The Ogallala Aquifer: A Vital Resource Under Threat
Related Articles: The Ogallala Aquifer: A Vital Resource Under Threat
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Ogallala Aquifer: A Vital Resource Under Threat. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ogallala Aquifer: A Vital Resource Under Threat
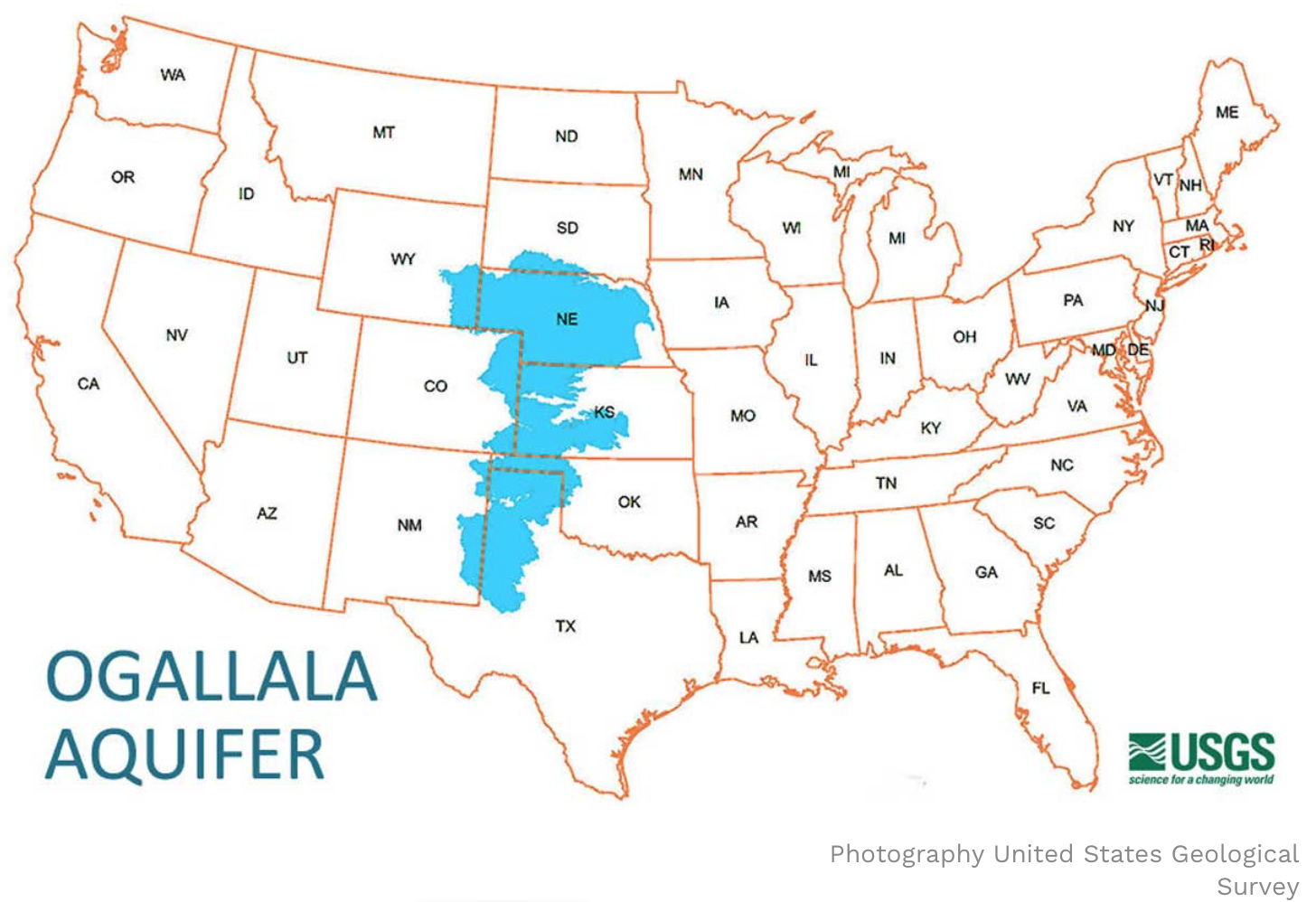
The Ogallala Aquifer, also known as the High Plains Aquifer, is a vast underground reservoir of water spanning eight states in the central United States: South Dakota, Nebraska, Wyoming, Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, and Texas. This aquifer is a vital resource, providing water for agriculture, industry, and domestic use for millions of people. However, the Ogallala Aquifer faces significant challenges, primarily due to over-pumping and depletion, making its future uncertain.
A Geological Marvel:
The Ogallala Aquifer formed over millions of years during the Pliocene Epoch, when the region was covered by a vast, shallow sea. As the sea retreated, sediment deposits from the Rocky Mountains accumulated, forming a massive layer of sand, gravel, and clay. Over time, this sediment layer became saturated with rainwater, creating the aquifer we know today.
Mapping the Aquifer:
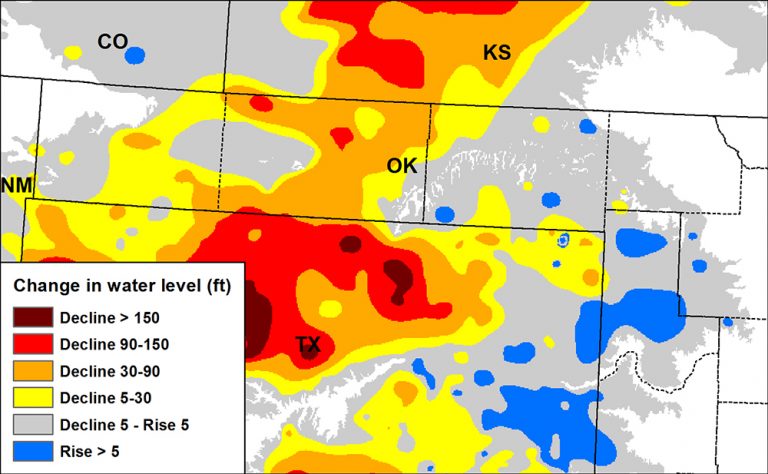
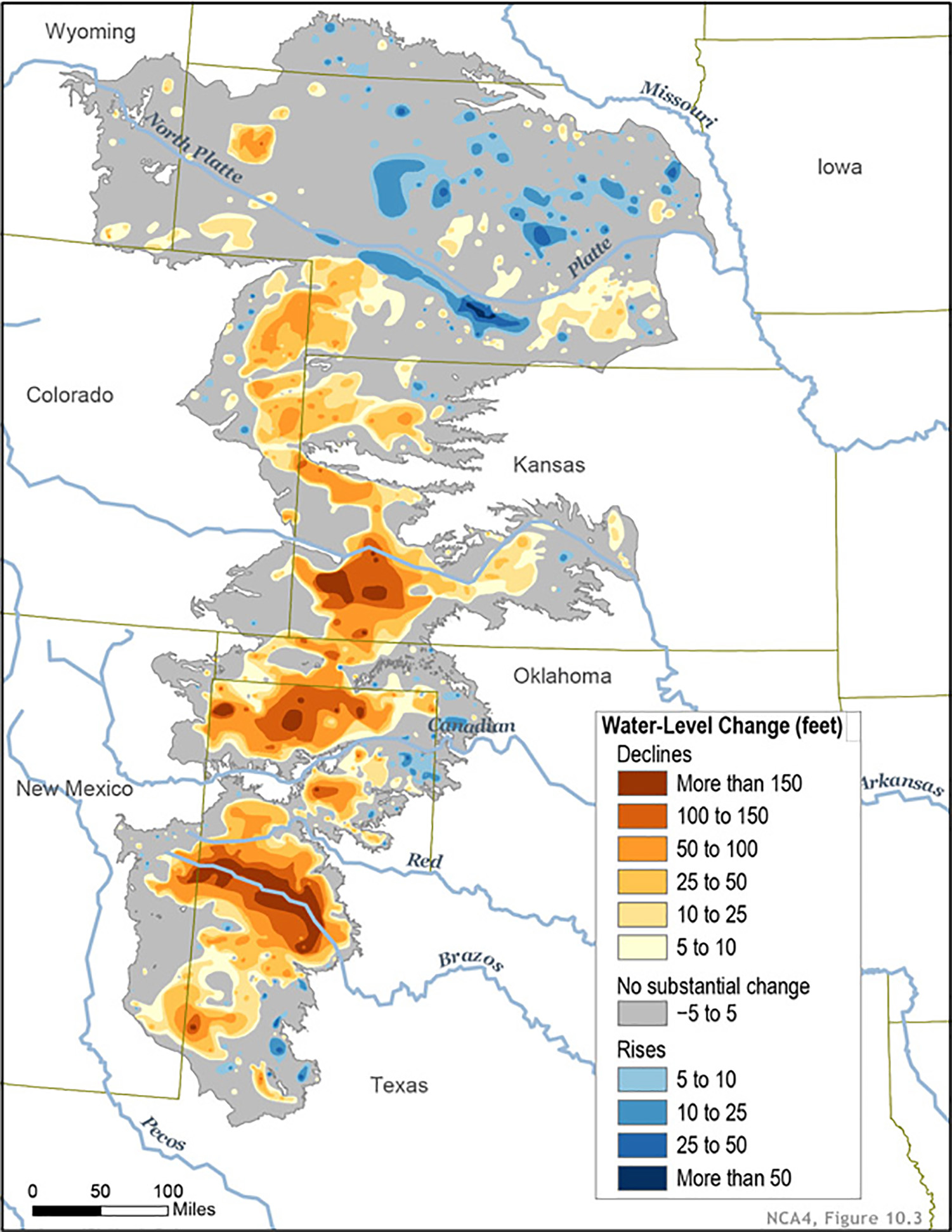
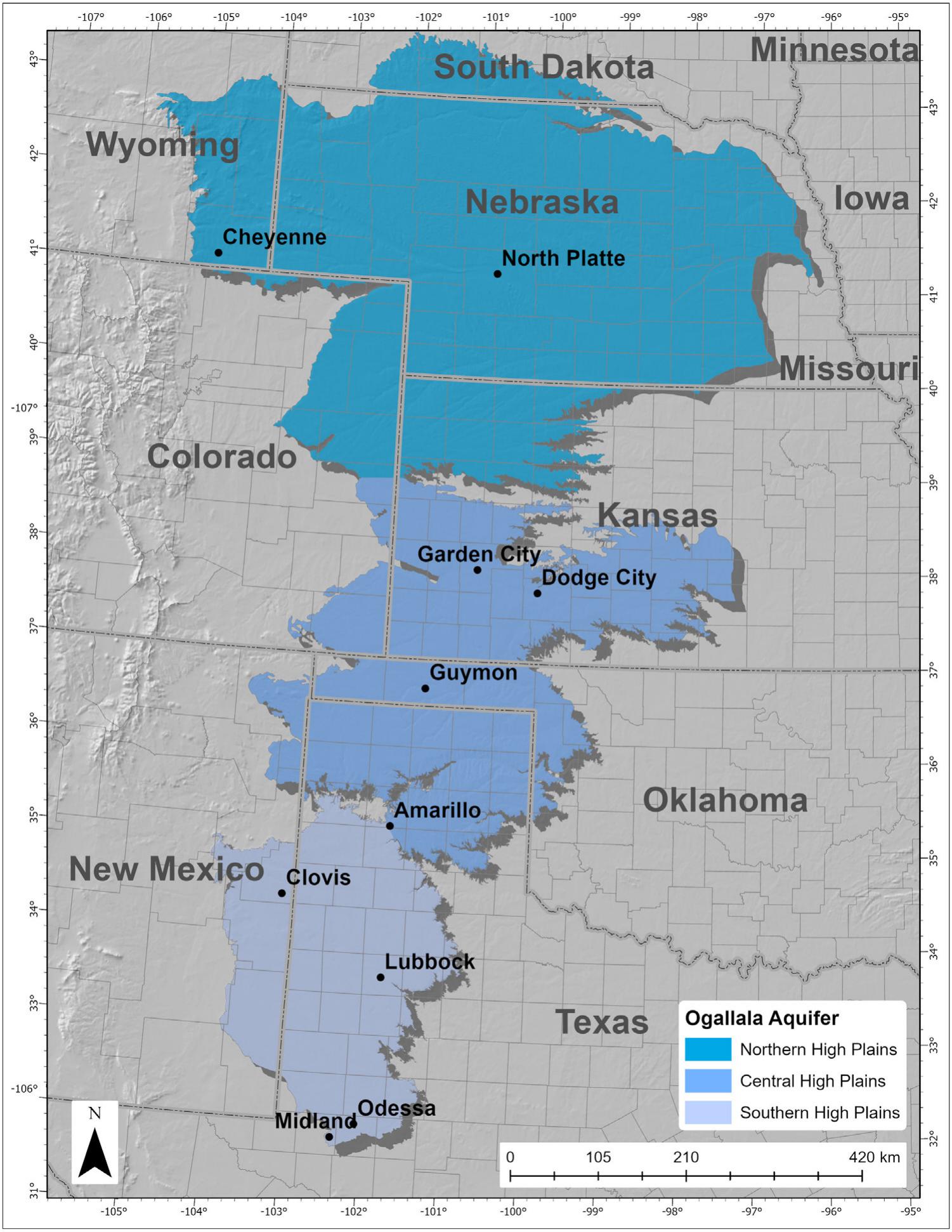
The Ogallala Aquifer is not uniform in its depth, thickness, or water quality. This variability is reflected in various maps that depict the aquifer’s characteristics. These maps are crucial for understanding the aquifer’s structure, its water resources, and the potential for sustainable management.
Key Features of the Ogallala Aquifer Map:
- Aquifer Extent: The map clearly delineates the geographic boundaries of the aquifer, indicating its presence across eight states.
- Aquifer Thickness: Different shades or contours on the map represent the depth of the aquifer at various locations. This information is crucial for understanding the volume of water available and potential for depletion.
- Water Table Elevation: The map displays the elevation of the water table, which is the upper surface of the groundwater. This data is essential for determining the depth of wells and the energy required to pump water.
- Water Quality: Some maps may include information on the quality of the water, such as salinity levels, mineral content, and the presence of contaminants. This information is essential for determining the suitability of the water for different uses.
- Groundwater Recharge Zones: The map may also highlight areas where groundwater recharge occurs naturally, such as through rainfall infiltration. This information is crucial for identifying areas where efforts to replenish the aquifer can be most effective.
The Importance of the Ogallala Aquifer:
The Ogallala Aquifer plays a vital role in the economic and social well-being of the High Plains region. It provides water for:
- Agriculture: The aquifer is the primary source of water for irrigation in the region, supporting a vast agricultural industry that produces significant amounts of wheat, corn, cotton, and livestock.
- Domestic Use: Many communities rely on the aquifer for drinking water, sanitation, and other domestic needs.
- Industry: The aquifer provides water for various industries, including manufacturing, energy production, and livestock processing.
The Challenges Facing the Ogallala Aquifer:
Despite its importance, the Ogallala Aquifer faces significant challenges, primarily due to:
- Over-pumping: The rate of water extraction from the aquifer exceeds the rate of natural replenishment. This imbalance leads to declining water levels and a shrinking aquifer.
- Climate Change: Changing rainfall patterns and increased temperatures contribute to reduced recharge rates, further exacerbating the depletion problem.
- Land Use Practices: Intensive agricultural practices, such as monoculture and excessive fertilizer use, can lead to soil degradation and reduced infiltration, further hindering recharge.
- Water Quality Degradation: Over-pumping can lead to increased salinity and contamination of the aquifer, making the water unsuitable for certain uses.
The Need for Sustainable Management:
The future of the Ogallala Aquifer depends on implementing sustainable management practices that balance the needs of water users with the need to protect the aquifer for future generations. These practices include:
- Conservation: Implementing water-saving technologies in agriculture, such as drip irrigation and drought-tolerant crops, can significantly reduce water consumption.
- Recharge: Enhancing recharge through rainwater harvesting, land management practices that promote infiltration, and artificial recharge projects can help replenish the aquifer.
- Water Allocation: Implementing equitable water allocation policies that ensure fair distribution of water resources among different users can help prevent overuse and depletion.
- Monitoring and Research: Continuous monitoring of the aquifer’s water levels, quality, and recharge rates is essential for tracking its health and informing management decisions.
FAQs:
- What are the main threats to the Ogallala Aquifer? The primary threats are over-pumping, climate change, land use practices, and water quality degradation.
- How is the Ogallala Aquifer being managed? Various organizations and agencies are involved in managing the aquifer, including state and federal governments, water conservation districts, and non-profit organizations. These organizations are working to implement sustainable management practices, such as water conservation, recharge enhancement, and water allocation policies.
- What can I do to help protect the Ogallala Aquifer? You can support efforts to conserve water, promote sustainable agricultural practices, and advocate for policies that protect the aquifer.
- Is the Ogallala Aquifer in danger of running dry? The Ogallala Aquifer is not in immediate danger of running dry, but its future is uncertain. The rate of depletion is a serious concern, and continued over-pumping could lead to significant water shortages in the future.
- What are the long-term consequences of depleting the Ogallala Aquifer? Depleting the Ogallala Aquifer could lead to significant economic and social disruptions, including agricultural decline, water shortages for communities, and displacement of populations.
Tips for Conserving Water:
- Install water-saving fixtures: Replace old toilets, showerheads, and faucets with water-efficient models.
- Water your lawn efficiently: Use a watering timer to avoid overwatering and water during cooler hours to reduce evaporation.
- Fix leaks promptly: A small leak can waste significant amounts of water over time.
- Collect rainwater: Install rain barrels to collect rainwater for watering plants and lawns.
- Choose drought-tolerant plants: Opt for plants that require less water, reducing the need for irrigation.
Conclusion:
The Ogallala Aquifer is a vital resource for the High Plains region, providing water for agriculture, industry, and domestic use. However, over-pumping, climate change, and unsustainable land use practices are putting the aquifer at risk. Effective management strategies are crucial to ensure the long-term sustainability of this precious resource. By implementing water conservation measures, promoting recharge, and advocating for responsible water allocation, we can help protect the Ogallala Aquifer for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ogallala Aquifer: A Vital Resource Under Threat. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!