Navigating the Climate of Mexico: A Geographical and Seasonal Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Climate of Mexico: A Geographical and Seasonal Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Climate of Mexico: A Geographical and Seasonal Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Climate of Mexico: A Geographical and Seasonal Guide

Mexico, a land of diverse landscapes, boasts an equally diverse climate. Understanding the nuances of its weather patterns is crucial for planning travel, understanding local ecosystems, and appreciating the country’s geographical complexity. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate relationship between geography and climate in Mexico, providing insights into its regional variations and seasonal shifts.
The Influence of Geography on Mexico’s Climate
Mexico’s climate is heavily influenced by its unique geographical features, including its location, topography, and proximity to major bodies of water.
-
Latitude: Situated between 14° and 33° north latitude, Mexico experiences a range of climates, from tropical in the south to temperate in the north. The Tropic of Cancer, which crosses the country, divides Mexico into two distinct climatic zones: tropical and subtropical.
-
Topography: Mexico’s diverse topography, characterized by high mountain ranges, vast deserts, and coastal plains, creates a complex patchwork of microclimates. The Sierra Madre Occidental and Oriental mountain ranges, running parallel to the Pacific and Gulf coasts, respectively, act as barriers, influencing precipitation patterns and temperature variations.
-
Ocean Currents: The warm Gulf Stream and the cold California Current, flowing along the coasts, significantly impact the country’s weather. The Gulf Stream brings warm, moist air to the east coast, leading to increased rainfall, while the California Current brings cooler, drier air to the west coast.
Regional Climate Variations
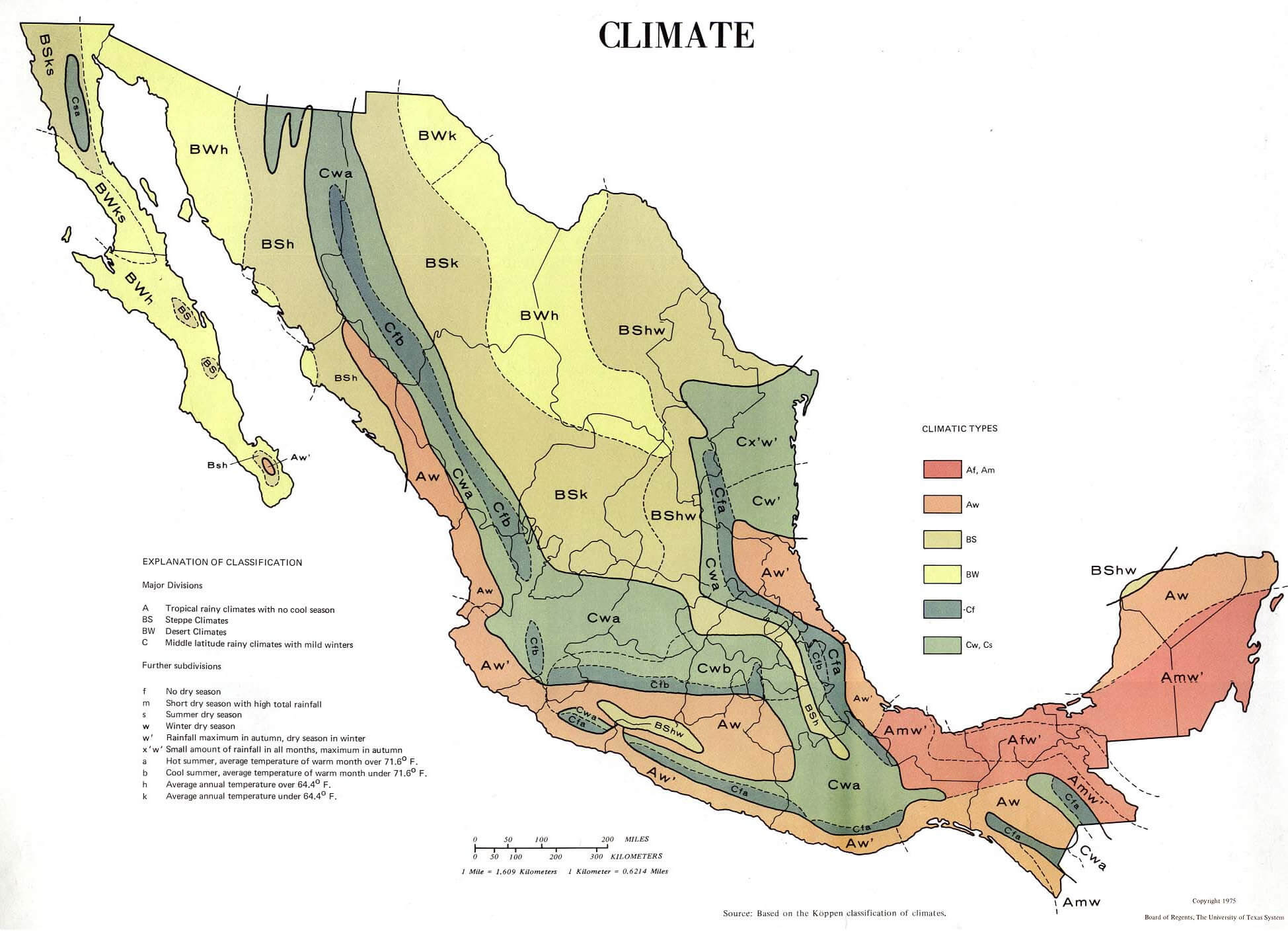
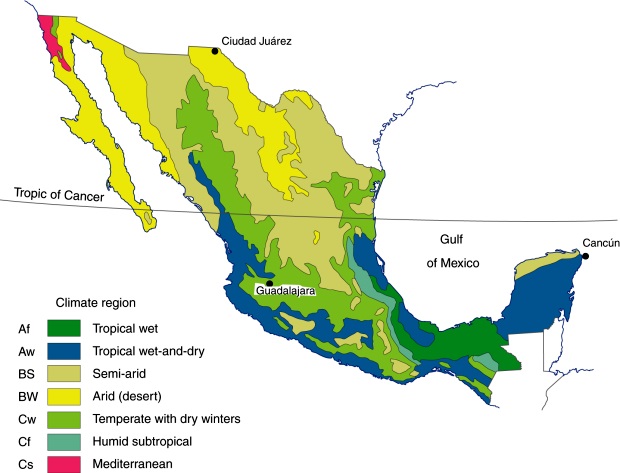
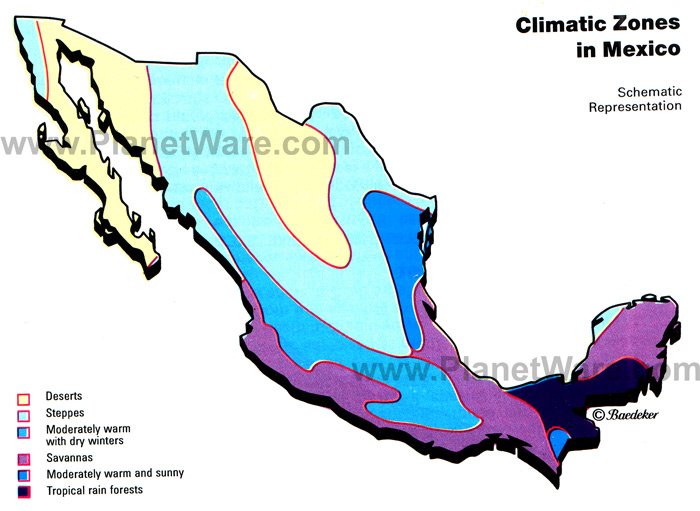
Mexico’s climate can be broadly divided into six distinct regions:
1. Tropical Wet Climate (Af): This climate prevails in the southernmost part of the country, including the Yucatan Peninsula and the Pacific coast. It is characterized by high temperatures throughout the year, with an average annual temperature above 18°C (64°F), and abundant rainfall exceeding 2000mm (79 inches).
2. Tropical Savanna Climate (Aw): This climate is found in the central and southern parts of Mexico, including the Gulf Coast and the Balsas River Valley. It features distinct wet and dry seasons, with a longer dry season than the tropical wet climate. Temperatures remain high year-round, but rainfall is less abundant, ranging from 1000mm to 2000mm (39 to 79 inches).
3. Subtropical Humid Climate (Cfa): This climate prevails in the central highlands of Mexico, including Mexico City and the surrounding areas. It is characterized by warm summers and mild winters, with an average temperature above 10°C (50°F) throughout the year. Rainfall is moderate, ranging from 750mm to 1500mm (30 to 59 inches), with a distinct rainy season during summer.
4. Semi-Arid Climate (BSk): This climate is prevalent in the northern and central regions of Mexico, including the states of Chihuahua, Sonora, and Coahuila. It features hot summers and mild winters, with low annual rainfall below 500mm (20 inches).
5. Arid Climate (BWk): This climate is found in the northernmost parts of Mexico, including Baja California and the Sonoran Desert. It is characterized by extremely hot summers and mild winters, with very low rainfall below 250mm (10 inches).
6. Mediterranean Climate (Csa): This climate is found in the Baja California Peninsula, with warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. Rainfall is concentrated during the winter months, with an average annual rainfall ranging from 250mm to 500mm (10 to 20 inches).
Seasonal Variations
Mexico experiences two distinct seasons: a rainy season and a dry season.
-
Rainy Season: The rainy season, known as the "huayuco" in some regions, typically runs from June to October, with the heaviest rainfall occurring during August and September. The Pacific coast, the Gulf Coast, and the southern regions of Mexico experience the most rainfall during this period.
-
Dry Season: The dry season, known as the "estiaje," typically lasts from November to May. This period is characterized by clear skies, sunshine, and low humidity, making it an ideal time for outdoor activities and tourism.
Understanding the Importance of Weather in Mexico
The understanding of weather patterns in Mexico is crucial for various aspects of life and development:
-
Agriculture: Mexico’s agriculture is heavily reliant on rainfall, particularly in the dryland regions. Knowledge of rainfall patterns and seasonal variations is essential for planting, harvesting, and irrigation planning.
-
Tourism: Tourists can plan their trips based on their preferred weather conditions. For example, those seeking warm, sunny weather would visit during the dry season, while those who enjoy cooler temperatures and rain may choose the rainy season.
-
Water Resources: Mexico’s water resources are heavily influenced by rainfall. Understanding rainfall patterns is essential for managing water resources, ensuring water security, and mitigating drought risks.
-
Infrastructure: Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and floods, can pose significant risks to infrastructure, particularly in coastal areas. Understanding weather patterns and implementing appropriate mitigation measures are crucial for protecting infrastructure and ensuring safety.
-
Biodiversity: Mexico’s diverse ecosystems are sensitive to climate change. Understanding weather patterns and their impact on biodiversity is essential for conservation efforts and sustainable management of natural resources.
FAQs about Weather in Mexico
1. What is the best time to visit Mexico?
The best time to visit Mexico depends on your preferences. For those seeking warm, sunny weather, the dry season (November to May) is ideal. For those who enjoy cooler temperatures and rain, the rainy season (June to October) may be more appealing.
2. What are the typical temperatures in Mexico?
Temperatures in Mexico vary significantly depending on the region and the time of year. In general, the southern regions experience higher temperatures than the northern regions. The average annual temperature ranges from 18°C (64°F) in the south to 10°C (50°F) in the north.
3. What is the best clothing to pack for a trip to Mexico?
Packing for a trip to Mexico depends on the time of year and the region you are visiting. In general, light, breathable clothing is recommended for the hot and humid climate. During the rainy season, bring a raincoat or umbrella. In the highlands, pack layers as temperatures can fluctuate.
4. What are the major weather events in Mexico?
Mexico is prone to various weather events, including hurricanes, floods, droughts, and wildfires. The hurricane season typically runs from June to November, with the most active period being August to October.
5. How does climate change affect Mexico?
Climate change is expected to have significant impacts on Mexico’s climate, including increased temperatures, changes in rainfall patterns, and more frequent and intense extreme weather events. These changes will have far-reaching consequences for agriculture, water resources, biodiversity, and human health.
Tips for Traveling in Mexico with Weather in Mind
-
Check the weather forecast before traveling: Stay updated on current weather conditions and potential weather events.
-
Pack appropriate clothing: Pack light, breathable clothing for hot and humid weather. Bring a raincoat or umbrella during the rainy season.
-
Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water, especially during hot weather.
-
Be aware of potential weather hazards: Be prepared for hurricanes, floods, and other extreme weather events.
-
Respect local weather customs: Be mindful of local customs and traditions related to weather, such as siesta during hot afternoons.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of Mexico’s diverse climate is crucial for appreciating the country’s unique geographical features and planning successful trips. From the tropical rainforests of the south to the arid deserts of the north, Mexico’s climate is a reflection of its rich and varied landscape. By understanding the interplay of latitude, topography, and ocean currents, travelers can navigate the country’s weather patterns effectively and experience its diverse beauty to the fullest.

/mexicos-weather-what-to-expect-1589004-FINAL1-5bb2af624cedfd002664143a.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Climate of Mexico: A Geographical and Seasonal Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!