Deciphering the Grid: Understanding the Latitude and Longitude Map of the United States
Related Articles: Deciphering the Grid: Understanding the Latitude and Longitude Map of the United States
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Grid: Understanding the Latitude and Longitude Map of the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Grid: Understanding the Latitude and Longitude Map of the United States
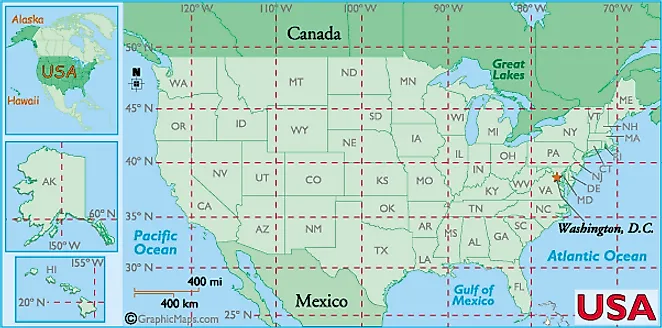
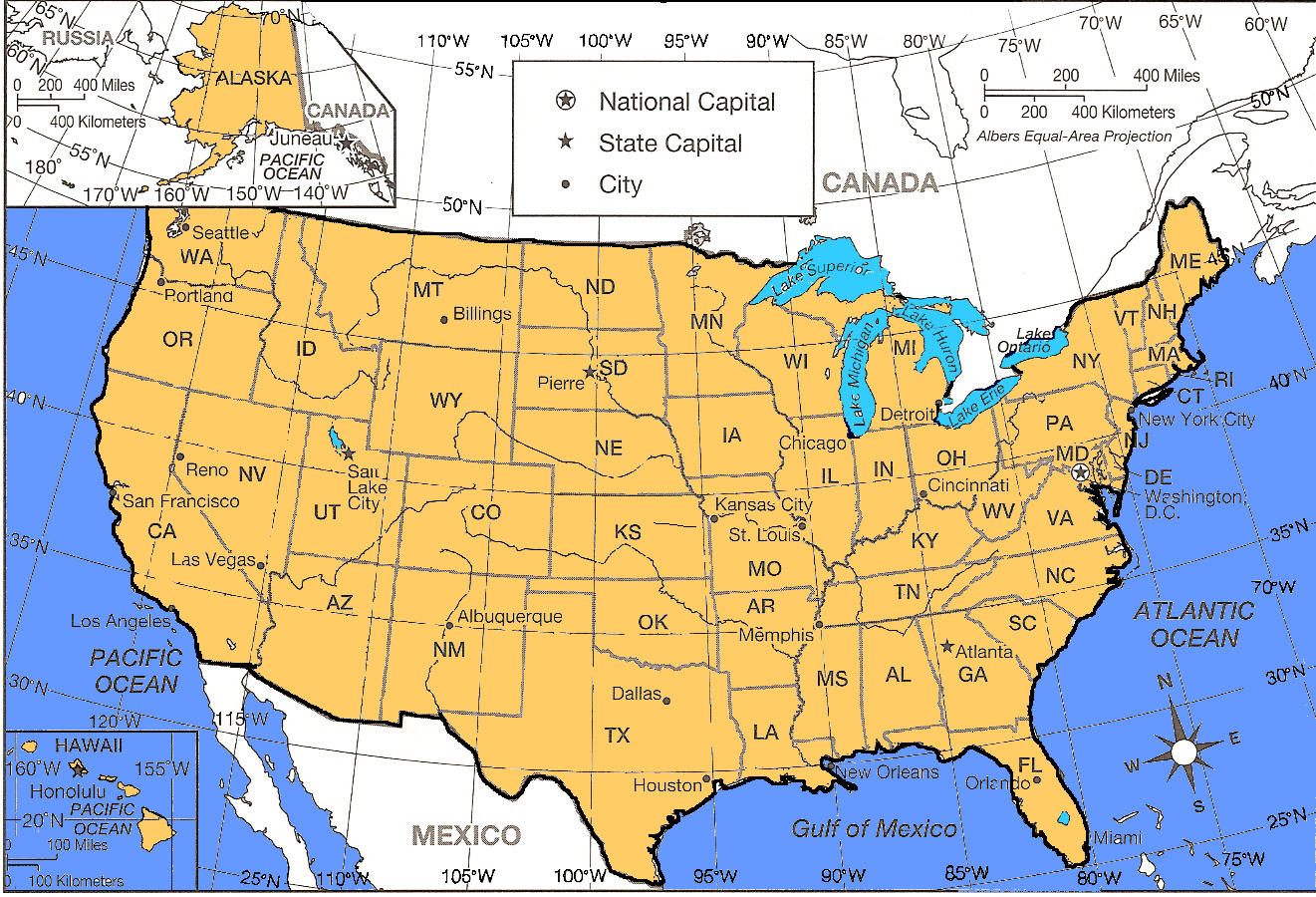
The United States, a vast and geographically diverse nation, is often depicted on maps that utilize a grid system of latitude and longitude lines. This seemingly simple framework serves as a fundamental tool for navigating, locating, and understanding the country’s spatial dimensions. By understanding the principles behind this grid, one can unlock a deeper appreciation for the geographical intricacies of the United States.
Latitude: Tracing Horizontal Lines
Latitude lines, also known as parallels, run horizontally around the Earth, parallel to the equator. The equator itself represents 0 degrees latitude, with values increasing northward towards the North Pole (90 degrees) and southward towards the South Pole (also 90 degrees). Each degree of latitude is further subdivided into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds. This system allows for precise location identification.
In the context of the United States, latitude lines play a crucial role in defining regional climates. For instance, the southernmost states like Florida and Texas, situated at lower latitudes, experience a tropical or subtropical climate characterized by warm temperatures and abundant rainfall. As one moves northward, latitudes increase, leading to cooler temperatures, shorter growing seasons, and a greater prevalence of deciduous forests.
Longitude: Defining Vertical Lines
Longitude lines, also known as meridians, run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, intersecting at the poles. The prime meridian, passing through Greenwich, England, is designated as 0 degrees longitude. Values increase eastward (up to 180 degrees) and westward (up to 180 degrees), with the 180th meridian marking the International Date Line.
Longitude lines are critical for understanding time zones. The Earth rotates 360 degrees in 24 hours, resulting in a shift of 15 degrees per hour. Consequently, each time zone encompasses approximately 15 degrees of longitude. In the United States, four standard time zones are established: Eastern, Central, Mountain, and Pacific. This system ensures consistent timekeeping across the vast expanse of the country.
The Intersection: Pinpointing Locations
The intersection of latitude and longitude lines provides a unique coordinate for every point on Earth. This system, known as the geographic coordinate system, is the foundation for global navigation and mapping. By specifying a specific latitude and longitude, one can pinpoint a location with remarkable accuracy.
For example, the coordinates 40.7128° N, 74.0060° W correspond to the iconic Times Square in New York City. This system is indispensable for various applications, including:
- Navigation: GPS devices and mapping applications rely heavily on latitude and longitude coordinates to guide users to their desired destinations.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software utilizes this system to analyze and visualize spatial data, enabling informed decision-making in fields like urban planning, environmental management, and disaster response.
- Scientific Research: Researchers in various disciplines, including geography, geology, and meteorology, use latitude and longitude to study and analyze spatial patterns and relationships.
Beyond the Grid: Understanding the Complexity
While the latitude and longitude map provides a fundamental framework for understanding the United States, it is crucial to acknowledge the inherent complexity of the country’s geography. Topography, elevation, and geological formations all contribute to the diverse landscape and climate patterns observed across the nation.
FAQs: Unraveling the Intricacies
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude lines run horizontally around the Earth, measuring distance north or south of the equator. Longitude lines run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, measuring distance east or west of the prime meridian.
Q: Why is the International Date Line located at 180 degrees longitude?
A: The International Date Line roughly follows the 180th meridian, marking the transition between calendar days. As one crosses the line eastward, the date advances by one day. Conversely, crossing westward results in a day being skipped.
Q: How can I use latitude and longitude to find my location?
A: Most smartphones and GPS devices can provide your current latitude and longitude coordinates. Online mapping tools also allow you to enter coordinates to locate specific points on a map.
Q: How does latitude affect climate?
A: Latitude influences climate primarily through its impact on solar radiation. Locations at lower latitudes receive more direct sunlight, leading to warmer temperatures and longer growing seasons. Higher latitudes experience less direct sunlight, resulting in cooler temperatures and shorter growing seasons.
Q: What are some of the benefits of using latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude and longitude provide a standardized system for locating and identifying points on Earth. This system is essential for navigation, mapping, geographic information systems, and scientific research.
Tips: Navigating the Grid
- Memorize key latitudes and longitudes: Familiarize yourself with the latitude and longitude of major cities and geographical features in the United States.
- Utilize online mapping tools: Explore interactive maps that allow you to zoom in and out, view specific locations, and measure distances.
- Consider the impact of latitude and longitude on climate and time zones: Understand how these factors influence regional variations in the United States.
Conclusion: A Framework for Exploration
The latitude and longitude map of the United States serves as a fundamental tool for understanding and navigating the country’s vast geography. By grasping the principles behind this grid system, one can gain valuable insights into the spatial dimensions of the nation, unlocking a deeper appreciation for its diverse landscape, climate patterns, and rich history. Whether for personal exploration, scientific research, or simply a greater understanding of the world around us, the latitude and longitude map remains an indispensable resource for navigating the complexities of the United States.
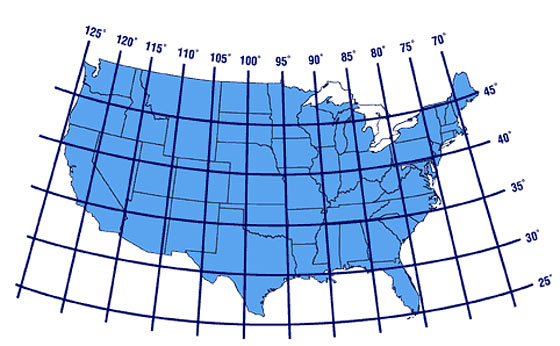


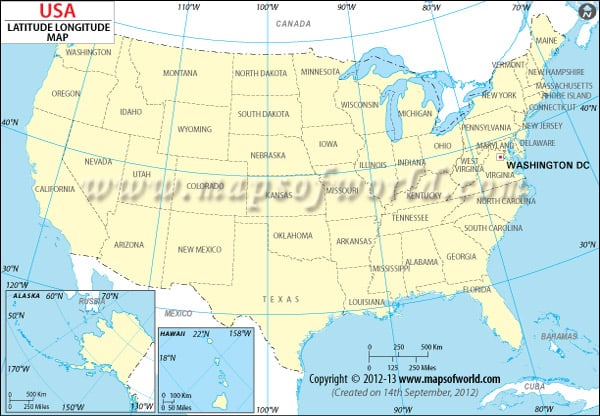

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Grid: Understanding the Latitude and Longitude Map of the United States. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!