Charting the Path to Conservation: Understanding Wildlife Management Areas Maps
Related Articles: Charting the Path to Conservation: Understanding Wildlife Management Areas Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Path to Conservation: Understanding Wildlife Management Areas Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Path to Conservation: Understanding Wildlife Management Areas Maps
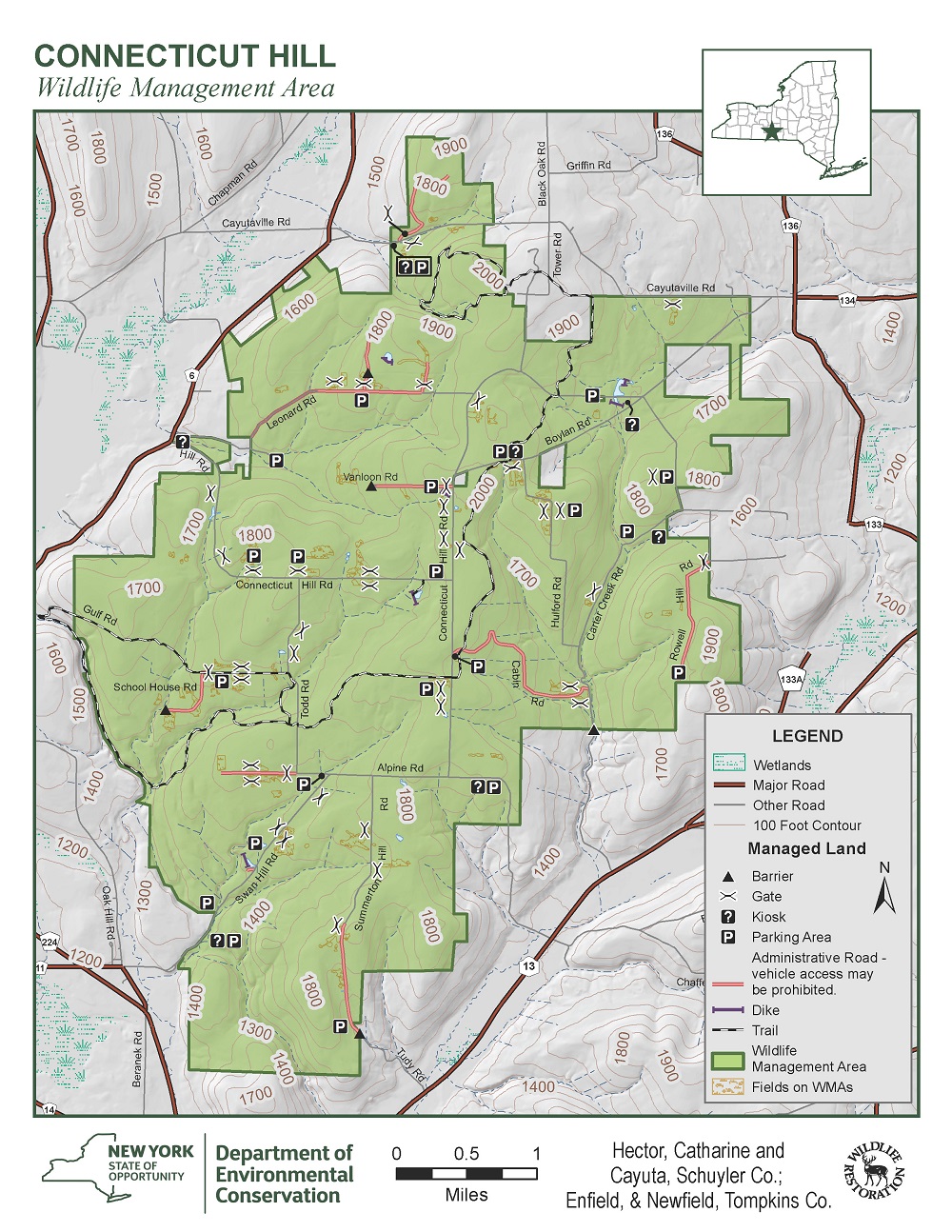
Wildlife management areas (WMAs) are critical tools for conservation efforts, encompassing designated lands where human activities are managed to protect and enhance wildlife populations and their habitats. These areas are not just geographical boundaries on a map; they represent a complex interplay of ecological considerations, human needs, and conservation goals. To understand the crucial role of WMAs, it is essential to delve into the intricacies of wildlife management areas maps, their construction, and their profound impact on conservation.
A Visual Representation of Conservation Efforts:
Wildlife management areas maps serve as visual representations of the intricate tapestry of conservation efforts. They depict the boundaries of designated areas, highlighting the diverse ecosystems and wildlife populations they encompass. These maps are not static documents but rather dynamic representations that evolve as scientific understanding of wildlife populations and their habitat requirements grows.
Key Components of Wildlife Management Areas Maps:
-
Boundaries: The most prominent feature of a WMA map is its clear delineation of boundaries. These boundaries are crucial for defining the area subject to specific management practices. They often follow natural features like rivers, ridges, or roads, but may also be established based on land ownership or ecological considerations.
-
Habitat Types: WMAs often encompass a variety of habitats, each supporting unique wildlife communities. Maps typically depict these habitats using color coding or symbols, providing a visual overview of the ecological diversity within the area. This information is vital for understanding the distribution of wildlife populations and for developing targeted management strategies.
-
Wildlife Distribution: Maps may include information about the distribution of specific wildlife species within the WMA. This could involve depicting known breeding grounds, migration routes, or areas of high concentration. This data is crucial for understanding the spatial dynamics of wildlife populations and for prioritizing conservation efforts.
-
Management Zones: Within a WMA, different zones may be designated with varying levels of human activity allowed. Maps typically depict these zones using different colors or patterns. For example, some areas may be designated for hunting, while others may be designated as "no-entry" zones to protect sensitive habitats.
-
Infrastructure: Maps may also include information about existing infrastructure within the WMA, such as roads, trails, and observation points. This information is essential for planning access and managing human activity within the area.
The Importance of Wildlife Management Areas Maps:
-
Planning and Management: Wildlife management areas maps provide a visual framework for planning and implementing conservation strategies. They allow for the identification of critical habitats, the assessment of potential threats, and the development of targeted management plans.
-
Public Education and Outreach: Maps are valuable tools for educating the public about the importance of wildlife conservation and for promoting responsible use of WMAs. They can help to raise awareness about the ecological values of these areas and to encourage public participation in conservation efforts.
-
Scientific Research: Wildlife management areas maps provide a baseline for scientific research. They can be used to monitor changes in habitat conditions, wildlife populations, and the effectiveness of conservation strategies.
-
Decision-Making: Maps provide crucial information for decision-makers involved in land use planning, resource management, and conservation policy. They help to inform decisions about the allocation of resources, the regulation of human activities, and the protection of sensitive ecosystems.
FAQs About Wildlife Management Areas Maps:
-
How are wildlife management areas maps created?
Wildlife management areas maps are typically created through a collaborative process involving wildlife biologists, ecologists, land managers, and other stakeholders. The process may involve field surveys, aerial imagery analysis, and GIS mapping techniques.
-
How often are wildlife management areas maps updated?
The frequency of updates varies depending on the specific WMA and the rate of change in the landscape. However, maps are generally reviewed and updated periodically to reflect new scientific information and changing management priorities.
-
Are wildlife management areas maps available to the public?
Many wildlife management areas maps are publicly available online or through government agencies. These maps can be accessed by researchers, conservationists, and the general public.
-
How can I get involved in wildlife management areas mapping?
There are many ways to get involved in wildlife management areas mapping. You can contact local conservation organizations, volunteer for citizen science projects, or participate in public comment periods on proposed management plans.
Tips for Using Wildlife Management Areas Maps:
-
Understand the scale and resolution of the map. Maps may vary in their level of detail, so it is important to consider the scale and resolution when interpreting the information.
-
Pay attention to the legend and symbols. The legend provides a key to understanding the different features and symbols depicted on the map.
-
Consider the context. It is important to understand the historical, ecological, and social context in which the WMA was established.
-
Use the map as a tool for planning and responsible use. Maps can help you to identify areas of interest, plan your activities, and minimize your impact on the environment.
Conclusion:
Wildlife management areas maps are essential tools for conservation, providing a visual representation of the intricate web of ecological considerations and human activities that shape the fate of wildlife populations and their habitats. These maps serve as a foundation for planning, management, research, and public education, promoting a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of nature and the crucial role humans play in its preservation. By utilizing and interpreting wildlife management areas maps, we can contribute to the long-term health and sustainability of our planet’s biodiversity.



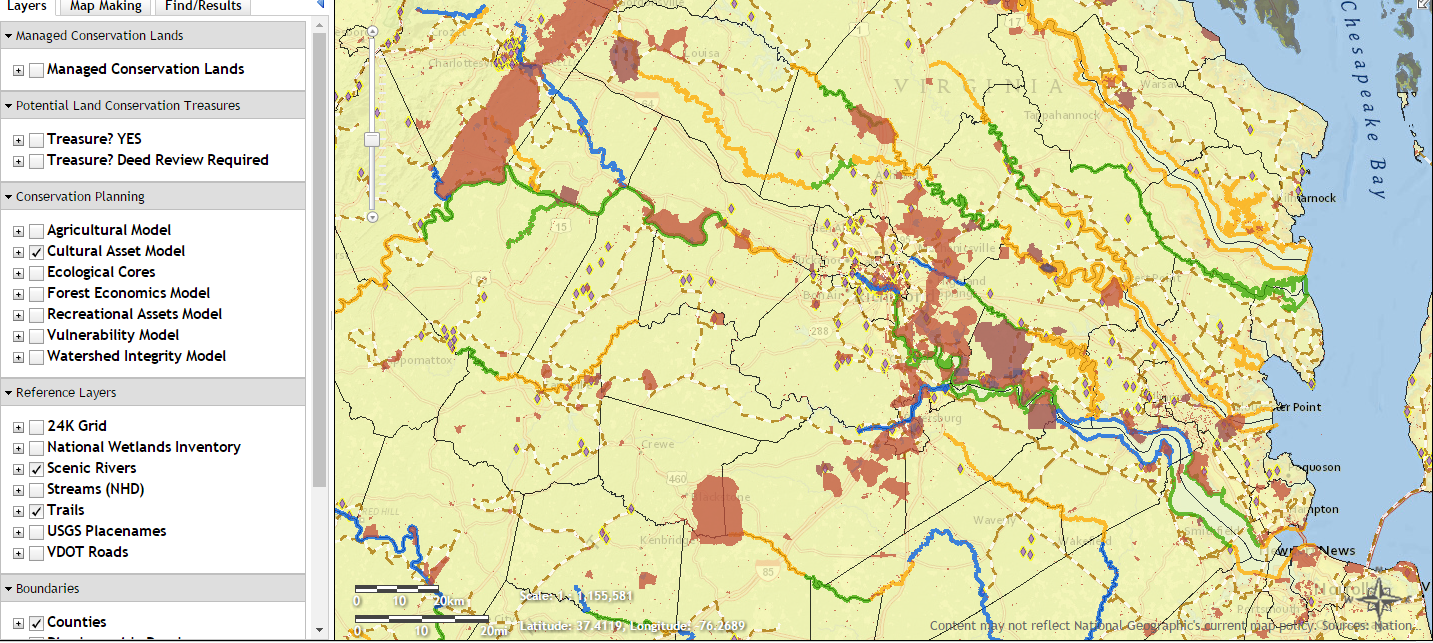

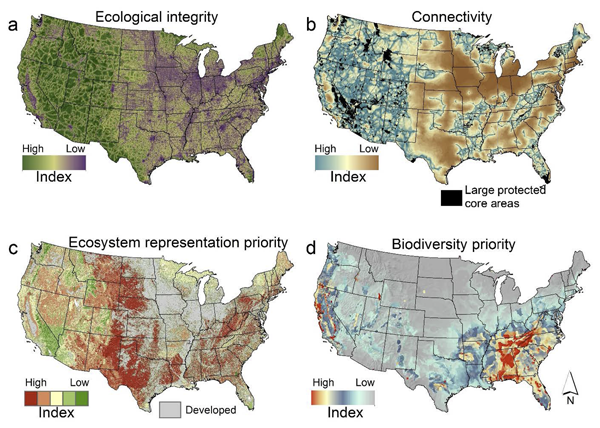


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Path to Conservation: Understanding Wildlife Management Areas Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!