The Ancient Supercontinent: A Journey Through Pangea
Related Articles: The Ancient Supercontinent: A Journey Through Pangea
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Ancient Supercontinent: A Journey Through Pangea. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ancient Supercontinent: A Journey Through Pangea
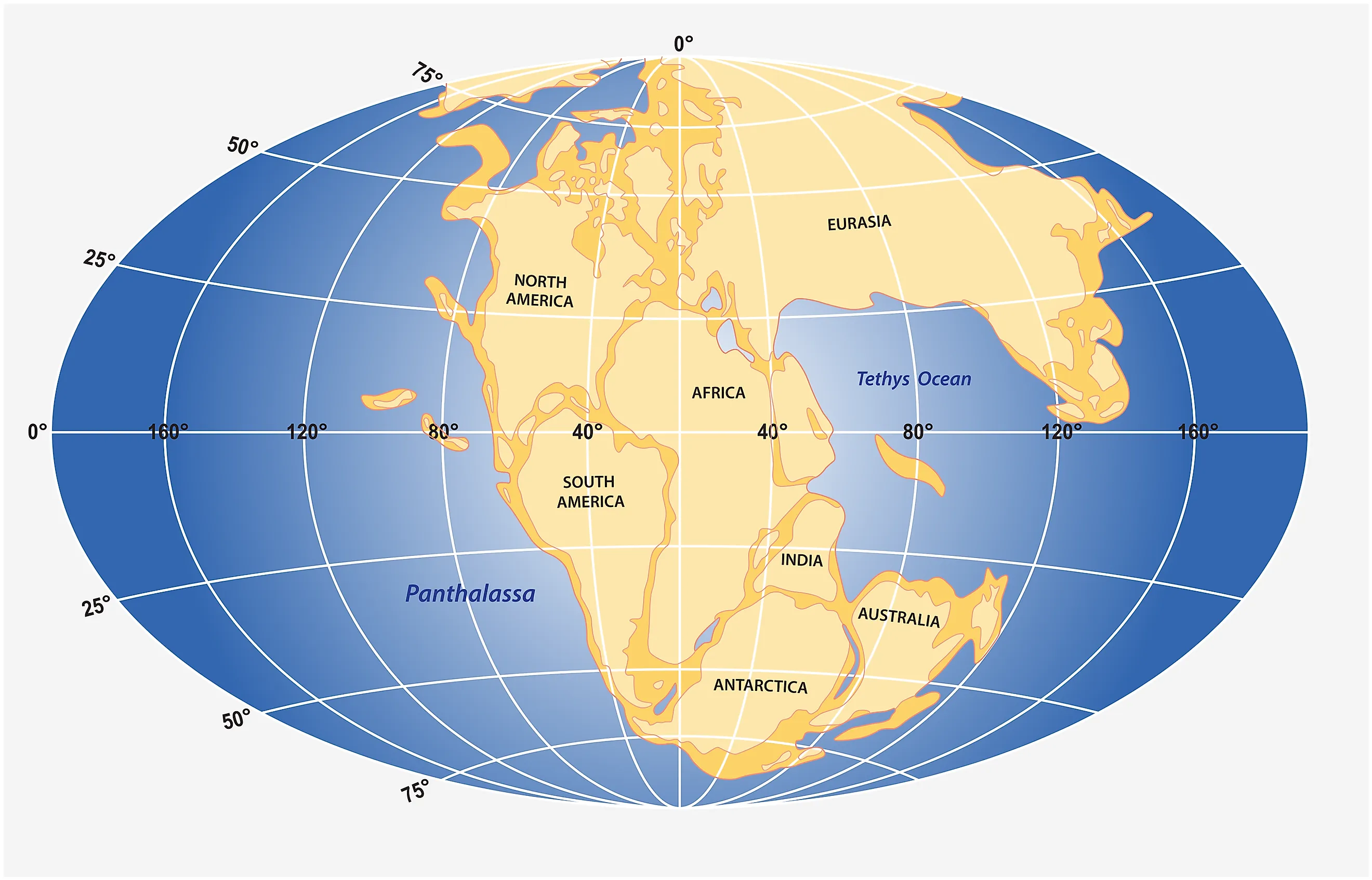
The Earth’s continents are not fixed entities; they are in constant motion, driven by the slow, powerful forces of plate tectonics. This dynamic process has shaped the planet’s surface over billions of years, leading to the formation and breakup of supercontinents. One such supercontinent, known as Pangea, dominated the Earth during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras, approximately 335 to 175 million years ago.
Pangea was a colossal landmass encompassing nearly all of the Earth’s continental crust. Its formation was a monumental event in Earth’s history, profoundly impacting climate, biodiversity, and the evolution of life. Understanding Pangea’s existence and its subsequent breakup is crucial for comprehending the geological and biological evolution of our planet.
Formation and Characteristics of Pangea:
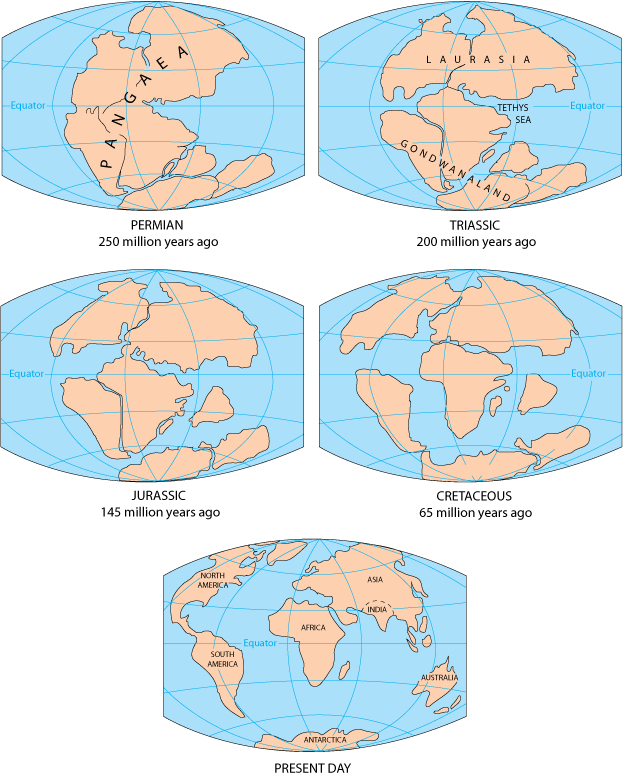
The formation of Pangea was a gradual process, driven by the convergence of multiple tectonic plates. Around 335 million years ago, during the Carboniferous period, the continents began to drift towards each other, eventually colliding to form a single massive landmass. This process involved the closure of ancient oceans, such as the Iapetus Ocean, and the formation of mountain ranges, such as the Appalachian Mountains in North America and the Ural Mountains in Russia.
Pangea had a distinctive shape, resembling a giant "C" or a puzzle piece. Its eastern side, facing the Tethys Ocean, extended from what is now North America through Europe and Asia. The western side, facing the Panthalassa Ocean, included South America, Africa, and Australia. The interior of Pangea was a vast, arid region characterized by extreme temperature fluctuations, with scorching summers and frigid winters.
Impact of Pangea on Climate and Life:
Pangea’s formation had a profound impact on global climate. The vast landmass created a continental interior far removed from the moderating influence of the oceans. This led to the development of a dry, arid climate with extreme temperature fluctuations. The interior of Pangea likely experienced significant seasonal changes, with hot, dry summers and cold, harsh winters.
The formation of Pangea also had a significant impact on the distribution of life on Earth. The merging of continents allowed for the migration of plants and animals, leading to a diversification of species. Pangea’s interior, with its arid climate, favored the evolution of drought-resistant plants and animals. The existence of a single large landmass also led to the development of unique ecosystems and the spread of certain species across vast distances.
Breakup of Pangea:
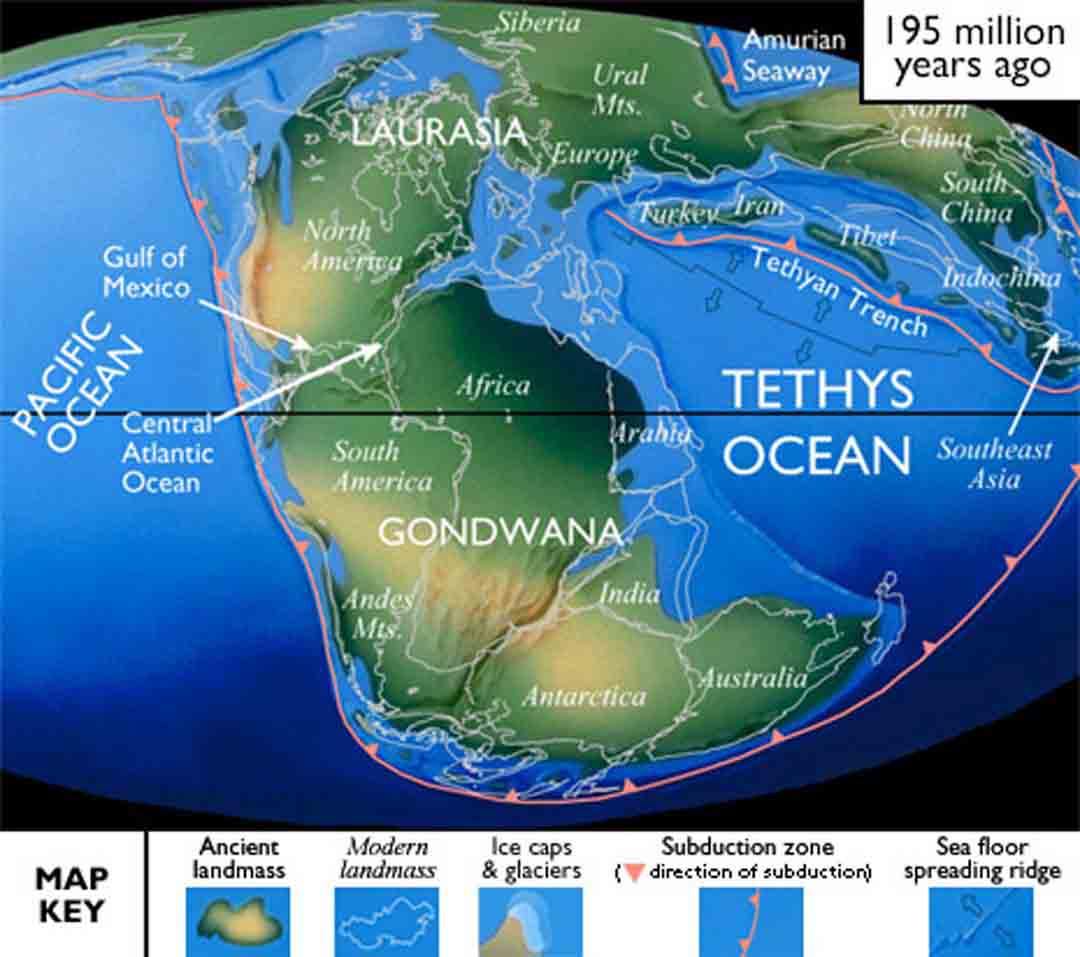
The breakup of Pangea began around 200 million years ago during the Triassic period. The process was driven by the same forces that led to its formation: plate tectonics. The interior of Pangea was subjected to intense heat from the Earth’s mantle, leading to the formation of rift valleys and volcanic activity. These rifts eventually widened, separating the continents and creating new oceans.
The breakup of Pangea resulted in the formation of the Atlantic Ocean and the separation of the continents that we know today. The process of continental drift continues, and the continents are still moving, albeit at a very slow pace.
Modern-Day Evidence of Pangea:
The existence of Pangea is supported by a wealth of geological evidence. The most compelling evidence comes from the fit of the continents, especially along the coastlines of South America and Africa. The geological formations, rock types, and fossil records of these continents also show striking similarities, suggesting that they were once connected.
Furthermore, the distribution of certain fossils across continents, such as the ancient reptile Mesosaurus, which is found in South America and Africa, provides further evidence of Pangea’s existence. The presence of similar plant and animal fossils on continents now separated by vast oceans indicates that they were once part of a single landmass.
FAQs on Pangea:
Q: How long did Pangea last?
A: Pangea existed for approximately 160 million years, from around 335 to 175 million years ago.
Q: Why did Pangea break up?
A: Pangea broke up due to the movement of tectonic plates. The interior of Pangea was subjected to intense heat from the Earth’s mantle, leading to the formation of rift valleys and volcanic activity. These rifts eventually widened, separating the continents and creating new oceans.
Q: What was the climate like in Pangea?
A: Pangea’s interior was characterized by a dry, arid climate with extreme temperature fluctuations. The vast landmass created a continental interior far removed from the moderating influence of the oceans.
Q: What is the significance of Pangea?
A: Pangea’s formation and breakup had a profound impact on Earth’s history, influencing climate, biodiversity, and the evolution of life. Understanding Pangea is crucial for comprehending the geological and biological evolution of our planet.
Q: What is the current state of the continents?
A: The continents are still moving, albeit at a very slow pace. The process of continental drift continues, and the continents are constantly shifting and reshaping the Earth’s surface.
Tips for Understanding Pangea:
- Visualize the continents fitting together: Use a world map to visualize how the continents would have fit together in Pangea.
- Study geological maps: Examine geological maps to see how rock formations and fossil records align across continents.
- Explore the fossil record: Learn about the distribution of fossils across continents to understand how life was distributed during Pangea’s existence.
- Read about plate tectonics: Understand the principles of plate tectonics to grasp the forces that drove the formation and breakup of Pangea.
Conclusion:
Pangea, the ancient supercontinent, is a testament to the dynamic nature of our planet. Its formation and breakup have left an indelible mark on Earth’s history, influencing climate, biodiversity, and the evolution of life. By studying Pangea, we gain a deeper understanding of the processes that have shaped our world and continue to influence its future. The ongoing movement of tectonic plates suggests that the Earth’s continents are not fixed entities and that future supercontinents may emerge in the distant future, further shaping the planet’s landscape and the course of life.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ancient Supercontinent: A Journey Through Pangea. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!