Mexico’s Geographic Position: A Bridge Between Continents
Related Articles: Mexico’s Geographic Position: A Bridge Between Continents
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mexico’s Geographic Position: A Bridge Between Continents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mexico’s Geographic Position: A Bridge Between Continents

Mexico, a nation rich in history, culture, and natural beauty, occupies a unique and strategically significant position on the North American continent. Its geographical location, straddling the narrowest point of the North American landmass, has played a pivotal role in shaping its history, influencing its diverse ecosystems, and contributing to its vibrant cultural tapestry.
A Land of Contrasts: Mexico’s Geographic Landscape
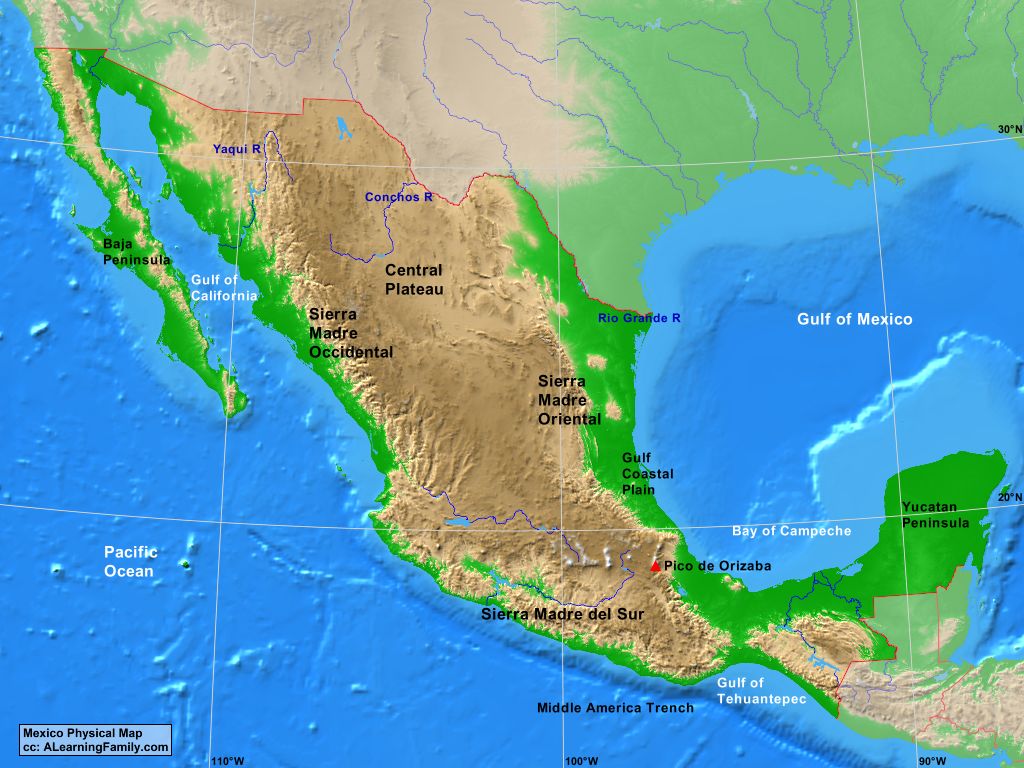
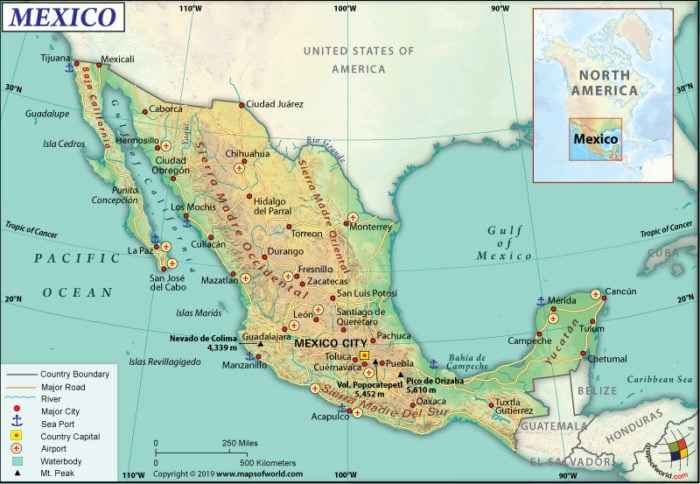
Mexico’s geography is a tapestry of contrasting landscapes, ranging from snow-capped mountains to sun-drenched beaches. Its 1,972,550 square kilometers (761,600 square miles) are divided into 31 states and one federal district, each with its own distinct character.
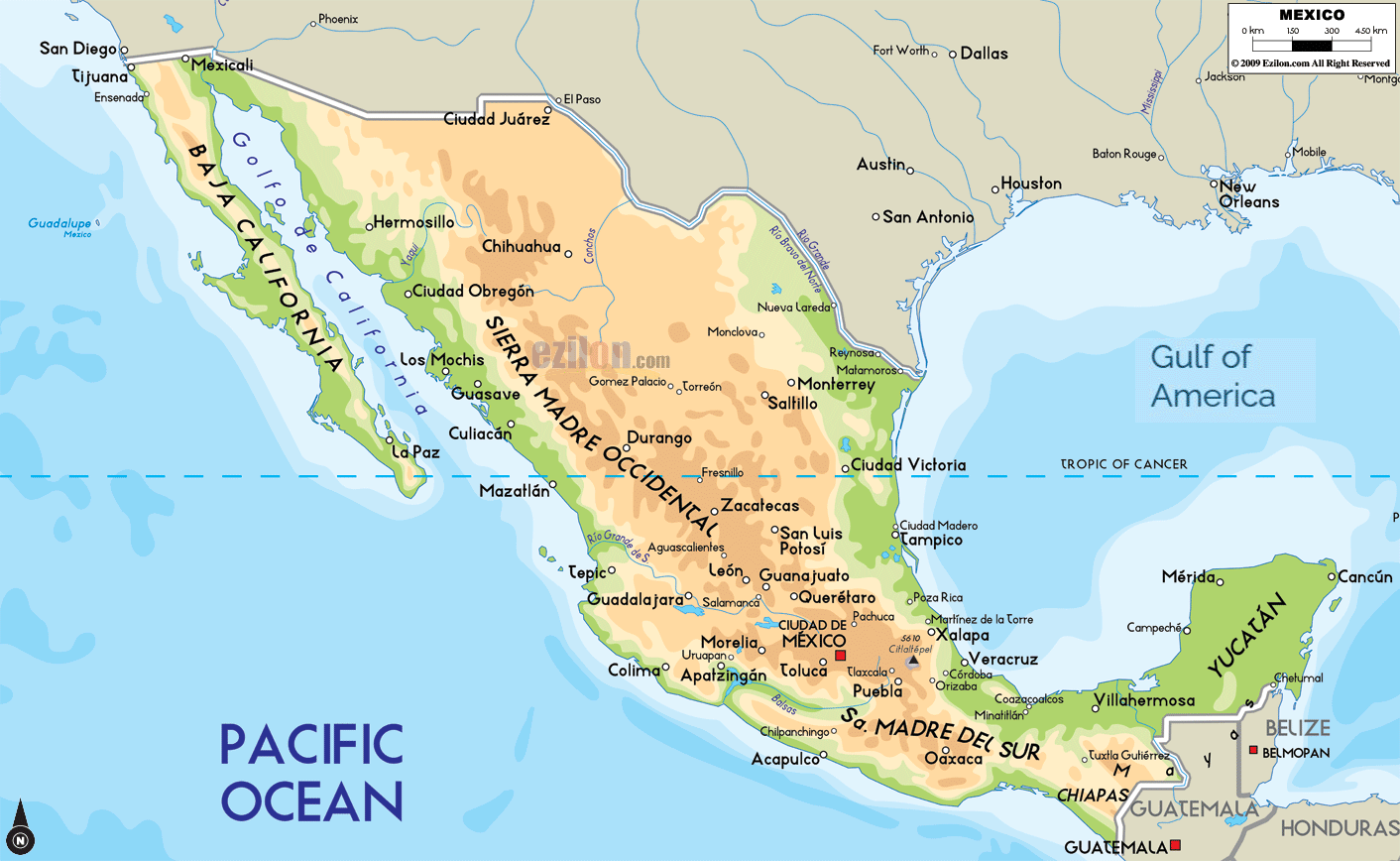
The North: This region encompasses the vast Chihuahuan Desert, characterized by arid landscapes and towering mountains, including the Sierra Madre Occidental. The northern states, such as Sonora, Chihuahua, and Baja California, are known for their vast agricultural lands, mineral resources, and burgeoning industries.
The Central Plateau: Known as the "Mexican Altiplano," this region is a high-altitude plateau dominated by the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt. It is home to Mexico City, the country’s capital, and several other major cities, as well as numerous volcanoes, including the iconic Popocatépetl and Iztaccíhuatl.
The South: This region is characterized by its lush, tropical landscapes, encompassing the Yucatan Peninsula, the Chiapas Highlands, and the Gulf Coast. The south is renowned for its ancient Mayan ruins, vibrant indigenous cultures, and diverse ecosystems, including rainforests, lagoons, and wetlands.
The Pacific Coast: Stretching along the western edge of the country, the Pacific Coast boasts a coastline dotted with pristine beaches, vibrant fishing villages, and bustling port cities. The region is known for its rich marine life, attracting tourists and surfers from around the world.
The Gulf Coast: Facing the Gulf of Mexico, this region features a humid climate and fertile plains, making it a major agricultural center. Its coastline is lined with beaches, lagoons, and wetlands, providing habitat for a diverse array of flora and fauna.
Mexico’s Strategic Location: A Gateway to the Americas
Mexico’s location at the crossroads of North and Central America makes it a vital link between the two continents. It shares a 3,145-kilometer (1,954-mile) land border with the United States to the north and a 933-kilometer (579-mile) border with Guatemala and Belize to the south. This strategic position has made Mexico a major trading partner for both North and Central America, facilitating the exchange of goods, services, and ideas.
Connecting the Oceans: The Panama Canal and Mexico’s Role
While not directly connected to the Panama Canal, Mexico’s geographical proximity to this vital waterway has significant implications for global trade. The Panama Canal, which connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, facilitates the movement of goods between the Americas and the rest of the world. Mexico’s strategic location allows it to serve as a hub for trans-shipment and distribution, connecting the Pacific Coast to the Gulf of Mexico and beyond.
A Rich Tapestry of Biodiversity: Mexico’s Unique Ecosystems
Mexico’s diverse geography and varied climates have resulted in a rich tapestry of biodiversity. The country is home to an estimated 10% of the world’s known species, including a wide range of mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and plants. This biodiversity is a vital resource for the nation, providing ecosystem services, supporting livelihoods, and contributing to the global pool of genetic diversity.
Mexico’s Geographic Influences: A Historical Perspective
Mexico’s geographic location has played a significant role in its history, shaping its cultural identity and influencing its political landscape. Its proximity to the United States has led to a complex and often intertwined relationship, marked by periods of cooperation and conflict. Mexico’s historical connections to Mesoamerica, particularly the Mayan and Aztec civilizations, have left an indelible mark on its culture and language.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Mexico’s Location
1. What are the major geographical features of Mexico?
Mexico’s geography is characterized by its contrasting landscapes, including the Chihuahuan Desert, the Mexican Altiplano, the Yucatan Peninsula, the Sierra Madre Occidental and Oriental mountain ranges, and the Pacific and Gulf Coasts.
2. What is the significance of Mexico’s location at the crossroads of North and Central America?
Mexico’s strategic location has made it a vital link between North and Central America, facilitating trade, cultural exchange, and migration.
3. How does Mexico’s geography affect its climate and biodiversity?
Mexico’s diverse geography and varied climates have resulted in a wide range of ecosystems, from arid deserts to lush rainforests, supporting a rich tapestry of biodiversity.
4. What are some of the challenges Mexico faces due to its geographical location?
Mexico’s location can present challenges, including vulnerability to natural disasters such as hurricanes and earthquakes, as well as potential conflicts over natural resources and border security.
5. How has Mexico’s geography influenced its history and culture?
Mexico’s location has played a significant role in shaping its history, cultural identity, and political landscape. Its proximity to the United States and its historical ties to Mesoamerica have left a lasting impact on its development.
Tips for Understanding Mexico’s Geography
- Use a map: A physical map of Mexico can provide a visual understanding of its geographical features, including its major mountain ranges, rivers, and coastlines.
- Explore online resources: Websites such as Google Maps, National Geographic, and Wikipedia offer detailed information about Mexico’s geography, including satellite imagery, maps, and articles.
- Read about Mexico’s history: Understanding the historical context of Mexico’s geography can provide insights into its current political and cultural landscape.
- Travel to Mexico: Experiencing Mexico firsthand can provide a deeper understanding of its diverse geography, culture, and people.
Conclusion: A Land of Opportunity and Challenges
Mexico’s geographical position has shaped its identity, influenced its development, and created opportunities for growth. Its diverse landscapes, rich biodiversity, and strategic location make it a nation of immense potential. However, it also faces challenges related to its vulnerability to natural disasters, economic disparities, and the complexities of its relationship with its northern neighbor. Understanding Mexico’s geography is essential for appreciating its unique character and the challenges and opportunities it faces in the 21st century.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mexico’s Geographic Position: A Bridge Between Continents. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!