Demarcating Democracy: A Comprehensive Look at Arizona’s Legislative District Map
Related Articles: Demarcating Democracy: A Comprehensive Look at Arizona’s Legislative District Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Demarcating Democracy: A Comprehensive Look at Arizona’s Legislative District Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demarcating Democracy: A Comprehensive Look at Arizona’s Legislative District Map

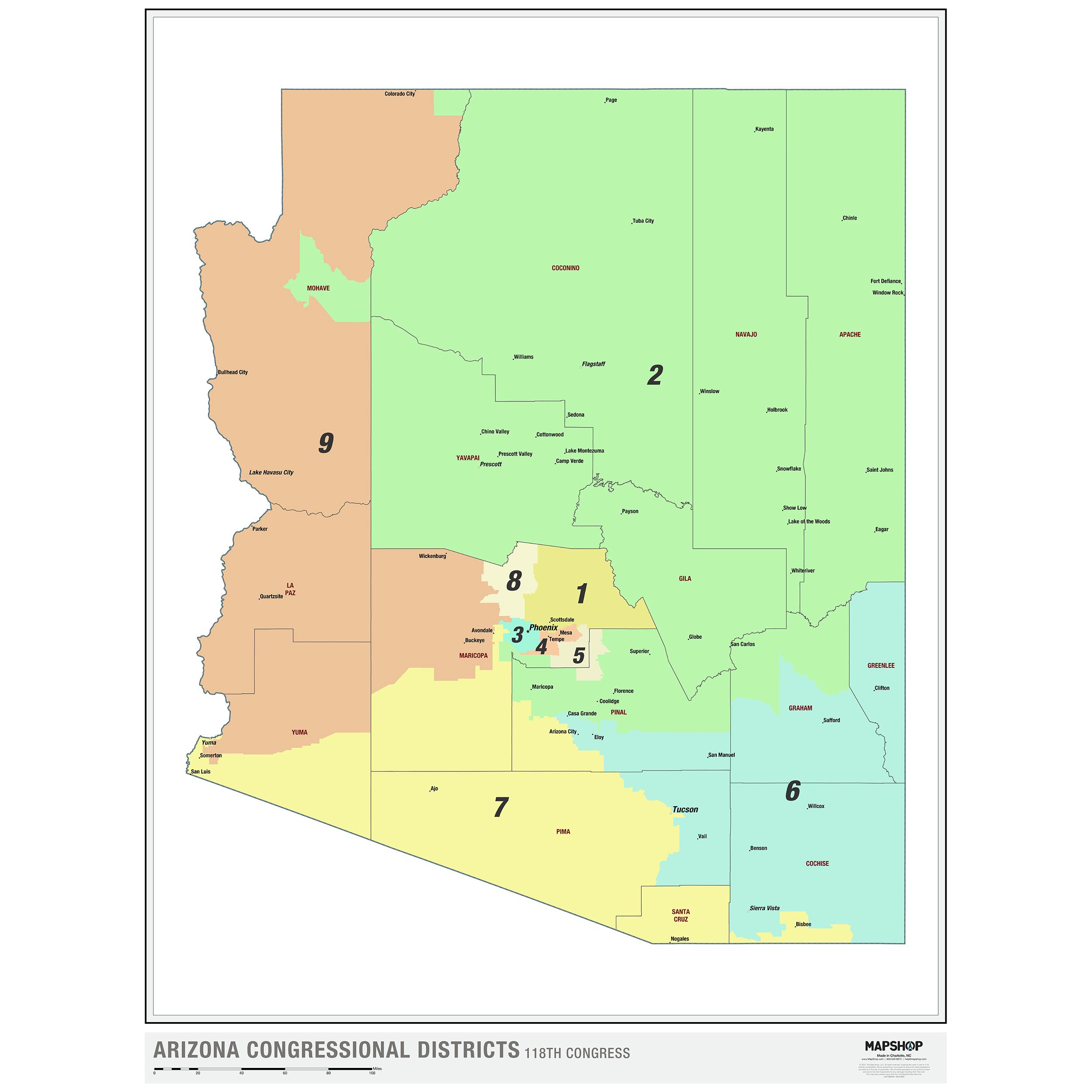
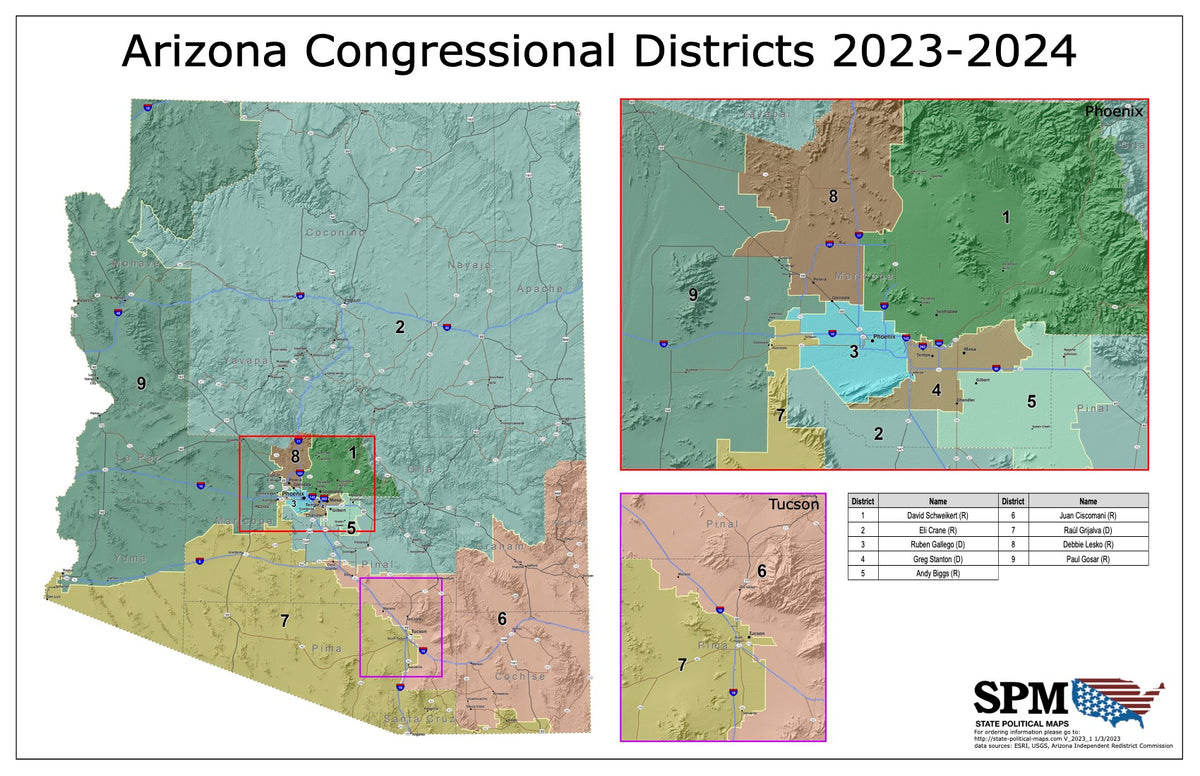
Arizona’s legislative district map, a crucial element of the state’s political landscape, serves as the blueprint for representation in the state legislature. This map, encompassing both the state House of Representatives and the state Senate, defines the geographic boundaries of each district, determining which constituents are represented by a particular legislator. The map undergoes a complex process of redrawing every ten years, following the decennial census, to ensure fair and equitable representation based on population shifts. This process, known as redistricting, is inherently political, with potential implications for the balance of power within the legislature.
Understanding the Importance of the Map:
The Arizona legislative district map holds significant weight, influencing the composition and dynamics of the state legislature. Its impact resonates across various facets of governance, including:
- Representation: The map directly impacts the representation of diverse communities within the legislature. By defining district boundaries, it determines which communities are grouped together for electoral purposes, shaping the voice of specific interests in the legislative process.
- Electoral Outcomes: The map can influence the outcome of elections by creating districts that favor one party or another. Gerrymandering, the practice of manipulating district boundaries for partisan advantage, can lead to uncompetitive elections and a skewed representation of the electorate’s will.
- Policy Decisions: The composition of the legislature, as determined by the map, can impact the policy priorities and decisions made by lawmakers. A legislature dominated by a single party may prioritize policies that align with that party’s platform, while a more balanced legislature may lead to more diverse policy outcomes.
- Accountability: The map plays a role in ensuring accountability of elected officials to their constituents. By defining district boundaries, it establishes a clear connection between legislators and the communities they represent, facilitating communication and engagement.
The Redistricting Process:
The process of redrawing Arizona’s legislative district map is a complex and often contentious endeavor. It involves a series of steps, including:
- Census Data: The decennial census provides population data that serves as the foundation for redistricting. This data highlights population shifts and growth patterns across the state, informing the redrawing of district boundaries.
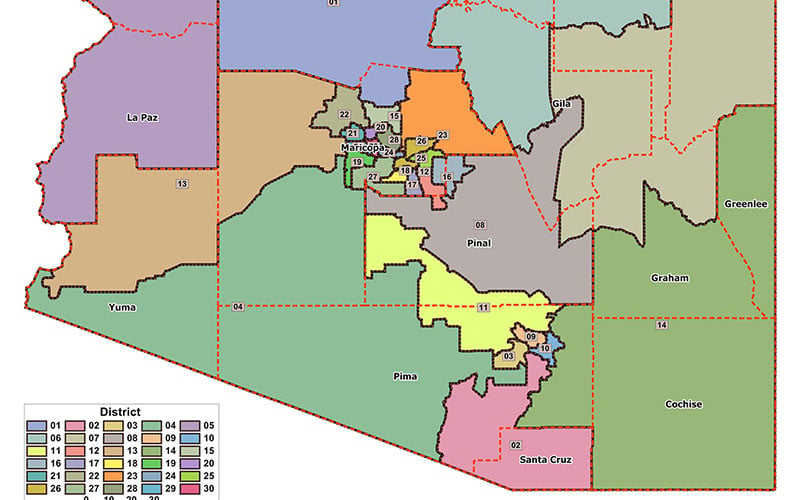
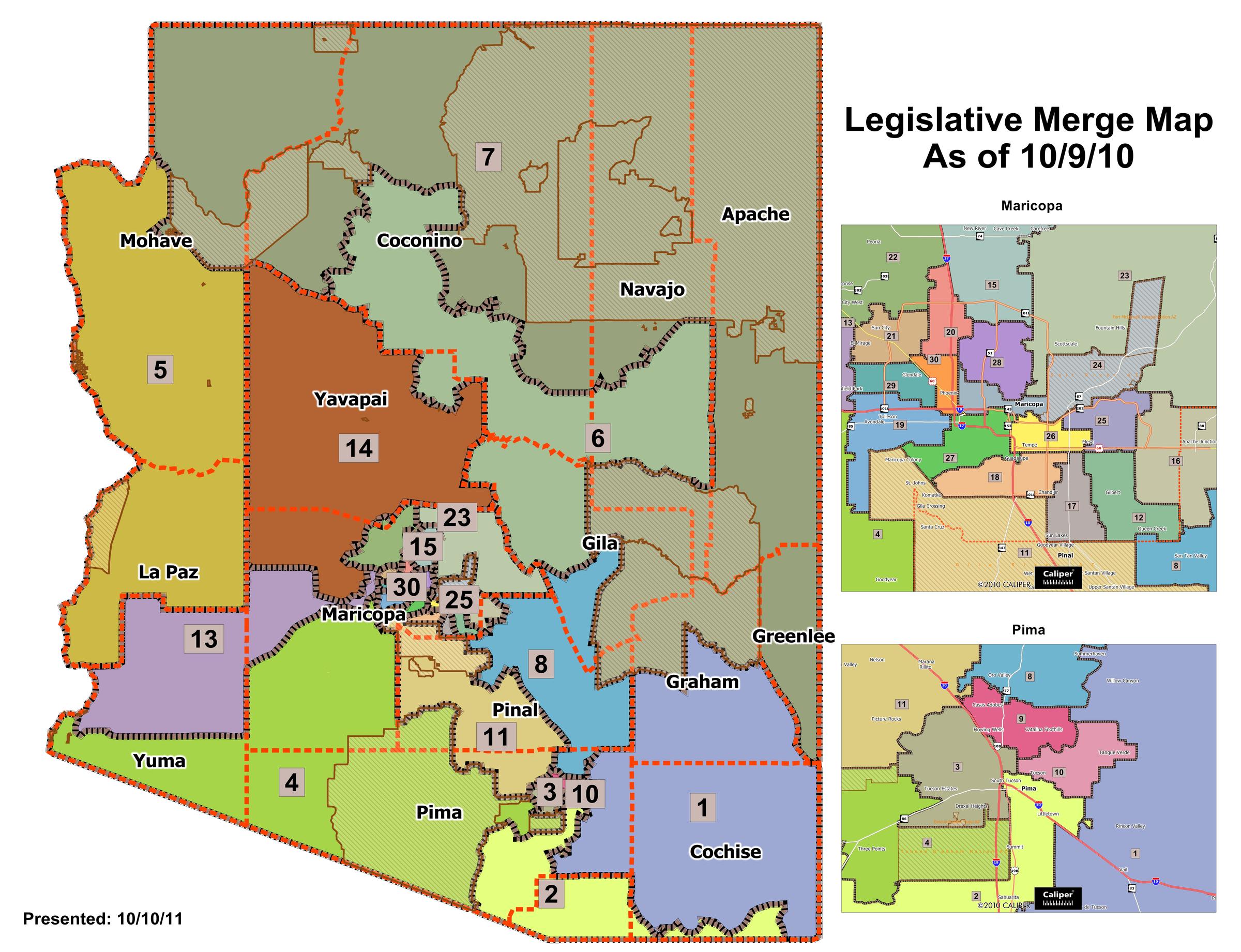
- Independent Commission: In Arizona, the responsibility of redrawing legislative district maps rests with an independent commission, the Arizona Independent Redistricting Commission (IRC). This commission, comprised of five members, is tasked with creating maps that adhere to legal requirements and principles of fairness.
- Public Input: The IRC actively solicits public input throughout the redistricting process. Public hearings, online forums, and other avenues provide opportunities for citizens to express their views on proposed map changes.
- Map Development: The IRC utilizes the census data, public input, and legal guidelines to develop multiple draft maps. These drafts are subject to public review and feedback before finalization.
- Final Maps: After a rigorous process of review and revision, the IRC approves final maps for both the state House of Representatives and the state Senate. These maps are then submitted to the Secretary of State for official adoption.
Challenges and Controversies:
The redistricting process in Arizona, as in other states, is not without its challenges and controversies. Key issues include:
- Partisan Influence: Despite the establishment of an independent commission, concerns about partisan influence in the redistricting process persist. Critics argue that the commission’s members may be biased towards one party or another, potentially leading to maps that favor specific political interests.
- Representation of Minority Communities: Ensuring fair representation of minority communities is a critical aspect of redistricting. Concerns arise when maps fail to adequately represent the interests of minority groups, leading to underrepresentation in the legislature.
- Community of Interest: The concept of "community of interest" plays a significant role in redistricting, emphasizing the need to keep communities with shared interests together within a district. However, defining and applying this principle can be subjective and contentious.
- Legal Challenges: Redistricting decisions are often subject to legal challenges, with lawsuits filed by individuals or groups seeking to overturn map changes or ensure fair representation. These challenges can further complicate the process and delay the implementation of new maps.
FAQs about Arizona’s Legislative District Map:
Q: How often is Arizona’s legislative district map redrawn?
A: Arizona’s legislative district map is redrawn every ten years, following the decennial census.
Q: Who is responsible for redrawing the map?
A: The Arizona Independent Redistricting Commission (IRC) is responsible for redrawing the legislative district map.
Q: What are the criteria used for redrawing the map?
A: The IRC uses criteria such as population equality, contiguity, compactness, and respect for communities of interest when redrawing the map.
Q: Can the public provide input on the redistricting process?
A: Yes, the IRC actively solicits public input throughout the redistricting process. Public hearings, online forums, and other avenues provide opportunities for citizens to express their views on proposed map changes.
Q: What are the potential consequences of a poorly drawn legislative district map?
A: A poorly drawn map can lead to unfair representation, uncompetitive elections, and a skewed legislative agenda.
Tips for Engaging with the Redistricting Process:
- Stay Informed: Keep informed about the redistricting process and the proposed map changes. Consult the Arizona Independent Redistricting Commission website for updates and information.
- Participate in Public Input: Attend public hearings, submit written comments, and participate in online forums to express your views on proposed map changes.
- Engage with Elected Officials: Contact your elected officials and express your concerns about the redistricting process and the impact of proposed maps on your community.
- Support Advocacy Groups: Support advocacy groups that are working to ensure fair and equitable redistricting.
Conclusion:
Arizona’s legislative district map serves as a critical foundation for democratic representation in the state. The redistricting process, while complex and often controversial, is essential for ensuring fair and equitable representation, fostering competitive elections, and enabling a responsive and accountable legislature. By understanding the process, participating in public input, and advocating for fair representation, citizens can play an active role in shaping the map and ensuring that it reflects the diverse voices of Arizona’s communities.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demarcating Democracy: A Comprehensive Look at Arizona’s Legislative District Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!