Mapping Indiana’s Political Landscape: A Look at the Congressional District Boundaries
Related Articles: Mapping Indiana’s Political Landscape: A Look at the Congressional District Boundaries
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Indiana’s Political Landscape: A Look at the Congressional District Boundaries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Indiana’s Political Landscape: A Look at the Congressional District Boundaries
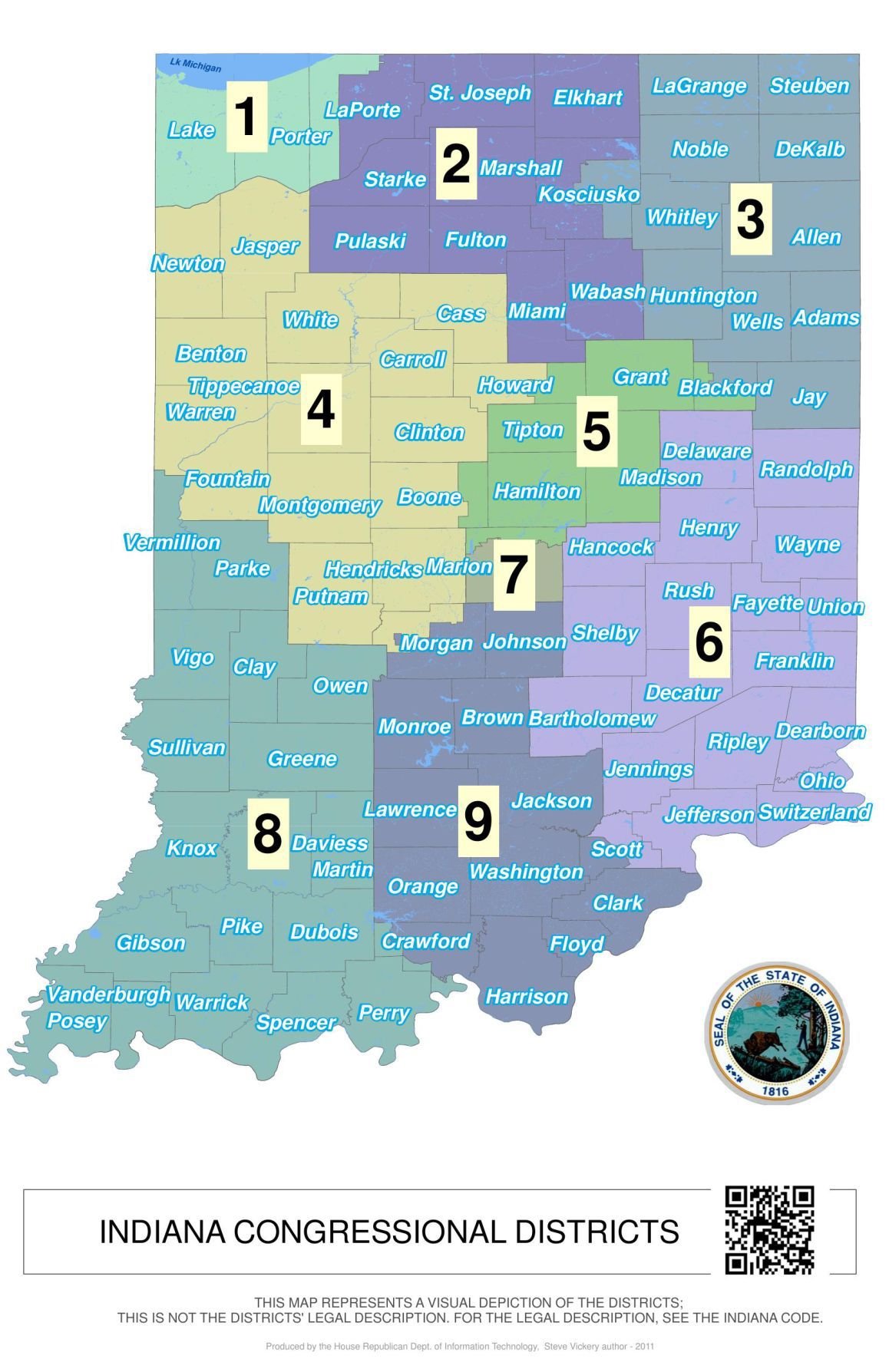
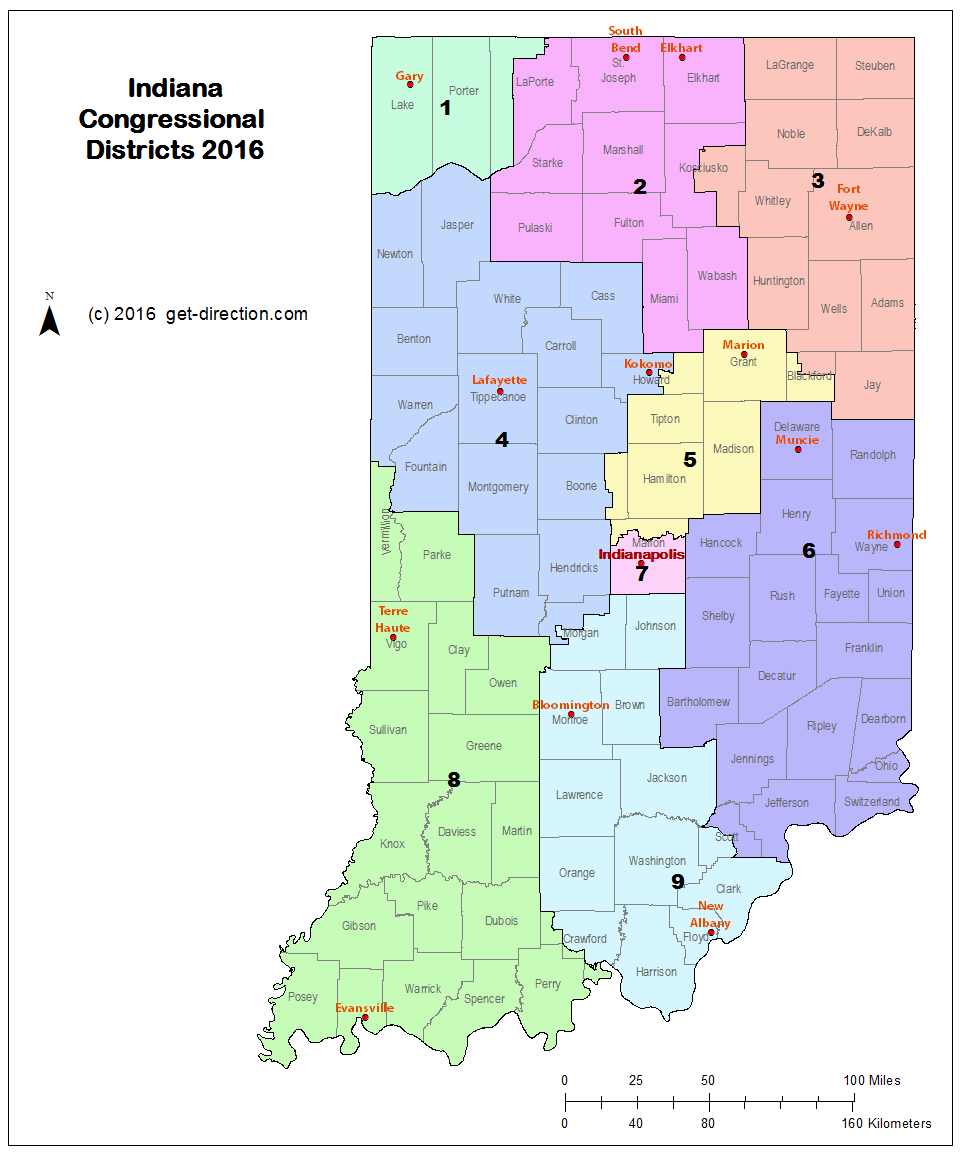
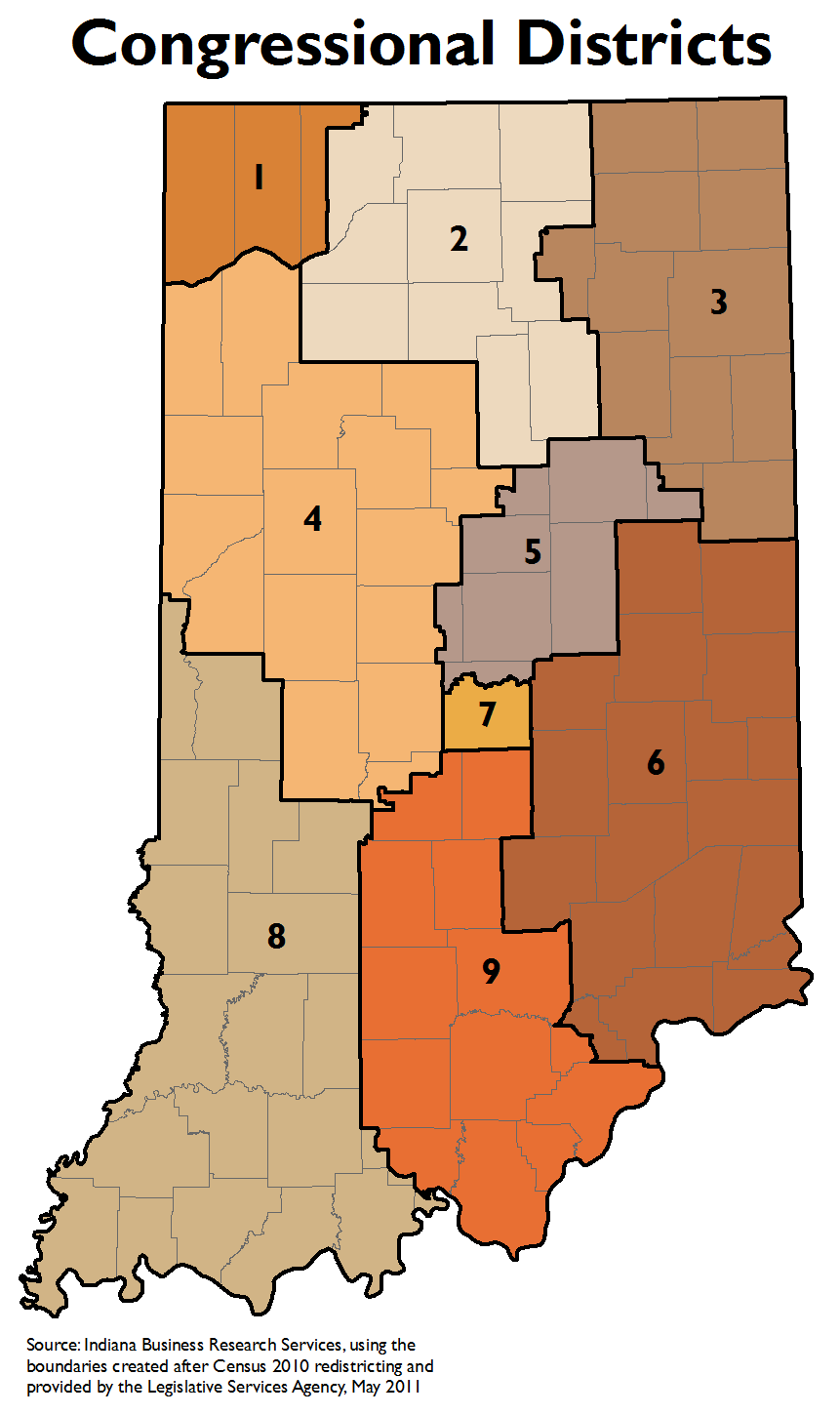
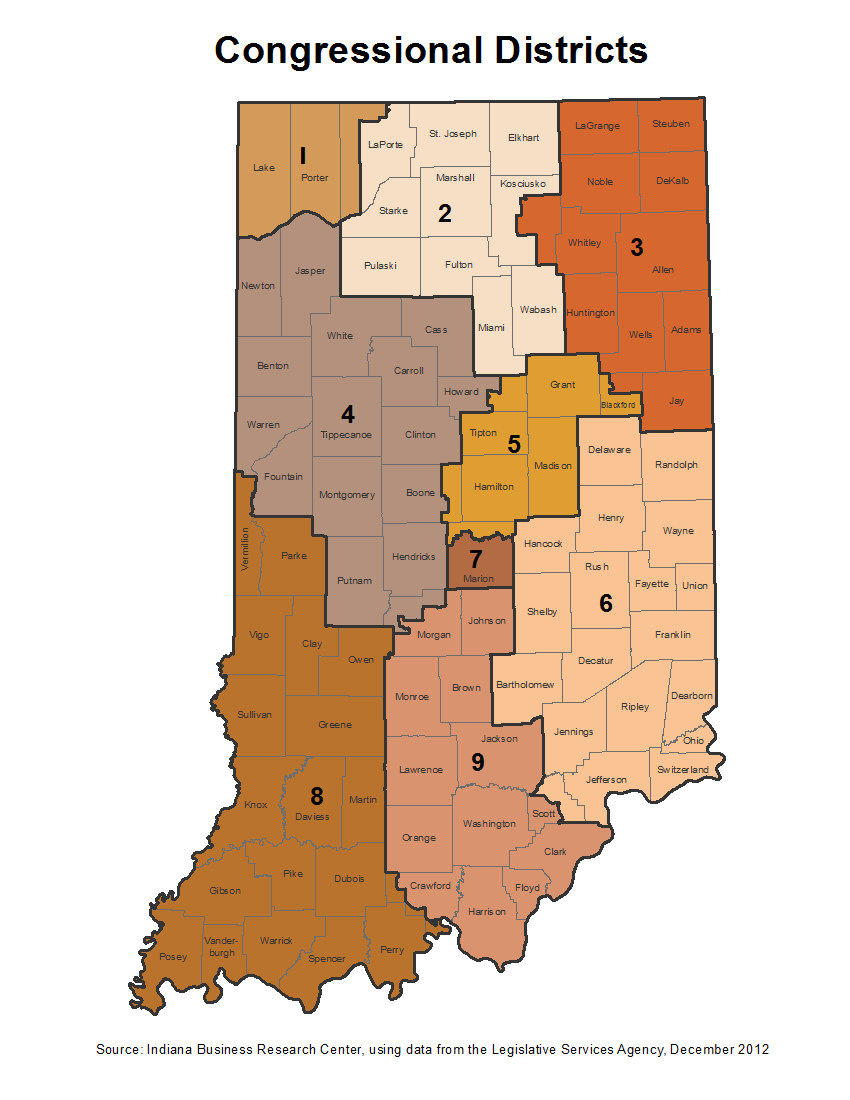
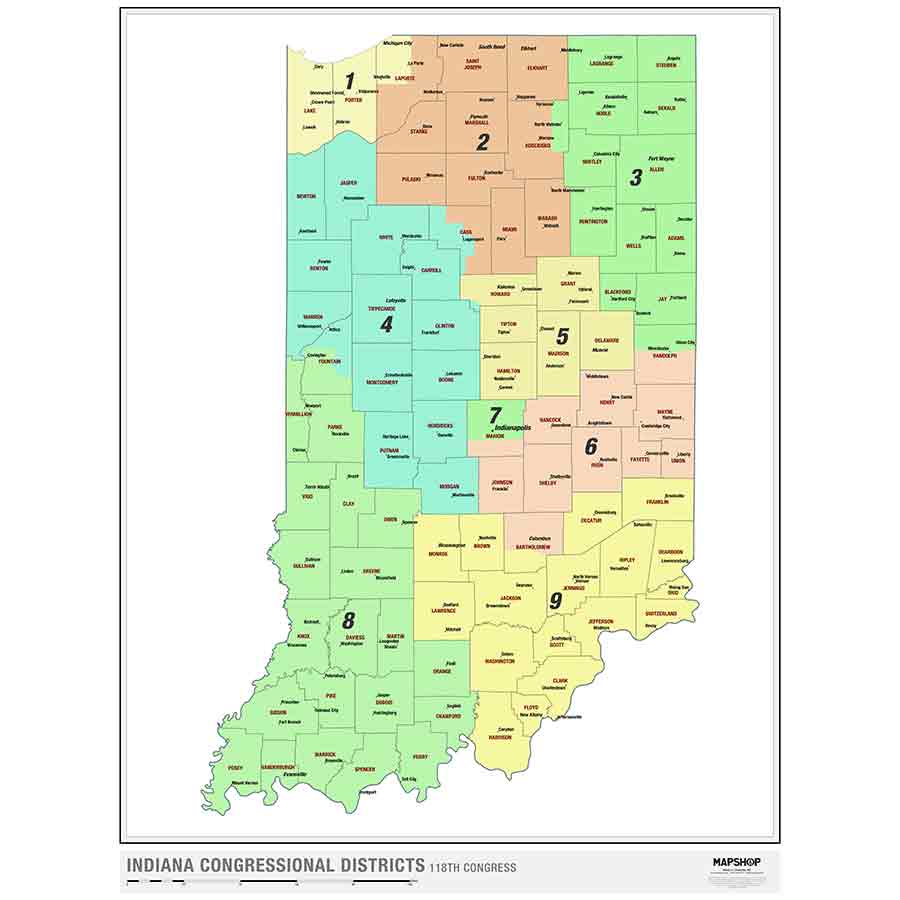
The Indiana congressional district map, a seemingly intricate patchwork of lines across the state, holds significant weight in shaping the political landscape. This map, which divides Indiana into nine districts, determines how the state’s representation in the U.S. House of Representatives is allocated. Understanding the map’s intricacies is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of Indiana’s political system and its impact on the national political scene.
Historical Context and Evolution
The current congressional district map in Indiana, like those in other states, is a product of a long and evolving process. The Constitution mandates that congressional districts be redrawn every ten years following the decennial census to ensure equal representation based on population changes. This process, known as redistricting, often becomes a source of political contention, with parties vying for control over the map’s configuration to favor their candidates.
Indiana’s redistricting history reflects this dynamic. The state initially had a single congressional district, encompassing the entire territory. As the population grew, the number of districts increased, reaching nine in 1911. Over the decades, the map has undergone numerous revisions, with each redistricting cycle bringing new challenges and controversies.
The 2020 Redistricting Cycle and its Impact
The 2020 redistricting cycle, following the 2020 census, was particularly noteworthy in Indiana. The state’s population growth was uneven, resulting in significant population shifts within the districts. This led to a contentious redistricting process, with Republicans, who controlled both houses of the state legislature, ultimately drawing the new map.
The new map, which took effect in 2023, sparked controversy due to its perceived partisan bias. Critics argued that the map unfairly favored Republican candidates by concentrating Democratic voters in a few districts while spreading out Republican voters across multiple districts. This strategy, known as "cracking" and "packing," aims to dilute the voting power of a particular party.
Understanding the Map’s Structure and Implications
The current Indiana congressional district map exhibits a complex structure, with districts ranging from urban areas to rural communities, each with its unique demographic makeup. The map’s configuration has several key implications for Indiana’s political landscape:
- Representation and Voting Power: The map determines the number of representatives each district sends to the U.S. House. Districts with larger populations have a greater say in national policymaking.
- Electoral Outcomes: The map’s design can influence the outcomes of congressional elections. Districts with a clear partisan lean can create a favorable environment for one party’s candidates.
- Political Polarization: The map’s partisan bias can contribute to political polarization, making it more difficult for candidates to win elections in districts with a strong opposing party presence.
Exploring the Benefits and Challenges of the Current Map
The current Indiana congressional district map has both benefits and challenges:
Benefits:
- Population Representation: The map ensures that each district represents a roughly equal number of people, fulfilling the principle of "one person, one vote."
- Geographic Considerations: The map attempts to balance the needs of urban and rural communities, ensuring that geographically diverse areas have representation.
Challenges:
- Partisan Gerrymandering: The map’s design has been criticized for favoring one party over the other, potentially undermining fair and competitive elections.
- Voter Disenfranchisement: The map’s configuration can create districts where certain groups of voters are concentrated, leading to their voices being marginalized.
- Limited Representation: The map’s design can result in districts that lack a diverse representation of voices and perspectives.
FAQs about the Indiana Congressional District Map
1. How are congressional districts drawn in Indiana?
Congressional districts in Indiana are drawn by the state legislature, with the process overseen by a redistricting commission. The commission is responsible for ensuring that districts adhere to legal requirements, including equal population and compliance with the Voting Rights Act.
2. What are the criteria for drawing congressional districts?
The criteria for drawing congressional districts are outlined in the U.S. Constitution and federal law. Districts must be contiguous, compact, and have roughly equal populations. They must also comply with the Voting Rights Act, which prohibits discriminatory practices in voting.
3. How often are congressional districts redrawn in Indiana?
Congressional districts in Indiana are redrawn every ten years following the decennial census. This ensures that representation in the U.S. House reflects population changes and maintains equal representation for all citizens.
4. Who can participate in the redistricting process in Indiana?
The redistricting process in Indiana is primarily led by the state legislature. However, public input is encouraged, and individuals and organizations can submit comments and proposals to the redistricting commission.
5. What are the consequences of partisan gerrymandering?
Partisan gerrymandering can have significant consequences for democracy. It can undermine fair and competitive elections, reduce voter turnout, and exacerbate political polarization. It can also lead to the underrepresentation of certain groups, such as minority communities.
Tips for Understanding the Indiana Congressional District Map
- Consult Official Resources: The Indiana Redistricting Commission website provides detailed information about the redistricting process, including maps, data, and reports.
- Engage with Local Organizations: Community groups and advocacy organizations often conduct research and analysis of redistricting plans. Their insights can provide a deeper understanding of the map’s impact on local communities.
- Follow News Coverage: Media outlets often provide coverage of redistricting debates and analysis of the map’s implications. Staying informed about these discussions can help you understand the complexities of the process.
- Participate in Public Hearings: Public hearings are held throughout the redistricting process, providing an opportunity for citizens to express their views on the proposed maps.
Conclusion
The Indiana congressional district map serves as a powerful tool for shaping the state’s political landscape. It determines representation in the U.S. House, influences electoral outcomes, and contributes to the dynamics of political polarization. While the map aims to ensure equal representation, its design can also have unintended consequences, potentially undermining fair elections and eroding public trust in the political system. Understanding the map’s intricacies, its historical context, and its potential impact on the political landscape is crucial for informed civic engagement and participation in the democratic process.
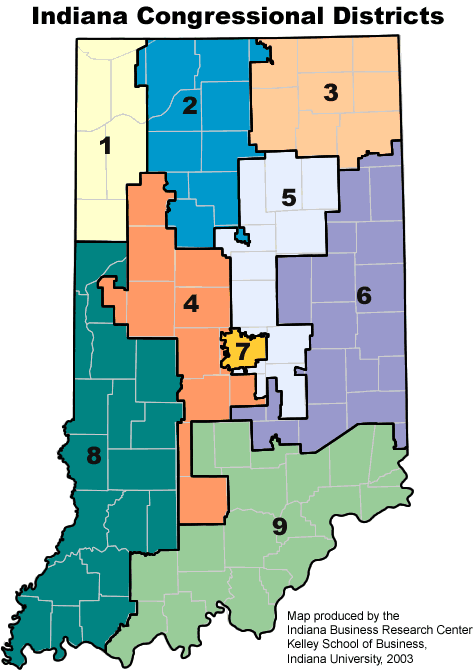

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Indiana’s Political Landscape: A Look at the Congressional District Boundaries. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!