The Punic Wars: A Cartographic Journey of Conflict
Related Articles: The Punic Wars: A Cartographic Journey of Conflict
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Punic Wars: A Cartographic Journey of Conflict. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Punic Wars: A Cartographic Journey of Conflict

The Punic Wars, a series of three brutal conflicts fought between Rome and Carthage from 264 to 146 BCE, stand as a pivotal turning point in the history of the ancient world. These wars, etched into the annals of history as some of the most significant military clashes, not only reshaped the Mediterranean landscape but also profoundly impacted the development of the Roman Republic and its transition into an empire. Understanding the Punic Wars requires a spatial perspective, a journey through the map, to grasp the strategic intricacies, geographical challenges, and ultimately, the consequences of these epic struggles.
A Clash of Civilizations: The Geographic Context
The map of the Punic Wars is not merely a backdrop, but a key player in the narrative. It highlights the geographical factors that fueled the conflict:
-
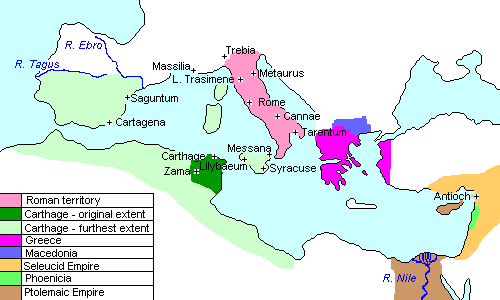
The Mediterranean Sea: This vast expanse of water served as both a bridge and a barrier between Rome and Carthage. It facilitated trade and communication, but also provided a strategic battleground for naval warfare. The control of the Mediterranean was crucial for both powers, as it allowed them to project their influence and secure vital resources.
-
The Italian Peninsula: Rome, the heart of the Roman Republic, was strategically located on the Italian Peninsula. This geographical advantage allowed Rome to control the land routes connecting the northern and southern parts of Italy, providing access to resources and manpower.
-
North Africa: Carthage, a powerful Phoenician city-state, dominated North Africa. Its strategic location gave it access to rich agricultural lands, mineral resources, and a vast network of trade routes. The control of North Africa was essential for Carthage’s economic prosperity and military strength.
-
Sicily: This strategically important island, located in the heart of the Mediterranean, became the main battleground for the Punic Wars. Its fertile lands, natural harbors, and strategic location made it a valuable prize for both Rome and Carthage.
Mapping the Battles: A Journey Through Time
The map of the Punic Wars is a tapestry woven with the threads of military engagements, each battle a distinct chapter in the saga:
-
The First Punic War (264-241 BCE): This conflict was primarily fought on the seas, with the Roman navy gradually gaining the upper hand. The map reveals key battles, including the Battle of Mylae (260 BCE), where the Romans decisively defeated the Carthaginian fleet, and the Battle of the Aegates Islands (241 BCE), which marked the end of the war.
-
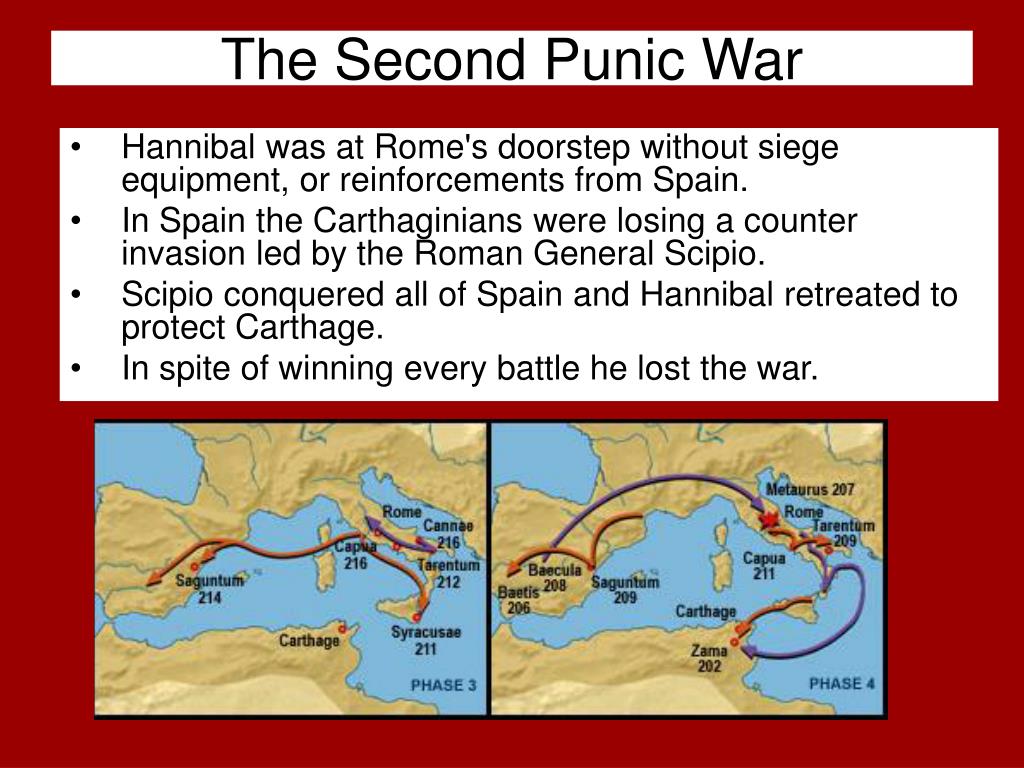
The Second Punic War (218-201 BCE): This war saw the rise of Hannibal, a brilliant Carthaginian general, who launched a daring invasion of Italy, traversing the Alps with his army. The map showcases Hannibal’s masterful campaigns, his victories at Trebia (218 BCE), Trasimene Lake (217 BCE), and Cannae (216 BCE), which shook the foundations of the Roman Republic.
-
The Third Punic War (149-146 BCE): This final conflict, fueled by Roman resentment and the desire to eliminate Carthage, was a brutal siege of the Carthaginian city. The map illustrates the gradual tightening of the Roman noose, culminating in the destruction of Carthage and the complete annihilation of its empire.
The Legacy of the Punic Wars: A New World Order
The map of the Punic Wars is not merely a record of past battles, but a window into the future. It highlights the consequences of these conflicts:
-
The Rise of Rome: The Punic Wars marked a turning point in Roman history. They honed the Roman military machine, expanded their territory, and propelled them towards becoming the dominant power in the Mediterranean.
-
The Decline of Carthage: The Punic Wars led to the destruction of Carthage, a once-mighty empire, and the end of its influence in the Mediterranean.
-
The Expansion of Roman Power: The map shows the expansion of Roman territory throughout the Punic Wars, culminating in the control of Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica, and eventually, North Africa.
-
The Development of Roman Military Strategy: The Punic Wars forced the Romans to adapt their military tactics and strategies, leading to the development of new weapons and formations, such as the Roman legions, which would become the foundation of their future military success.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Punic Wars
1. What were the main reasons for the Punic Wars?
The main reasons for the Punic Wars were competition for resources, control of trade routes, and territorial expansion. The conflict began with a dispute over the control of Sicily, a strategically important island with rich agricultural lands and natural harbors. Both Rome and Carthage saw Sicily as a crucial prize in their quest for dominance in the Mediterranean.
2. What were the main strategies used by Rome and Carthage?
Rome primarily focused on land warfare, utilizing its disciplined legions and effective siege tactics. Carthage, on the other hand, relied heavily on naval power, with its powerful fleet controlling the Mediterranean Sea. However, Carthage also employed skilled generals like Hannibal, who excelled in strategic maneuvers and ambushes.
3. What were the key battles of the Punic Wars?
The key battles of the Punic Wars include:
-
The Battle of Mylae (260 BCE): This naval battle marked the beginning of Roman dominance at sea, where the Romans decisively defeated the Carthaginian fleet.
-
The Battle of Cannae (216 BCE): This battle was a major victory for Hannibal, where he surrounded and annihilated a large Roman army.
-
The Siege of Carthage (149-146 BCE): This final siege marked the complete destruction of Carthage and the end of its empire.
4. What were the long-term consequences of the Punic Wars?
The Punic Wars had profound consequences for both Rome and Carthage. Rome emerged as the dominant power in the Mediterranean, while Carthage was completely destroyed. The wars also led to the expansion of Roman territory, the development of Roman military strategy, and the rise of Rome as a major world power.
Tips: Navigating the Map of the Punic Wars
-
Focus on the key locations: Pay attention to the strategic locations that played a significant role in the Punic Wars, such as Sicily, North Africa, and the Italian Peninsula.
-
Trace the major battles: Identify the locations of key battles on the map, such as the Battle of Mylae, the Battle of Cannae, and the Siege of Carthage.
-
Consider the geographical factors: Analyze how geographical factors, such as the Mediterranean Sea, the Alps, and the location of key cities, influenced the course of the wars.
-
Explore the historical context: Use the map as a starting point to delve deeper into the historical context of the Punic Wars, reading about the political, social, and economic factors that shaped these conflicts.
Conclusion: A Legacy Etched in Stone
The map of the Punic Wars is not merely a collection of lines and dots, but a testament to the enduring power of human conflict. It speaks of ambition, strategy, and the relentless pursuit of power. The Punic Wars, though long over, continue to captivate our imaginations, reminding us of the enduring impact of history and the importance of understanding the past to navigate the present. Through the lens of the map, we can gain a deeper understanding of these epic battles, the rise and fall of empires, and the lasting consequences of conflict. It is a reminder that the world is a stage where empires rise and fall, and the map is a silent witness to the unfolding drama of human history.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Punic Wars: A Cartographic Journey of Conflict. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!