A Borderland of History and Exchange: Understanding the Mexico-Texas Map
Related Articles: A Borderland of History and Exchange: Understanding the Mexico-Texas Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Borderland of History and Exchange: Understanding the Mexico-Texas Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Borderland of History and Exchange: Understanding the Mexico-Texas Map

The Mexico-Texas border, a line drawn across a landscape of vibrant culture, rich history, and shared resources, is more than just a political boundary. It is a dynamic zone of interaction, a tapestry woven with threads of trade, migration, and cultural exchange. Understanding the complexities of this border, both geographically and historically, is crucial for appreciating the multifaceted relationship between Mexico and Texas.
The Physical Landscape:
The Mexico-Texas border stretches for over 1,240 miles, traversing diverse landscapes from the arid Chihuahuan Desert to the fertile Rio Grande Valley. It is a mosaic of mountains, rivers, plains, and coastal regions, each contributing to the unique character of the borderland.
The Rio Grande: A Defining Feature
The Rio Grande, the longest river in the United States, serves as the natural boundary for much of the Texas-Mexico border. Its course, winding through canyons and plains, has shaped the history and culture of the region. The river’s waters, once a source of sustenance and irrigation, have also been a source of conflict, with disputes over water rights and access fueling tensions between the two nations.
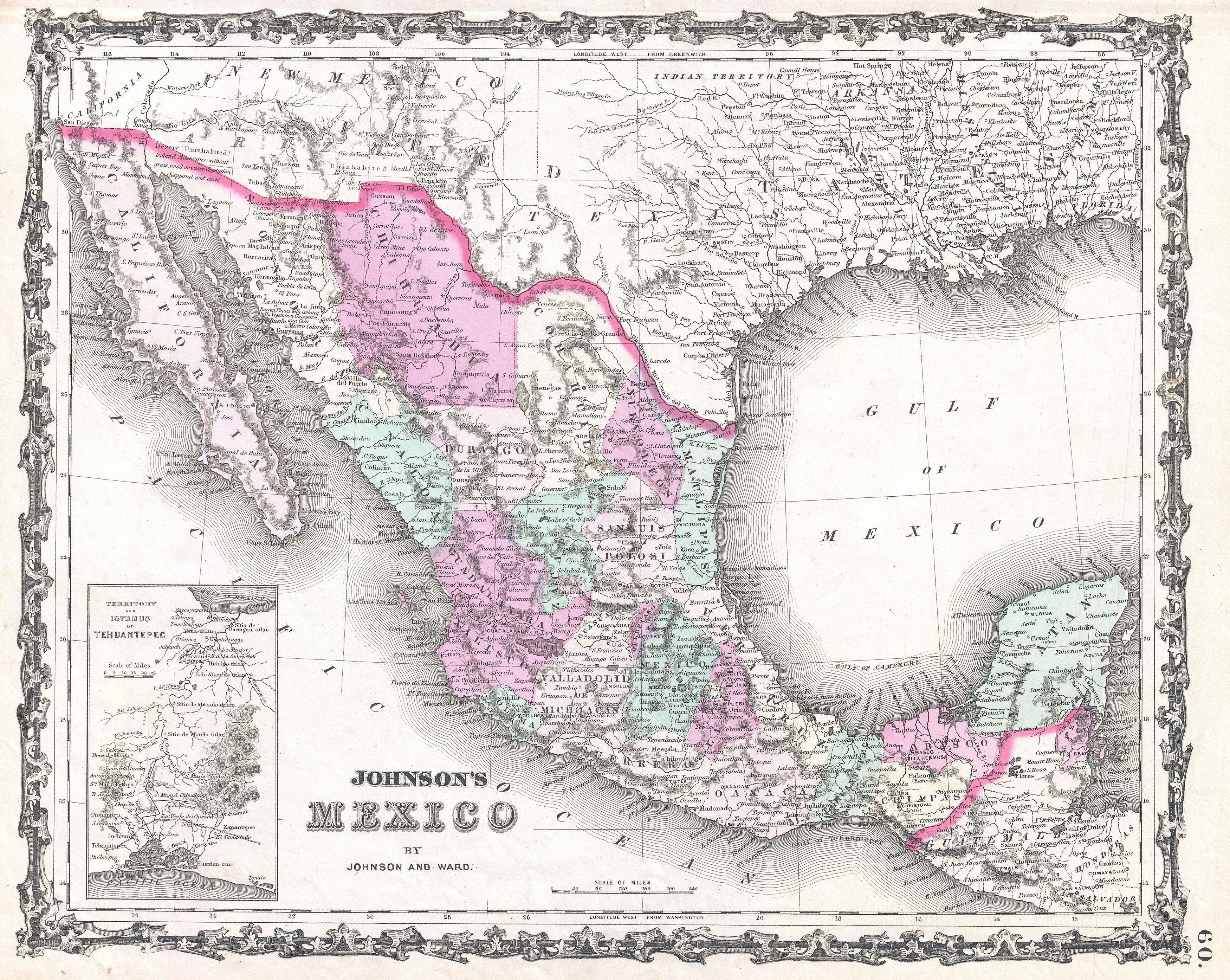
Historical Context:
The history of the Mexico-Texas border is a complex tapestry woven with threads of colonization, revolution, and conflict. The region was once part of the vast Spanish Empire, later becoming part of Mexico. In 1836, Texas declared independence from Mexico, leading to the Mexican-American War (1846-1848). The war ended with the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which ceded vast territories, including present-day Texas, to the United States.
The Border’s Impact on Texas:
The Mexico-Texas border has profoundly shaped the identity of Texas, influencing its culture, economy, and demographics. The state’s diverse population, a blend of Anglo, Hispanic, and Native American heritage, is a testament to the historical and ongoing exchange across the border. The border region has also played a pivotal role in the state’s economy, with trade, agriculture, and tourism all significantly influenced by its proximity to Mexico.
Understanding the Border’s Significance:
The Mexico-Texas border is not merely a geographical line; it is a dynamic space where cultures collide, economies intertwine, and histories converge. Understanding its complexity requires acknowledging its historical context, its physical landscape, and the multifaceted nature of the relationship between Mexico and Texas.
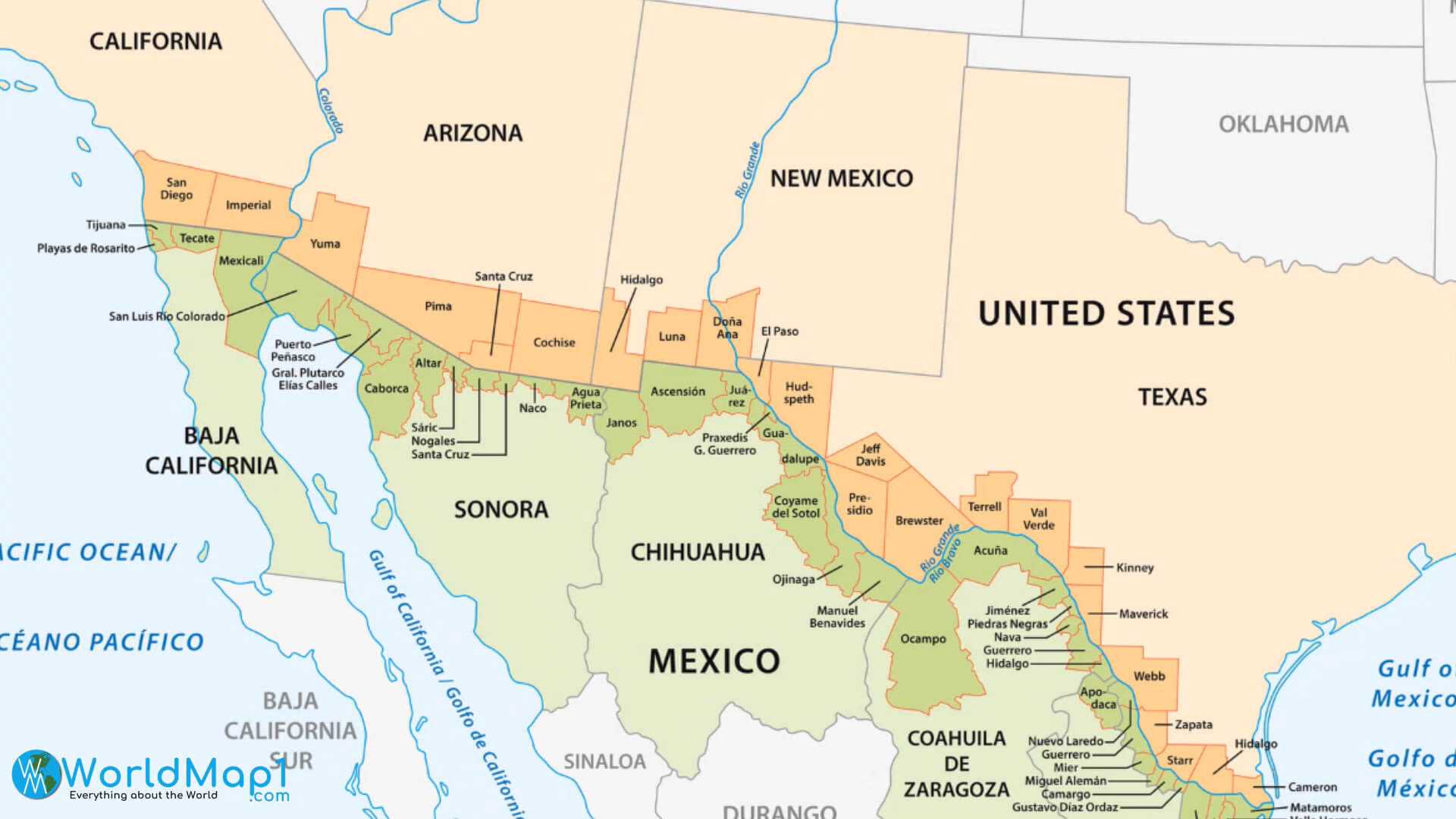
Exploring the Mexico-Texas Map: Key Features
- Major Cities: Examining the map reveals major cities on both sides of the border, such as El Paso, Texas, and Ciudad Juarez, Mexico. These cities serve as hubs for trade, transportation, and cultural exchange.
- Border Crossings: The map highlights numerous official border crossings, serving as vital points of entry for people and goods. The busiest crossing, the Laredo-Nuevo Laredo crossing, serves as a major gateway for trade between the two countries.
- Natural Features: The map showcases the diverse landscape of the border, including the Rio Grande, the Chihuahuan Desert, and the Sierra Madre Occidental mountains.
- Economic Zones: The map reveals the presence of free trade zones and economic development corridors along the border, showcasing the importance of trade and investment in the region.
- Cultural Diversity: The map highlights the diverse cultural heritage of the border region, with communities reflecting a blend of Mexican, Texan, and Native American influences.
FAQs on the Mexico-Texas Map
Q: What is the significance of the Rio Grande in the Mexico-Texas border?
A: The Rio Grande, serving as the natural boundary for a significant portion of the border, has historically played a crucial role in shaping the region’s culture, economy, and politics. Its waters have provided sustenance and irrigation, while disputes over water rights and access have contributed to tensions between Mexico and the United States.
Q: What are the major border crossings between Mexico and Texas?
A: The Mexico-Texas border is dotted with numerous official border crossings, each serving as a vital point of entry for people and goods. Some of the busiest crossings include:
- Laredo-Nuevo Laredo
- El Paso-Ciudad Juarez
- Brownsville-Matamoros
- McAllen-Reynosa
Q: What are the key economic sectors in the Mexico-Texas border region?
A: The border region is a hub for various economic activities, including:
- Trade: The region is a major gateway for trade between Mexico and the United States, with industries like manufacturing, agriculture, and energy playing significant roles.
- Tourism: The border region attracts visitors from both sides, drawn to its unique cultural attractions, historical sites, and natural landscapes.
- Agriculture: The fertile Rio Grande Valley is a major agricultural production area, with crops like cotton, citrus fruits, and vegetables contributing significantly to the regional economy.
Tips for Understanding the Mexico-Texas Map
- Historical Context: Explore the historical events that shaped the border, from Spanish colonization to the Mexican-American War, to gain a deeper understanding of the region’s complexities.
- Geographical Features: Pay attention to the diverse landscape, including mountains, rivers, and deserts, as these features have influenced the region’s development and cultural identity.
- Cultural Exchange: Recognize the cultural exchange that has occurred across the border, influencing the region’s art, music, cuisine, and language.
- Economic Interdependence: Understand the economic ties between Mexico and Texas, recognizing the mutual benefits and challenges associated with their shared economic landscape.
Conclusion:
The Mexico-Texas map is a powerful tool for understanding the complex and dynamic relationship between two nations. By recognizing the historical context, the geographical features, and the multifaceted nature of the border, we gain a deeper appreciation for the shared heritage, cultural exchange, and economic interdependence that define this unique region. The border, far from being a mere line on a map, represents a living tapestry of shared history, vibrant culture, and ongoing interaction, shaping the destinies of both Mexico and Texas.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Borderland of History and Exchange: Understanding the Mexico-Texas Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!