A Tapestry of Wealth: Exploring the African Resource Map
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Wealth: Exploring the African Resource Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Wealth: Exploring the African Resource Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Wealth: Exploring the African Resource Map
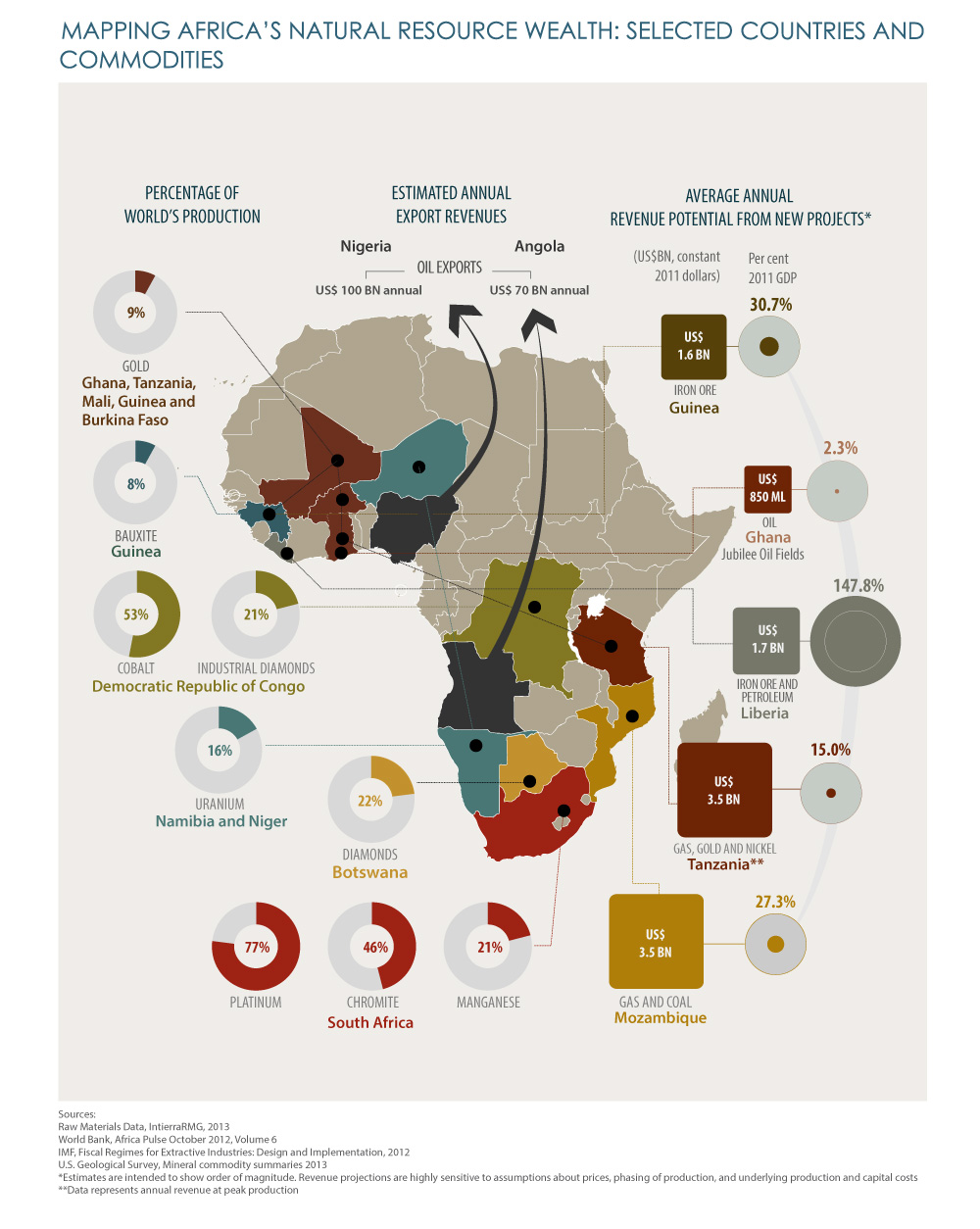
Africa, the second-largest continent, is often referred to as the "continent of opportunity," a title earned through its vast and diverse natural resources. The African resource map, a visual representation of these resources, paints a picture of immense potential, showcasing the continent’s wealth in minerals, energy, agriculture, and more. Understanding this map is crucial for navigating the complexities of Africa’s development, fostering sustainable growth, and ensuring equitable distribution of its riches.
A Diverse Landscape of Resources:
The African resource map is a kaleidoscope of colors, each representing a different resource. From the mineral-rich regions of Southern Africa, home to diamonds, platinum, and gold, to the oil and gas reserves of West Africa, the continent boasts a remarkable variety of assets. Here’s a closer look at some key sectors:
1. Minerals:
Africa is a global powerhouse in mineral production, holding significant reserves of precious metals, industrial minerals, and strategic minerals.
- Precious Metals: South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Ghana are major producers of gold, while South Africa is the world’s leading platinum producer.
- Industrial Minerals: The continent possesses abundant deposits of iron ore, manganese, copper, bauxite, and phosphate rock, crucial for industrial development.
- Strategic Minerals: Cobalt, tantalum, and lithium, vital for the electronics and renewable energy sectors, are found in significant quantities in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Rwanda, and Zimbabwe.
2. Energy:
Africa is blessed with abundant energy resources, both conventional and renewable.
- Oil and Gas: Nigeria, Angola, and Algeria are major oil producers, while Algeria, Nigeria, and Egypt are significant natural gas exporters.
- Renewable Energy: Africa has immense potential in solar, wind, geothermal, and hydropower. The Sahara Desert, for example, receives abundant sunshine, making it ideal for solar energy development.
3. Agriculture:
With vast fertile lands and diverse climates, Africa possesses enormous agricultural potential.
- Cash Crops: Coffee, cocoa, tea, cotton, and rubber are key agricultural exports, generating significant revenue.
- Food Crops: Maize, cassava, rice, sorghum, and millet are essential food staples for the continent’s growing population.
- Livestock: Cattle, sheep, goats, and poultry are vital sources of protein and income.
4. Water:
Water is a critical resource, essential for agriculture, industry, and human life.
- Freshwater: Africa has numerous rivers and lakes, including the Nile, Congo, and Niger, but access to clean water remains a challenge for many communities.
- Groundwater: The continent holds substantial groundwater reserves, offering potential for irrigation and drinking water supply.
The Importance of the African Resource Map:
Understanding the African resource map is crucial for several reasons:
1. Economic Development:
The map provides a roadmap for sustainable economic growth. By leveraging its natural resources, Africa can create jobs, boost GDP, and improve living standards. This requires responsible resource management, investing in infrastructure, and promoting value addition through processing and manufacturing.
2. Regional Integration:
The map highlights the potential for regional cooperation and collaboration. Countries with complementary resources can work together to create regional value chains, fostering trade and economic growth.
3. Investment Opportunities:
The map attracts foreign direct investment, essential for developing the continent’s resources. However, attracting investment requires a stable political environment, transparent governance, and a conducive investment climate.
4. Environmental Sustainability:
The map underscores the importance of responsible resource management. Mining, oil and gas extraction, and agricultural practices must be carried out sustainably to minimize environmental damage and ensure long-term resource availability.
FAQs about the African Resource Map:
Q1: What are the challenges associated with managing Africa’s resources?
A: The challenges include:
- Resource Curse: The paradox of resource-rich countries experiencing poverty and inequality.
- Corruption and Mismanagement: Lack of transparency and accountability can lead to resource depletion and economic instability.
- Environmental Degradation: Unsustainable resource extraction can lead to deforestation, pollution, and biodiversity loss.
- Conflict and Instability: Resource competition can trigger conflicts and instability, hindering development.
Q2: What are the opportunities for sustainable resource management in Africa?
A: Opportunities include:
- Investing in Renewable Energy: Harnessing the continent’s abundant solar, wind, and geothermal potential.
- Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: Adopting sustainable farming practices to ensure food security and protect the environment.
- Developing Value Chains: Adding value to raw materials through processing and manufacturing.
- Promoting Green Technologies: Adopting technologies that minimize environmental impact and promote resource efficiency.
Q3: How can the African Resource Map be used to promote inclusive growth?
A: By:
- Investing in Education and Skills Development: Equipping the workforce with the skills needed to participate in the resource sector.
- Promoting Local Participation: Ensuring that local communities benefit from resource extraction through employment, revenue sharing, and community development projects.
- Supporting Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): Creating opportunities for SMEs to participate in the resource value chains.
Tips for Utilizing the African Resource Map:
- Focus on Value Addition: Shifting from exporting raw materials to producing finished goods and services.
- Promote Diversification: Reducing reliance on a single resource and diversifying the economy.
- Invest in Infrastructure: Developing roads, railways, ports, and energy infrastructure to facilitate resource extraction and transportation.
- Promote Transparency and Good Governance: Ensuring accountability, transparency, and good governance in the resource sector.
Conclusion:
The African resource map is a testament to the continent’s vast potential. By embracing responsible resource management, promoting regional integration, and attracting investment, Africa can unlock its wealth and create a more prosperous future for its people. The path ahead is not without challenges, but by leveraging its resources wisely, Africa can emerge as a global economic powerhouse, contributing to a more sustainable and equitable world.

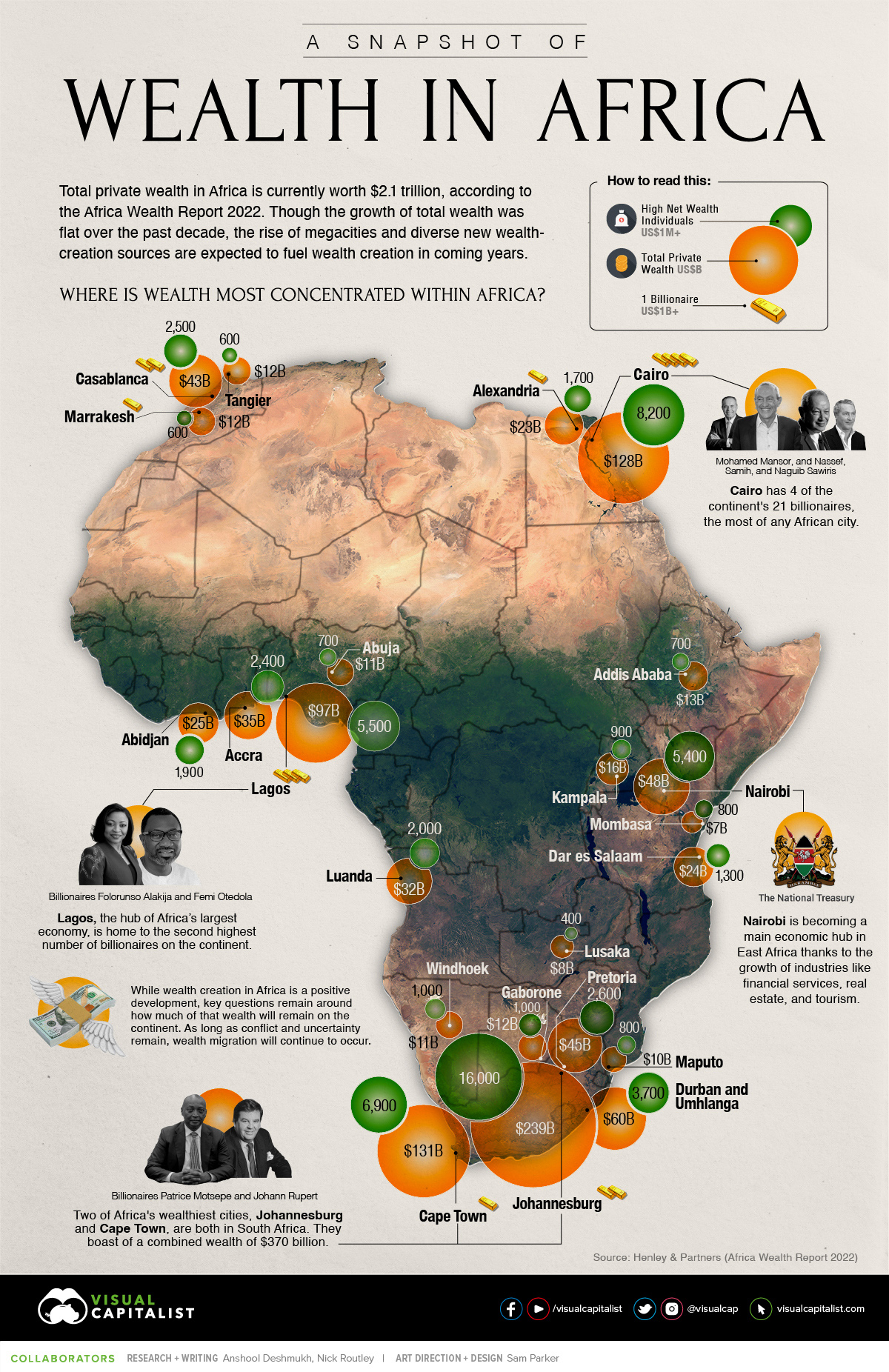




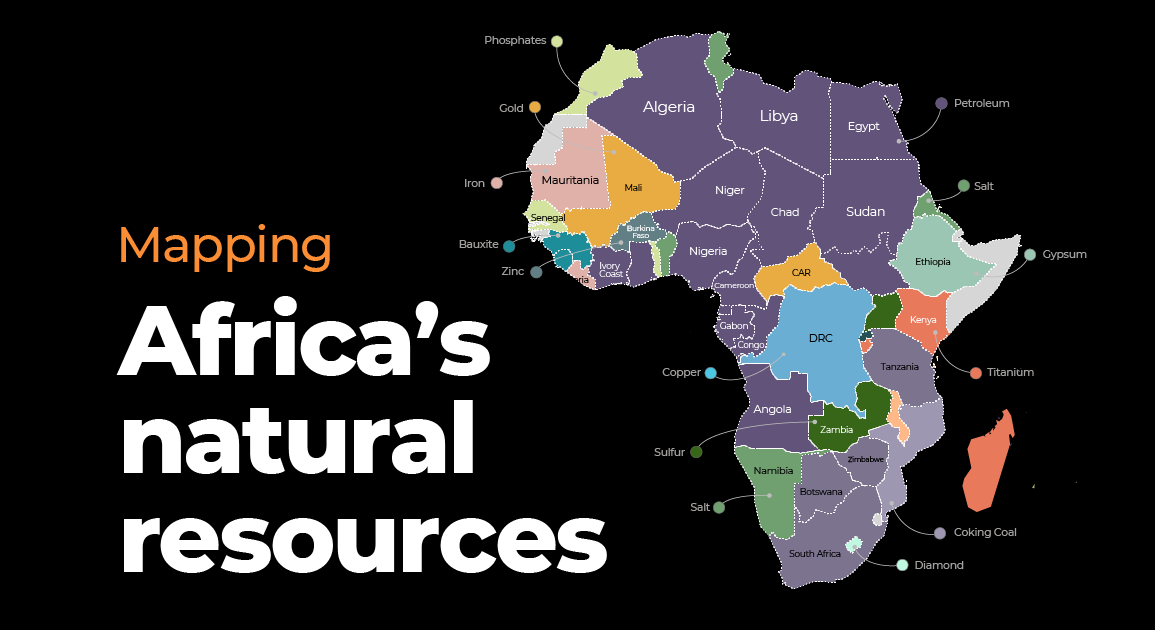

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Wealth: Exploring the African Resource Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!