Understanding the Role of a 3-Bar MAP Sensor in GM Vehicles
Related Articles: Understanding the Role of a 3-Bar MAP Sensor in GM Vehicles
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Role of a 3-Bar MAP Sensor in GM Vehicles. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Role of a 3-Bar MAP Sensor in GM Vehicles
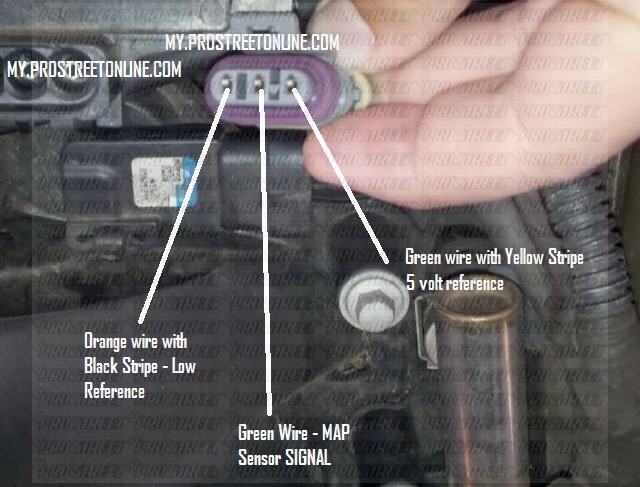
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is a critical component in modern gasoline engines, particularly those manufactured by General Motors (GM). This sensor plays a crucial role in determining the amount of fuel injected into the engine’s cylinders, ultimately influencing engine performance and fuel efficiency. While various types of MAP sensors exist, the 3-bar MAP sensor is commonly found in GM vehicles, particularly those equipped with higher-performance engines.
How a 3-Bar MAP Sensor Functions
A 3-bar MAP sensor, like its counterparts, measures the pressure within the intake manifold. This pressure, known as manifold absolute pressure, directly correlates with the amount of air entering the engine. The sensor converts this pressure into an electrical signal that the engine control unit (ECU) interprets.
The 3-bar MAP sensor distinguishes itself from other sensors through its higher pressure range. This means it can accurately measure pressure levels up to 3 bars (approximately 43.5 psi), exceeding the capabilities of standard 1-bar sensors. This higher pressure range is particularly beneficial in engines with forced induction systems, such as turbochargers or superchargers, which generate significantly higher manifold pressures.
The Significance of a 3-Bar MAP Sensor
In vehicles equipped with forced induction, a 3-bar MAP sensor is essential for accurate engine management. By providing the ECU with precise pressure readings, it allows the system to:
- Optimize Fuel Injection: The ECU uses the pressure information to calculate the ideal amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders, ensuring optimal combustion and performance. This is crucial for maximizing power output and minimizing fuel consumption.
- Control Boost Pressure: In turbocharged engines, the ECU can utilize the MAP sensor readings to regulate the boost pressure generated by the turbocharger. This ensures safe and efficient operation while preventing damage to the engine.
- Enhance Engine Performance: The accurate pressure readings provided by the 3-bar sensor allow for more precise engine tuning, resulting in smoother acceleration, increased power output, and improved throttle response.
Identifying a 3-Bar MAP Sensor
The 3-bar MAP sensor is typically located in the intake manifold, close to the throttle body. It is usually a small, cylindrical component with a single electrical connector. To identify a 3-bar sensor, look for markings or labels indicating its pressure range (e.g., "3-bar"). Alternatively, consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a reliable online resource for specific sensor identification.
Potential Issues with a 3-Bar MAP Sensor
Like any other sensor, a 3-bar MAP sensor can experience malfunctions. Common symptoms of a faulty sensor include:
- Rough Idle: An inaccurate pressure reading can lead to inconsistent fuel delivery, resulting in a rough engine idle.
- Stalling Engine: A malfunctioning sensor may provide incorrect pressure information, causing the ECU to shut down the engine.
- Reduced Power Output: A faulty sensor can limit the engine’s ability to deliver its full power potential.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Inaccurate pressure readings can cause the ECU to overcompensate with fuel injection, leading to increased fuel consumption.
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning MAP sensor will trigger the check engine light, alerting the driver to a potential issue.
FAQs about 3-Bar MAP Sensors in GM Vehicles
Q: Can I replace a 1-bar MAP sensor with a 3-bar sensor?
A: While it may seem like a simple upgrade, replacing a 1-bar sensor with a 3-bar sensor is generally not recommended. The ECU is programmed to work with a specific pressure range, and using a different sensor can lead to unexpected behavior and potential damage to the engine.
Q: What are the signs of a faulty 3-bar MAP sensor?
A: Symptoms include rough idle, stalling engine, reduced power output, increased fuel consumption, and a check engine light.
Q: How do I diagnose a faulty 3-bar MAP sensor?
A: A qualified mechanic can use a scan tool to read the sensor’s output and compare it to expected values. They can also perform a visual inspection of the sensor for damage or corrosion.
Q: How often should I replace my 3-bar MAP sensor?
A: There is no set replacement schedule for MAP sensors. However, regular maintenance and inspection can help identify any potential issues early on. If you notice any symptoms of a faulty sensor, it’s best to have it checked by a professional.
Q: Can I adjust the 3-bar MAP sensor myself?
A: Adjusting the sensor is not recommended, as it can negatively affect engine performance and potentially damage the engine.
Tips for Maintaining a 3-Bar MAP Sensor
- Regular Inspections: Visually inspect the sensor for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Clean the Sensor: If necessary, gently clean the sensor with a non-abrasive cleaner and a soft cloth.
- Avoid Contaminants: Keep the sensor area clean and free of dirt, oil, and other contaminants.
- Professional Maintenance: Regularly have your vehicle serviced by a qualified mechanic to ensure proper operation and identify any potential issues early on.
Conclusion
The 3-bar MAP sensor plays a critical role in ensuring optimal performance and fuel efficiency in GM vehicles equipped with forced induction systems. By accurately measuring manifold pressure, it provides the ECU with essential data for precise fuel injection and boost pressure control. Understanding the function and importance of this sensor can help you identify potential issues early on and ensure the long-term health and performance of your vehicle.

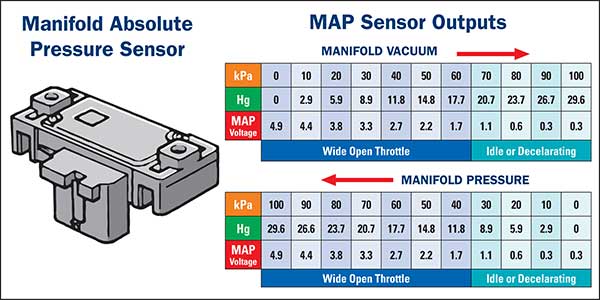



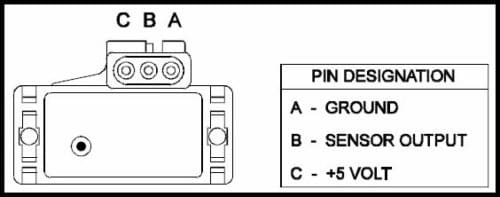


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Role of a 3-Bar MAP Sensor in GM Vehicles. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!