Navigating the World: Understanding the Equator and its Significance
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding the Equator and its Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding the Equator and its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding the Equator and its Significance
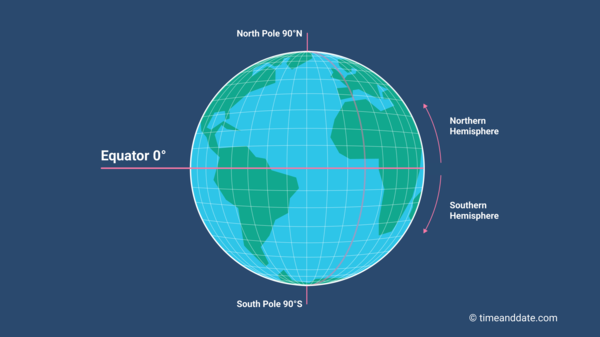
The Earth, a dynamic sphere spinning through space, is divided by an imaginary line that serves as a fundamental reference point in geography and navigation: the equator. This line, an invisible circle encircling the globe at 0 degrees latitude, plays a crucial role in understanding our planet’s climate, time zones, and cultural diversity.
Defining the Equator: A Line of Latitude and Balance
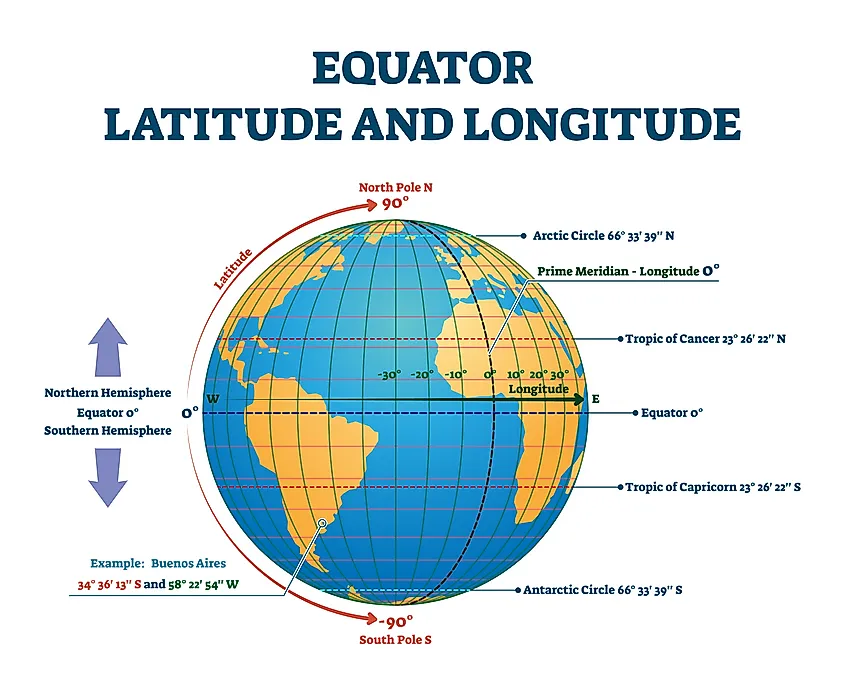
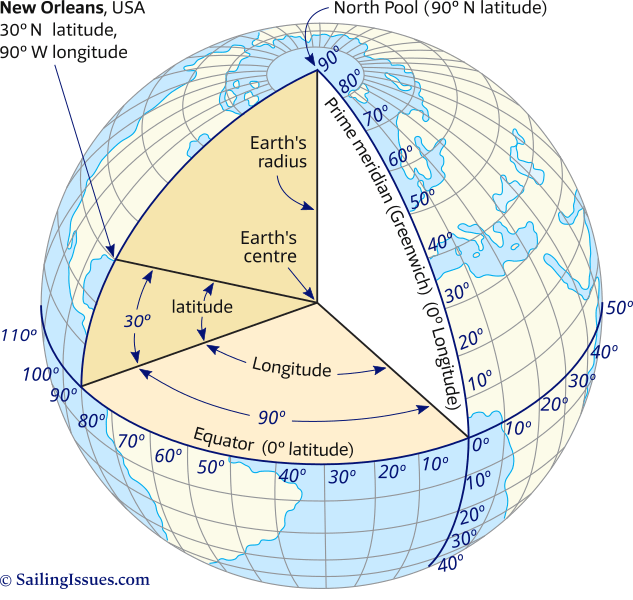
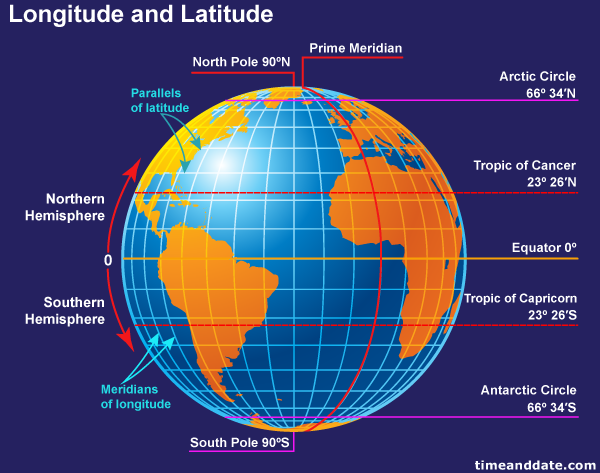
The equator is a line of latitude, a system of imaginary circles that run parallel to the equator and measure distance north or south of it. It is the largest of these circles, dividing the Earth into the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. Its significance lies in its position as the Earth’s widest point, equidistant from both poles.
The Equator’s Influence on Climate and Time Zones
The equator’s location directly impacts the Earth’s climate patterns. Due to its position, the equatorial region receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall. This creates the tropical climate zone, characterized by lush vegetation, diverse ecosystems, and a plethora of unique plant and animal species.
The Earth’s rotation also plays a crucial role in understanding the impact of the equator on time zones. The equator is the reference point for the 24 time zones that divide the globe. As the Earth rotates eastward, each time zone experiences a one-hour difference from the adjacent zone. This system ensures that the sun rises and sets at roughly the same time within each time zone, regardless of its location relative to the equator.
Cultural Diversity and the Equator’s Influence
The equatorial region is a melting pot of cultures, languages, and traditions. Throughout history, its fertile lands and abundant resources have attracted diverse populations, leading to a rich tapestry of cultural heritage. From the bustling cities of South America to the vibrant villages of Southeast Asia, the equator is home to a myriad of societies, each with its own unique customs, beliefs, and artistic expressions.
Mapping the Equator: A Visual Representation of the World’s Heart
Maps with the equator line prominently displayed serve as powerful tools for understanding the Earth’s geography and the relationships between different regions. These maps visually illustrate the equator’s central role in dividing the planet and connecting its diverse inhabitants.
The equator’s presence on maps provides a visual reference for:
- Latitude and Longitude: Understanding the relationship between the equator and other lines of latitude, as well as lines of longitude, which run vertically around the globe, helps to accurately pinpoint locations on the Earth’s surface.
- Global Distribution of Resources: The equator’s presence on maps allows for a clear visualization of the distribution of natural resources, such as rainforests, mineral deposits, and agricultural land, across the globe.
- Climate Zones and Biomes: Maps with the equator line help to understand the distribution of different climate zones, such as tropical, temperate, and polar regions, and the unique ecosystems they support.
- Cultural and Linguistic Diversity: By visualizing the location of diverse cultures and languages along the equator, maps highlight the interconnectedness and influence of different societies.
Understanding the Equator: A Gateway to Global Awareness
The equator is not just a line on a map; it is a symbol of the Earth’s interconnectedness and the diverse beauty of its inhabitants. By understanding the equator’s impact on climate, time zones, and cultural diversity, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of our planet and the global community we share.
FAQs about the Equator
1. Is the equator the only line of latitude?
No, the equator is just one of many lines of latitude. Other lines of latitude run parallel to the equator and are measured in degrees north or south of it.
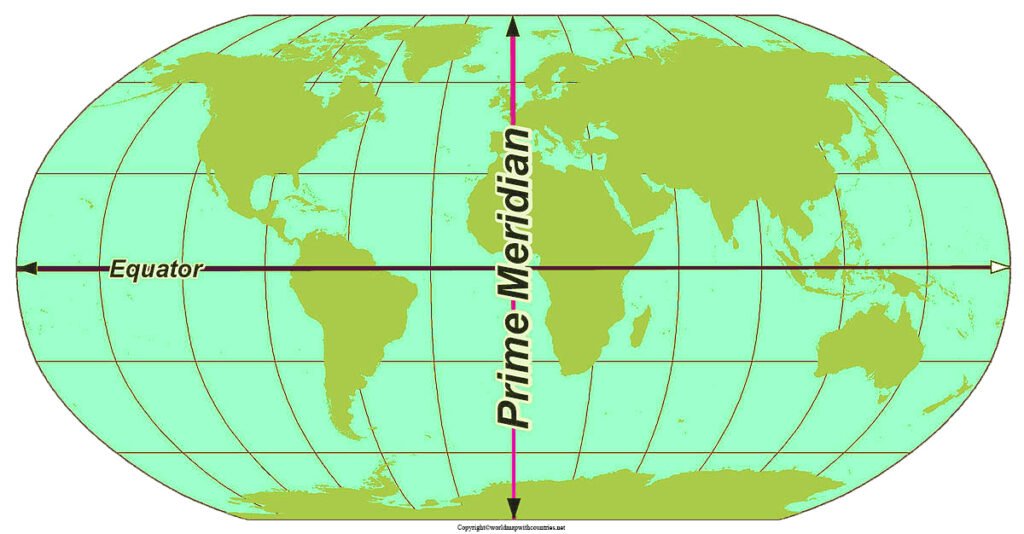
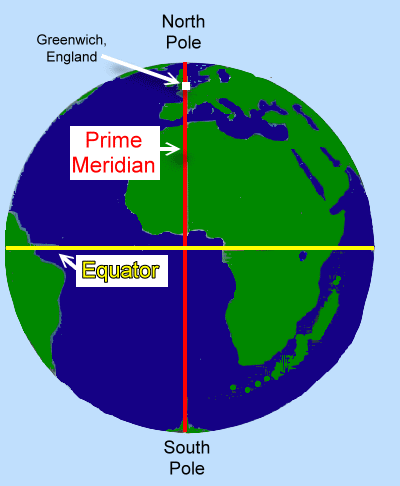
2. What is the difference between the equator and the prime meridian?
The equator is a line of latitude that runs horizontally around the Earth, while the prime meridian is a line of longitude that runs vertically through Greenwich, England, dividing the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
3. What is the significance of the equator in terms of Earth’s rotation?
The equator is the Earth’s widest point, and its rotation around this axis influences the Earth’s climate and time zones.
4. Are there any countries that are completely located on the equator?
Yes, several countries are completely located on the equator, including Ecuador, Colombia, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
5. What is the importance of the equator in terms of navigation?
The equator serves as a key reference point in navigation, providing a starting point for measuring latitude and longitude.
Tips for Using Maps with the Equator
- Focus on the Relationship between the Equator and Other Lines of Latitude: Understand how the equator’s position influences the locations of other lines of latitude, and how this affects climate, time zones, and geographic features.
- Visualize the Global Distribution of Resources: Use maps with the equator to understand how natural resources are distributed across the globe, and how this impacts different regions and societies.
- Explore the Diversity of Cultures and Languages: Utilize maps to identify the location of diverse cultures and languages along the equator, gaining insight into the interconnectedness of different societies.
- Use Maps to Track Climate Change: Observe how the equator’s position and climate patterns are affected by climate change, and understand its potential impact on different regions and ecosystems.
Conclusion
The equator, a seemingly simple line on a map, holds profound significance for understanding the Earth’s geography, climate, and cultural diversity. Its presence serves as a visual reminder of the planet’s interconnectedness and the rich tapestry of life that thrives across its surface. By studying and appreciating the equator’s influence, we gain a deeper understanding of our planet and the intricate web of life that sustains us.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding the Equator and its Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!