The Sahel: A Band of Life in a Sea of Sand
Related Articles: The Sahel: A Band of Life in a Sea of Sand
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Sahel: A Band of Life in a Sea of Sand. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Sahel: A Band of Life in a Sea of Sand

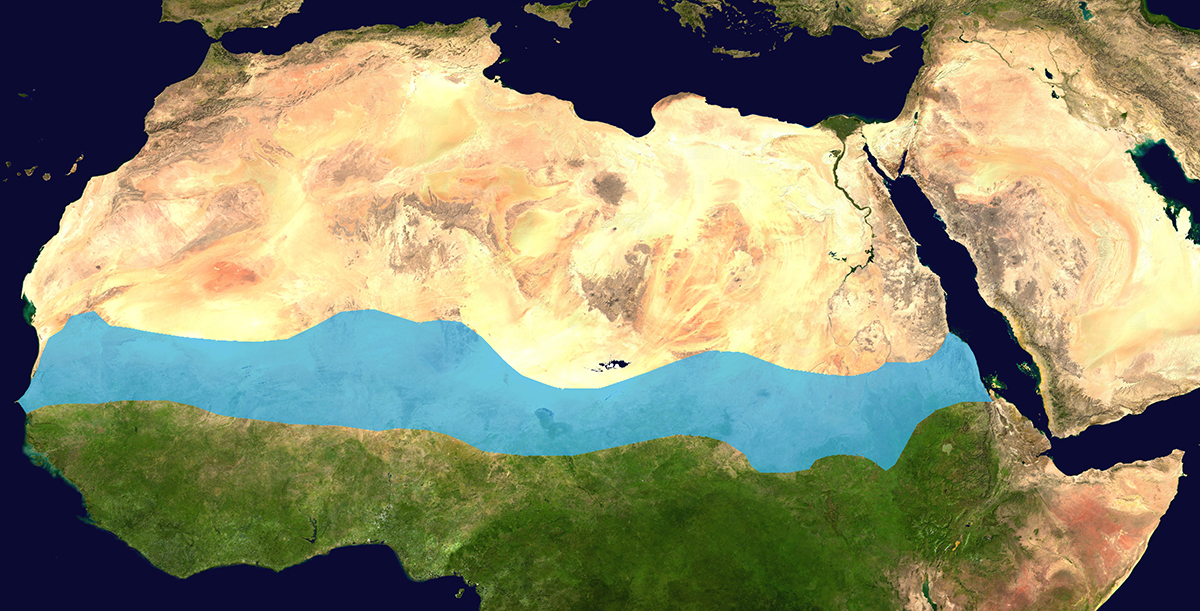
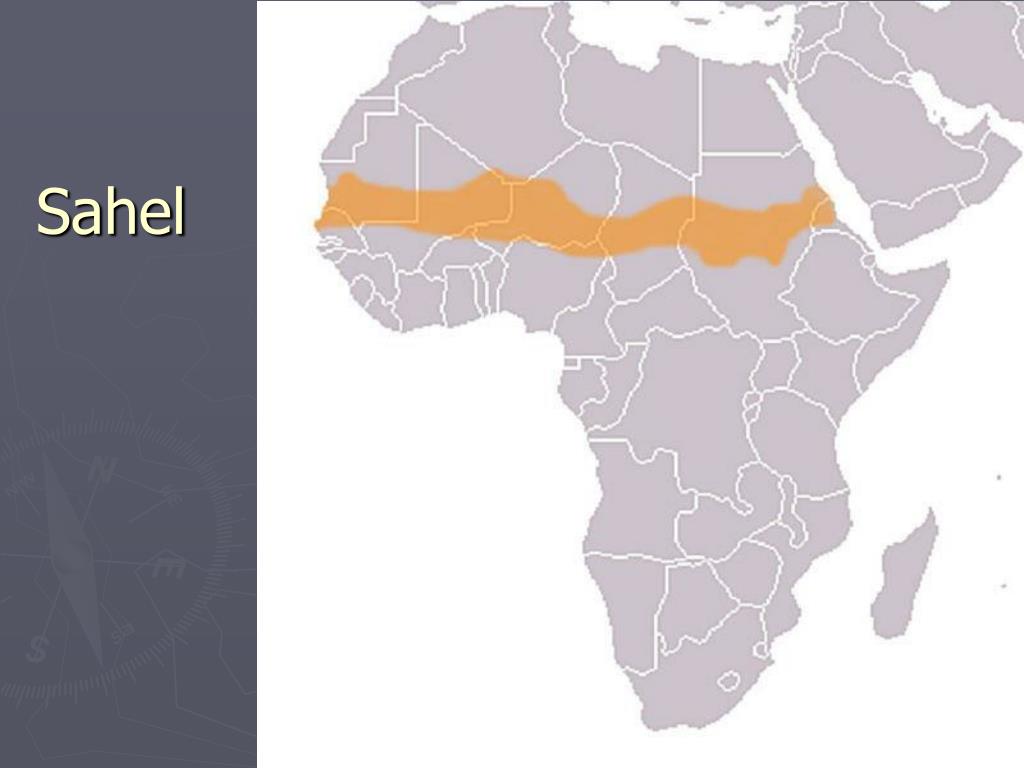
The Sahel, a semi-arid region spanning across the African continent, is a band of life nestled between the Sahara Desert to the north and the savannas and forests of Sudanian Africa to the south. Its unique position, stretching from Senegal in the west to Eritrea in the east, makes it a critical geographical and ecological zone. Understanding the Sahel’s intricate landscape, its people, and its challenges is crucial for comprehending the complexities of Africa and the world at large.
A Tapestry of Landscapes:
The Sahel is not a monolithic entity; it is a diverse mosaic of landscapes, each with its own distinct features.
- The Northern Edge: The Sahel’s northern boundary is marked by the Sahara Desert, a vast expanse of sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and salt flats. This region receives minimal rainfall, making it a harsh environment for life.
- The Sahel Proper: This central zone is characterized by savanna grasslands, acacia woodlands, and seasonal rivers. While rainfall is scarce, it is sufficient to support a diverse array of plant and animal life, including migratory birds, gazelles, and lions.
- The Southern Edge: The Sahel gradually blends into the Sudanian savanna, where rainfall is more abundant and vegetation denser. This transition zone is marked by a greater variety of trees, including baobab and shea butter trees.
A Lifeline for People and Wildlife:
Despite the harsh conditions, the Sahel has long been home to a diverse array of people and wildlife.
- Nomadic Pastoralists: For centuries, nomadic pastoralists have traversed the Sahel, adapting to the changing seasons and utilizing the land’s resources for their livestock. They have developed sophisticated systems for managing their herds and navigating the arid landscape.
- Agriculture and Farming: In areas with sufficient rainfall, communities engage in subsistence agriculture, cultivating crops such as millet, sorghum, and peanuts. These communities play a vital role in food security, providing sustenance not only for themselves but also for surrounding regions.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The Sahel is a crucial habitat for numerous species, including migratory birds, antelopes, and endangered animals like the African wild dog. The region’s unique ecosystems provide a vital refuge for these creatures, showcasing the rich biodiversity that exists in this challenging environment.
Challenges Facing the Sahel:
The Sahel is facing a multitude of challenges, many of which are exacerbated by climate change.
- Drought and Desertification: The Sahel is highly susceptible to drought, which can lead to desertification, the degradation of land into barren desert. This process is driven by factors such as overgrazing, deforestation, and climate change.
- Climate Change: The Sahel is experiencing rising temperatures and unpredictable rainfall patterns. These changes are impacting the region’s fragile ecosystems, leading to increased drought, desertification, and food insecurity.
- Conflict and Instability: The Sahel is plagued by conflict and instability, fueled by poverty, resource scarcity, and competition for land. These conflicts disrupt livelihoods, displace populations, and undermine development efforts.
- Population Growth: The Sahel’s population is growing rapidly, placing increasing pressure on the region’s already scarce resources. This growth exacerbates existing challenges, such as land degradation, water scarcity, and food insecurity.
The Importance of the Sahel:
The Sahel’s importance extends beyond its unique geographical features and ecological significance. It plays a crucial role in:
- Regional Stability: The Sahel’s stability is intertwined with the stability of the entire African continent. Conflict and instability in the region can have ripple effects, destabilizing neighboring countries and hindering regional development.
- Global Security: The Sahel is increasingly becoming a focal point for international security concerns, with the presence of extremist groups and transnational criminal networks posing a threat to regional and global stability.
- Food Security: The Sahel is a key food production region for Africa. Drought and other challenges threaten the region’s ability to produce food, impacting not only the Sahel itself but also neighboring countries and global food security.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The Sahel is home to a wealth of biodiversity, including endangered species. Conserving this biodiversity is crucial for maintaining the ecological balance of the region and for preserving the planet’s genetic diversity.
The Sahel: A Region in Transition:
The Sahel is a region in transition, facing a multitude of challenges and opportunities. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on:
- Climate Change Adaptation: Investing in climate change adaptation measures, such as drought-resistant crops, water conservation technologies, and sustainable land management practices, is crucial for building resilience in the Sahel.
- Conflict Resolution and Peacebuilding: Addressing the root causes of conflict, promoting dialogue and reconciliation, and investing in sustainable development are essential for achieving lasting peace in the Sahel.
- Sustainable Development: Investing in sustainable development initiatives, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure, is crucial for improving livelihoods, empowering communities, and fostering economic growth in the Sahel.
- International Cooperation: The Sahel’s challenges require a collaborative response, involving governments, international organizations, and civil society. Shared efforts are needed to address the region’s complex problems and to build a more sustainable future.
FAQs about the Sahel:
Q: What is the Sahel?
A: The Sahel is a semi-arid region in Africa that stretches across the continent from Senegal in the west to Eritrea in the east. It is characterized by savanna grasslands, acacia woodlands, and seasonal rivers.
Q: Why is the Sahel important?
A: The Sahel is important for its ecological diversity, its role in regional stability, and its contribution to global food security. It is also a significant cultural and historical region with a rich history of human adaptation to challenging environments.
Q: What are the challenges facing the Sahel?
A: The Sahel faces numerous challenges, including drought and desertification, climate change, conflict and instability, and population growth. These challenges threaten the region’s fragile ecosystems, livelihoods, and security.
Q: What can be done to address the challenges facing the Sahel?
A: Addressing the challenges facing the Sahel requires a multifaceted approach, including climate change adaptation, conflict resolution and peacebuilding, sustainable development, and international cooperation.
Tips for Understanding the Sahel:
- Explore the region’s history: Understanding the Sahel’s history, including its cultural traditions, nomadic lifestyles, and interactions with neighboring regions, provides valuable context for understanding its present challenges.
- Learn about the region’s ecosystems: Understanding the Sahel’s diverse ecosystems, from the Sahara Desert to the Sudanian savanna, is crucial for appreciating the region’s unique biodiversity and the challenges it faces.
- Engage with local communities: Connecting with local communities in the Sahel provides valuable insights into the region’s challenges and opportunities, fostering empathy and understanding.
- Support sustainable development initiatives: Supporting organizations working on sustainable development projects in the Sahel contributes to building a more resilient and prosperous future for the region.
Conclusion:
The Sahel is a region of immense importance, both for Africa and the world. Understanding its unique landscape, its people, and its challenges is crucial for fostering a more sustainable and equitable future. By engaging with the region’s complex realities and supporting efforts to address its challenges, we can help build a more resilient and prosperous Sahel, contributing to a more stable and sustainable future for all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Sahel: A Band of Life in a Sea of Sand. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!