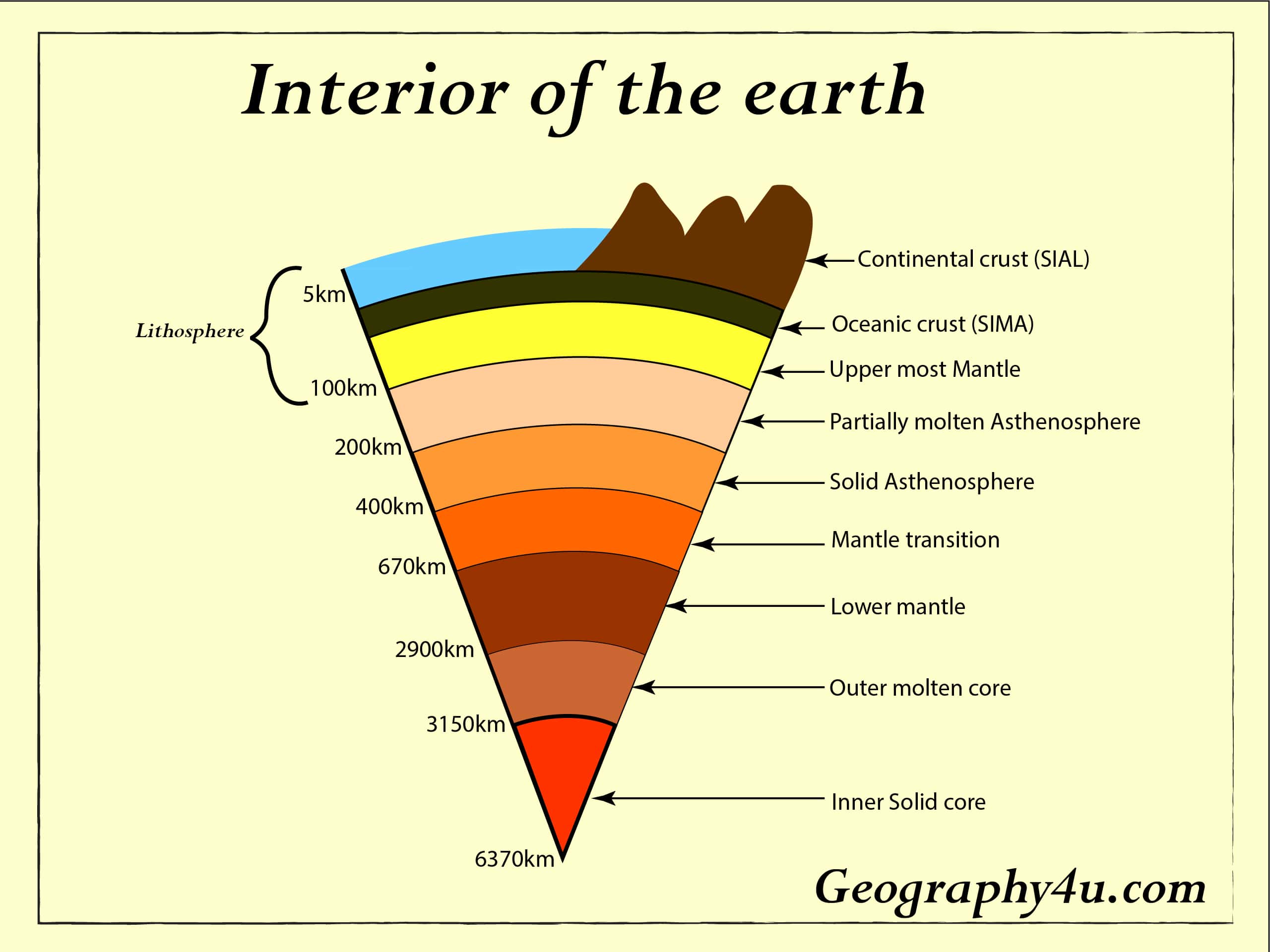
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Hidden Layers: A Comprehensive Guide to Soil Map Surveys. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!