Unraveling the Mysteries of the United States: A Guide to Magnetic Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Mysteries of the United States: A Guide to Magnetic Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Mysteries of the United States: A Guide to Magnetic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Mysteries of the United States: A Guide to Magnetic Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Mysteries of the United States: A Guide to Magnetic Maps
- 3.1 Unveiling the Invisible: The Nature of Magnetic Maps
- 3.2 Applications of Magnetic Maps in the United States
- 3.3 FAQs about Magnetic Maps of the United States
- 3.4 Tips for Understanding and Using Magnetic Maps
- 3.5 Conclusion: The Importance of Magnetic Maps in Understanding the United States
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Mysteries of the United States: A Guide to Magnetic Maps

The United States, a vast and diverse nation, holds within its borders a complex tapestry of geological formations, each contributing to the intricate web of Earth’s magnetic field. This magnetic field, invisible yet ever-present, plays a crucial role in various aspects of our lives, from navigation and communication to the very formation of our planet. Understanding this magnetic field requires specialized tools, and among them, magnetic maps stand out as invaluable aids in deciphering the secrets hidden beneath the surface.
Unveiling the Invisible: The Nature of Magnetic Maps
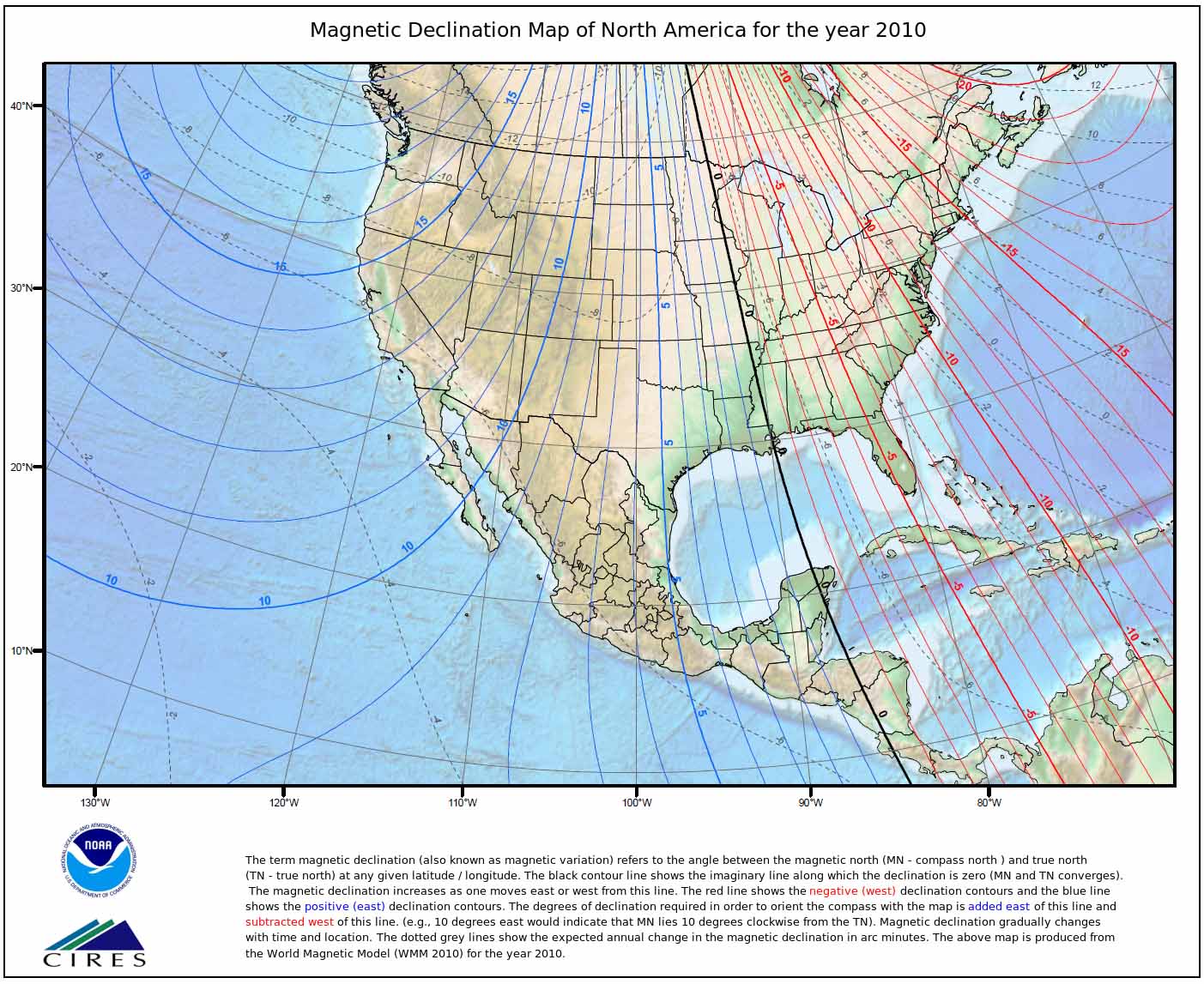
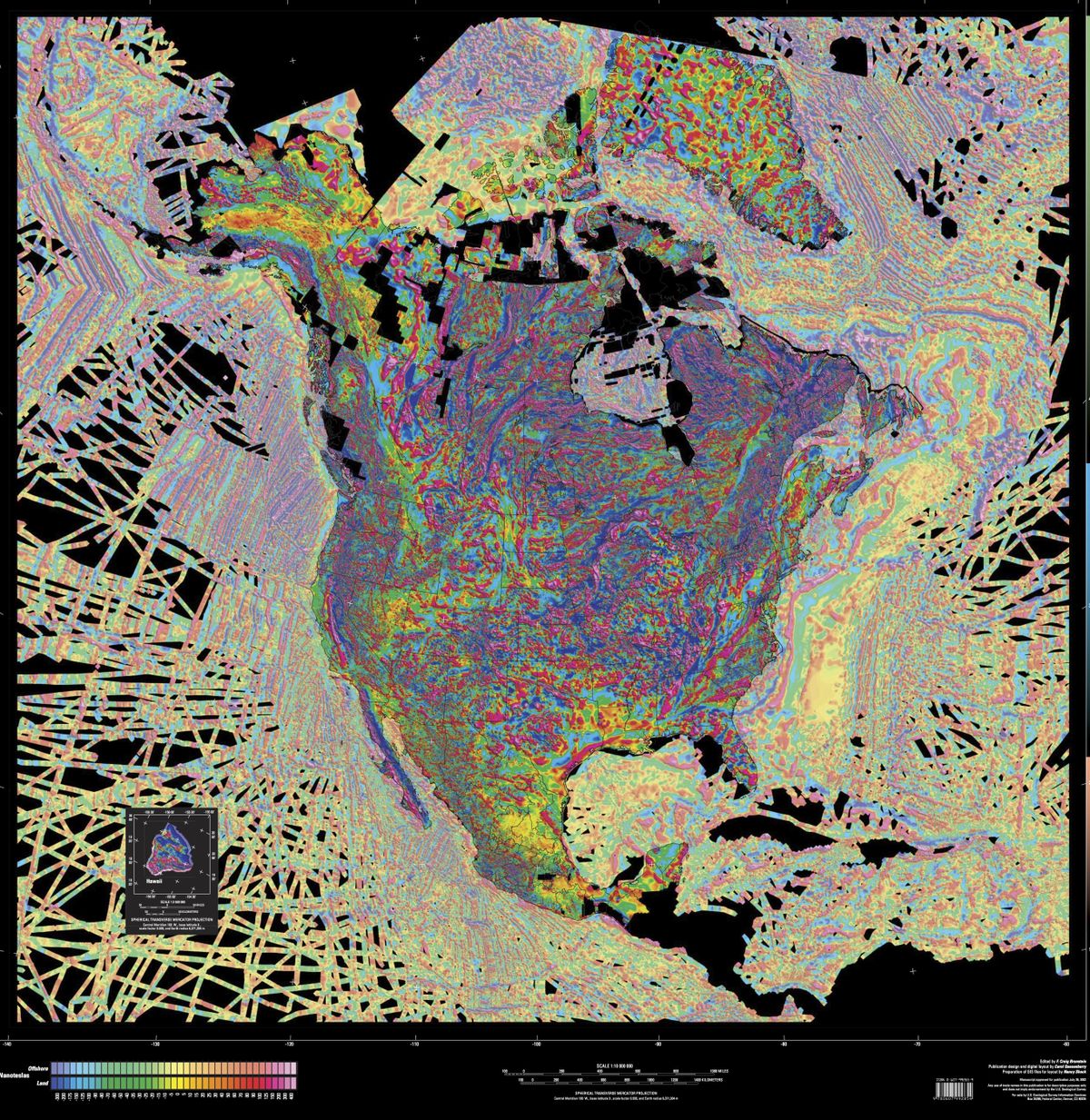
Magnetic maps, specifically those focused on the United States, provide a visual representation of the Earth’s magnetic field strength and direction at various locations across the country. These maps are not merely static depictions but rather dynamic representations, reflecting the constantly changing nature of the magnetic field. The data used to create these maps is collected through meticulous measurements taken by specialized instruments, such as magnetometers, deployed on land, sea, and even in space.
The data collected by these instruments reveals variations in the magnetic field intensity and direction, creating a unique fingerprint for each location. These variations are influenced by several factors, including:
- The Earth’s Core: The Earth’s core, a molten ball of iron and nickel, acts as a giant dynamo, generating the magnetic field. The movement of this molten metal creates electric currents, which in turn produce a magnetic field that extends far beyond the Earth’s surface.
- Geological Formations: Different rock formations possess varying magnetic properties, influencing the local magnetic field strength. This is particularly evident in areas with significant iron ore deposits or volcanic activity.
- Human Activities: Human activities, such as the construction of power lines and pipelines, can also impact the local magnetic field. These artificial sources of magnetism can be identified and mapped, providing valuable information for various purposes.
Applications of Magnetic Maps in the United States
The applications of magnetic maps in the United States are diverse and far-reaching, encompassing various fields, including:
- Mineral Exploration: Geologists use magnetic maps to identify areas with high concentrations of magnetic minerals, such as iron ore, which are valuable resources for industries like steel production. By analyzing magnetic anomalies, they can pinpoint potential locations for mineral exploration and extraction.
- Hydrocarbon Exploration: Magnetic maps are also crucial in oil and gas exploration. These maps help identify geological structures, such as faults and folds, which can trap hydrocarbons. By understanding the magnetic field variations associated with these structures, exploration teams can target areas with higher potential for oil and gas discoveries.
- Geohazard Assessment: Magnetic maps play a vital role in assessing geological hazards, such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. By mapping the magnetic field variations, scientists can identify areas with increased tectonic activity, providing crucial information for disaster preparedness and mitigation.
- Navigation and Positioning: Magnetic maps are indispensable for navigation and positioning systems, especially in remote areas where GPS signals may be unreliable. By understanding the magnetic field direction and inclination, navigation systems can accurately determine location and heading.
- Archaeological Research: Magnetic maps can aid in archaeological research by identifying buried structures and artifacts. These maps reveal anomalies in the magnetic field caused by the presence of buried objects, helping archaeologists pinpoint potential excavation sites.
- Military Applications: Magnetic maps have significant applications in military operations, particularly in areas where traditional navigation systems are ineffective. These maps provide crucial information for navigation, target identification, and the detection of buried objects.
FAQs about Magnetic Maps of the United States
1. What are the different types of magnetic maps available for the United States?
Magnetic maps of the United States are available in various forms, including:
- Aeromagnetic Maps: These maps are created using data collected by airborne magnetometers, providing a comprehensive overview of the magnetic field across large areas.
- Ground Magnetic Maps: These maps are created using data collected by magnetometers placed on the ground, providing detailed information about the magnetic field in specific locations.
- Marine Magnetic Maps: These maps are created using data collected by magnetometers towed behind ships, providing insights into the magnetic field variations in ocean basins.
- Satellite Magnetic Maps: These maps are created using data collected by satellites, providing a global perspective on the Earth’s magnetic field, including the United States.
2. How are magnetic maps created?
Magnetic maps are created through a process that involves collecting data, processing it, and then presenting it in a visually understandable format. This process typically involves:
- Data Acquisition: Data is collected using magnetometers, which measure the strength and direction of the magnetic field at various locations.
- Data Processing: The collected data is processed to remove noise and other unwanted signals, resulting in a clean and accurate representation of the magnetic field.
- Map Creation: The processed data is then used to create maps, either in the form of contour lines representing magnetic field intensity or as color-coded images depicting variations in the magnetic field.
3. Are magnetic maps accurate?
The accuracy of magnetic maps depends on various factors, including the quality of the data used, the processing techniques employed, and the scale of the map. However, with advancements in technology and data processing techniques, modern magnetic maps provide highly accurate representations of the Earth’s magnetic field.
4. How often are magnetic maps updated?
Magnetic maps are constantly updated as new data becomes available. The frequency of updates depends on the purpose of the map and the specific data source. For example, maps used for navigation may be updated more frequently than maps used for geological research.
5. How can I access magnetic maps of the United States?
Magnetic maps of the United States are available from various sources, including:
- Government Agencies: The United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) provide access to magnetic map data and publications.
- Academic Institutions: Many universities and research institutions conduct magnetic surveys and make their data available to the public.
- Private Companies: Several private companies specialize in magnetic data acquisition and analysis, offering access to their maps and services.
Tips for Understanding and Using Magnetic Maps
- Interpreting Magnetic Anomalies: When examining magnetic maps, focus on identifying anomalies, or areas where the magnetic field deviates significantly from the surrounding area. These anomalies can indicate the presence of magnetic minerals, geological structures, or human-made objects.
- Understanding the Scale: Pay attention to the scale of the map, as it determines the level of detail and the resolution of the data. Larger-scale maps provide more detailed information about specific areas, while smaller-scale maps provide a broader overview.
- Considering the Data Source: Be aware of the data source used to create the map, as it influences the accuracy and reliability of the information. Data collected by different methods, such as airborne or ground surveys, may have different levels of precision.
- Using the Right Tools: Employ appropriate software and tools for analyzing magnetic map data, such as GIS software, to visualize and interpret the data effectively.
- Consulting with Experts: If you are unfamiliar with magnetic maps or require specialized knowledge, consult with experts in geophysics, geology, or other relevant fields to ensure accurate interpretation and application.
Conclusion: The Importance of Magnetic Maps in Understanding the United States
Magnetic maps are indispensable tools for understanding the hidden complexities of the United States, providing valuable insights into its geological formations, natural resources, and environmental hazards. By unraveling the mysteries of the Earth’s magnetic field, these maps contribute to advancements in mineral exploration, hydrocarbon discovery, geohazard assessment, navigation, archaeological research, and military operations. As technology continues to evolve, magnetic maps are expected to play an even more prominent role in shaping our understanding of the United States and its natural world.

![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Mysteries of the United States: A Guide to Magnetic Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!