The Anatolian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Geography
Related Articles: The Anatolian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Anatolian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Anatolian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Geography

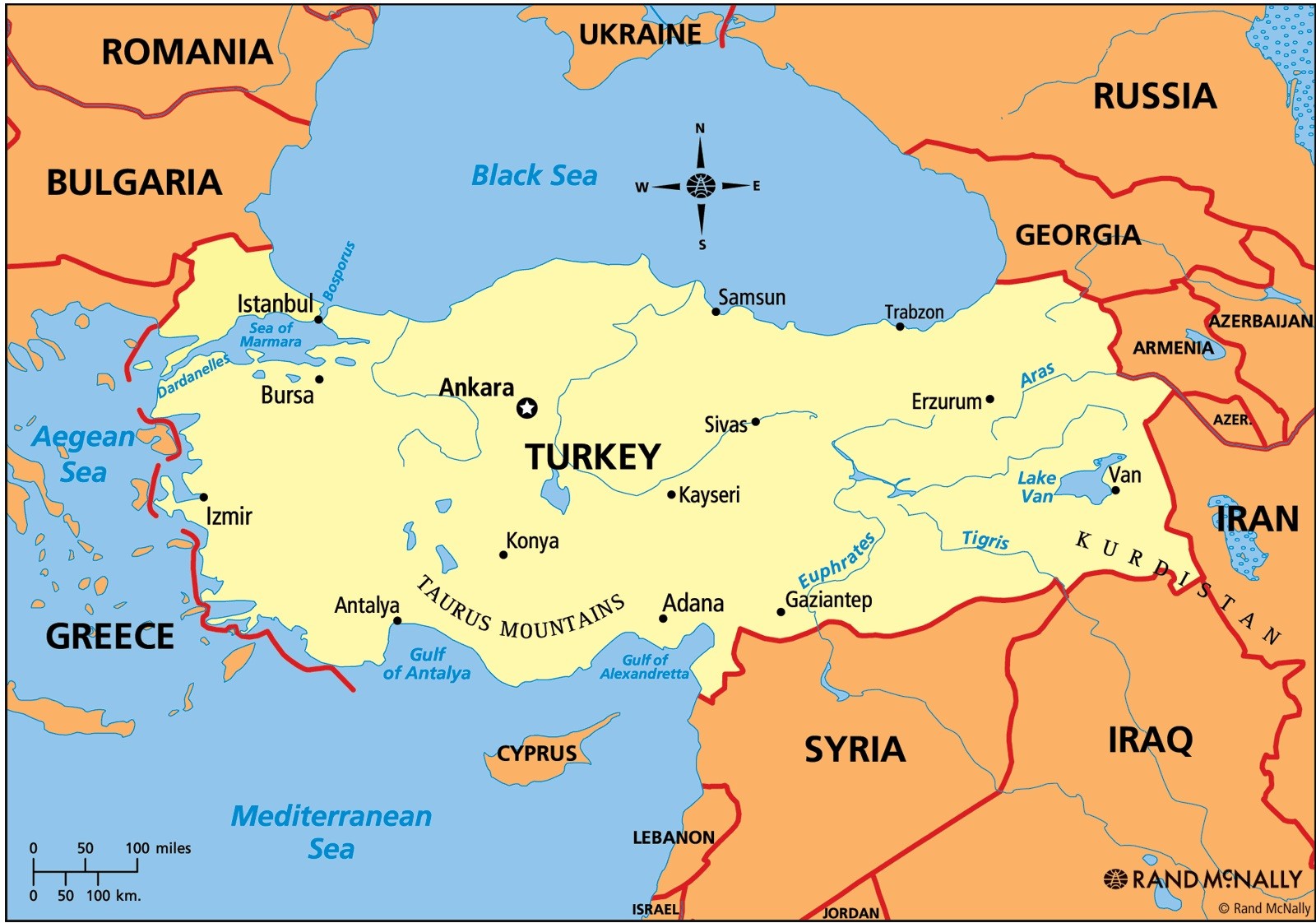
The Anatolian Peninsula, often referred to as Asia Minor, is a geographically and historically significant region situated in Western Asia. It is a land bridge connecting Europe to Asia, with its northern shores bordering the Black Sea, its western shores facing the Aegean Sea, and its southern shores overlooking the Mediterranean Sea. This strategic location has made the peninsula a crossroads for civilizations, cultures, and trade routes for millennia.
A Land of Diverse Landscapes:
The Anatolian Peninsula is characterized by its diverse topography. The central plateau, known as the Anatolian Plateau, is a vast, elevated plain dominated by semi-arid steppe and dry grasslands. This plateau is ringed by mountain ranges, including the Pontic Mountains in the north, the Taurus Mountains in the south, and the Amanos Mountains in the southeast. These mountains act as natural barriers, influencing the region’s climate and contributing to the formation of distinct ecological zones.
The peninsula’s coastal regions are marked by fertile valleys, rolling hills, and picturesque beaches. The Aegean coastline is dotted with numerous islands and harbors, while the Mediterranean coast boasts a long history of maritime trade and cultural exchange. The Black Sea coast, with its lush forests and abundant rainfall, provides a stark contrast to the drier inland regions.
A Cradle of Civilizations:
The Anatolian Peninsula has been home to numerous ancient civilizations, each leaving behind a legacy of art, architecture, and cultural influence. The Hittites, a powerful Bronze Age empire, established their capital at Hattusa, located in central Anatolia. Their sophisticated legal system, advanced military technology, and impressive architectural achievements left an indelible mark on the region.
The Phrygians, who succeeded the Hittites, established a kingdom in western Anatolia, known for their distinctive art and religious practices. The Lydians, renowned for their coinage and their prosperous trade, ruled over the western coast. The Greeks, attracted by the peninsula’s fertile land and strategic location, established colonies along the Aegean coast, laying the foundation for the Hellenistic period.
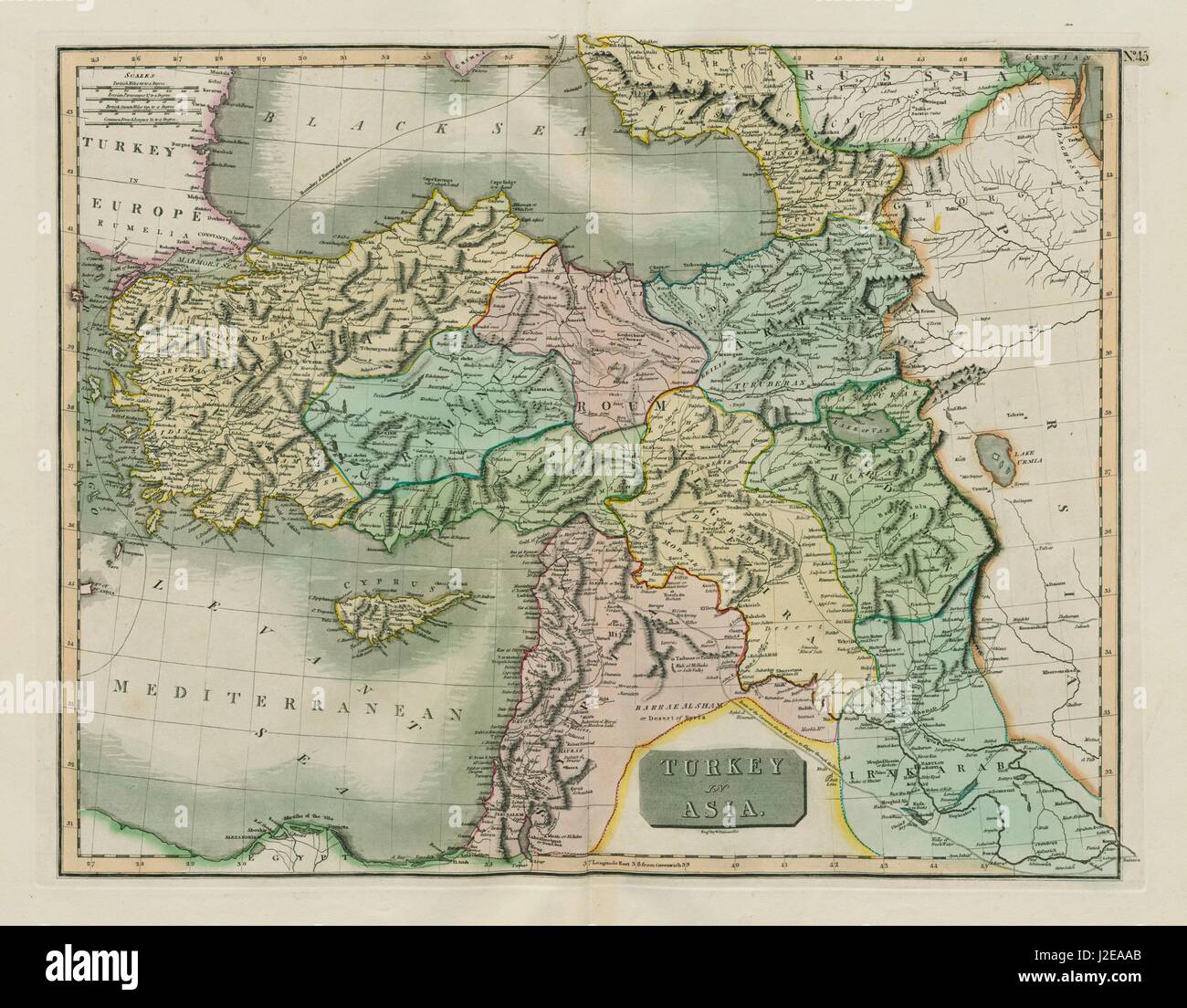
The Roman Empire, expanding eastward, conquered Anatolia in the 1st century BC, incorporating it into its vast territory. This period witnessed the construction of roads, aqueducts, and cities, leaving a lasting impact on the region’s infrastructure and urban development.
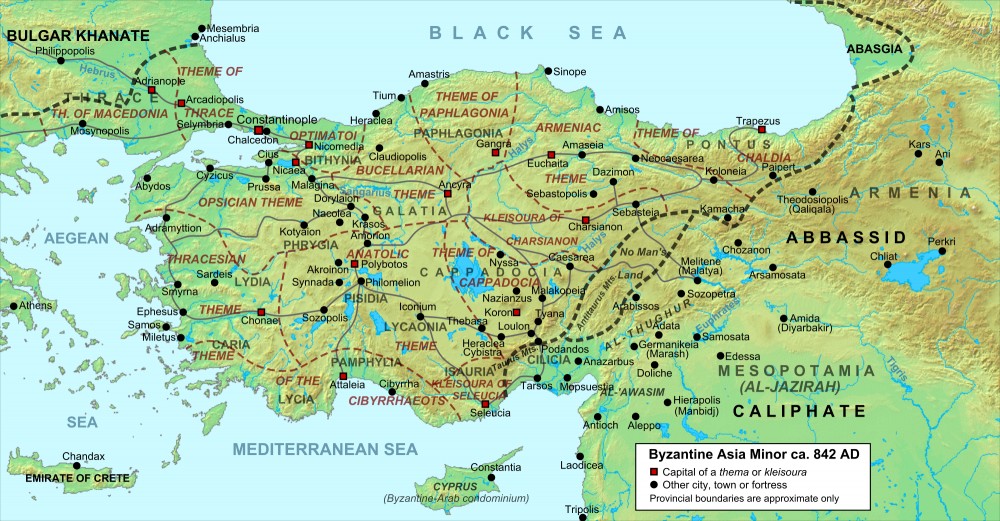
The Legacy of the Ottoman Empire:
The Ottoman Empire, originating in Anatolia, ruled over a vast territory spanning three continents for centuries. The peninsula served as the heartland of the empire, with its capital city, Constantinople (now Istanbul), becoming a center of commerce, culture, and learning. The Ottoman Empire’s influence is still evident in the region’s architecture, language, and cuisine.
Modern Turkey and the Anatolian Peninsula:
The Republic of Turkey, established in 1923, encompasses the Anatolian Peninsula. The peninsula’s diverse geography and rich history have shaped the modern Turkish identity, contributing to its cultural heritage, economic development, and geopolitical significance.
Importance and Benefits:
The Anatolian Peninsula’s strategic location, diverse landscapes, and rich history have made it a vital region for trade, culture, and diplomacy.
- Trade and Transportation: The peninsula’s central position between Europe and Asia has made it a crucial hub for trade routes, connecting continents and facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas. Its extensive coastline, with numerous harbors and ports, has also played a significant role in maritime trade throughout history.
- Cultural Exchange and Diversity: The Anatolian Peninsula has been a melting pot of cultures, with civilizations from different regions and eras leaving their mark on the region. This cultural exchange has enriched the peninsula’s artistic traditions, religious practices, and linguistic diversity.
- Natural Resources: The peninsula possesses a wealth of natural resources, including fertile land for agriculture, mineral deposits, and abundant water resources. These resources have contributed to the region’s economic development and played a crucial role in supporting its population.
- Geopolitical Significance: The Anatolian Peninsula’s strategic location, bordering the Black Sea, the Aegean Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea, has made it a key player in regional and global politics. Its role in international relations and its influence on regional stability are undeniable.
FAQs about the Anatolian Peninsula:
Q: What is the significance of the Anatolian Peninsula in world history?
A: The Anatolian Peninsula has been a crucial crossroads of civilizations for millennia, hosting empires like the Hittites, Phrygians, and Romans. Its strategic location has facilitated cultural exchange, trade, and political power struggles, shaping the course of history in the region and beyond.
Q: What are the major geographical features of the Anatolian Peninsula?
A: The Anatolian Peninsula is characterized by the central Anatolian Plateau, surrounded by mountain ranges like the Pontic Mountains, Taurus Mountains, and Amanos Mountains. Its diverse coastline includes the Black Sea, Aegean Sea, and Mediterranean Sea, each contributing to its unique geography and climate.
Q: What are the main cultural influences on the Anatolian Peninsula?
A: The Anatolian Peninsula has been shaped by a rich tapestry of cultures, including Hittite, Phrygian, Greek, Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman influences. This fusion of cultures is evident in its art, architecture, language, and religious practices.
Q: What are the economic benefits of the Anatolian Peninsula?
A: The Anatolian Peninsula offers significant economic benefits, including fertile land for agriculture, mineral resources, and a strategic location for trade and transportation. Its natural resources and geographic position have contributed to its economic growth and development.
Q: What is the future of the Anatolian Peninsula?
A: The Anatolian Peninsula’s future is intertwined with the complex dynamics of regional and global politics, economic development, and cultural exchange. Its strategic location, natural resources, and diverse population will continue to shape its future, making it a region of significant interest and potential.
Tips for Studying the Anatolian Peninsula:
- Explore the region’s history: Delve into the fascinating history of ancient civilizations like the Hittites, Phrygians, and Lydians, understanding their impact on the region’s cultural landscape.
- Study its geography: Understand the diverse landscapes of the Anatolian Peninsula, from the central plateau to the coastal regions, and their influence on the region’s climate, resources, and cultural development.
- Investigate its cultural heritage: Explore the rich cultural traditions of the Anatolian Peninsula, including its art, architecture, music, and cuisine, recognizing the influence of different civilizations throughout history.
- Analyze its geopolitical significance: Understand the Anatolian Peninsula’s strategic location and its role in regional and global politics, considering its impact on international relations and security.
Conclusion:
The Anatolian Peninsula stands as a testament to the enduring power of history and geography. Its strategic location, diverse landscapes, and rich cultural heritage have made it a crossroads of civilizations, a cradle of empires, and a vital region for trade, culture, and diplomacy. As the peninsula continues to evolve, its unique blend of history, geography, and cultural diversity will continue to shape its future, making it a region of enduring interest and significance.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Anatolian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Geography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!